Treatment process for isothermal normalizing with exhaust heat of forgeable piece smithing
A technology of isothermal normalizing and treatment process, applied in the field of heat treatment of forgings, can solve the problems of increasing surface oxidation of forgings, increasing forging costs, not suitable for the production requirements of precision forgings, etc., to achieve stable product quality, balanced production, and reduced surface oxidation conditions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
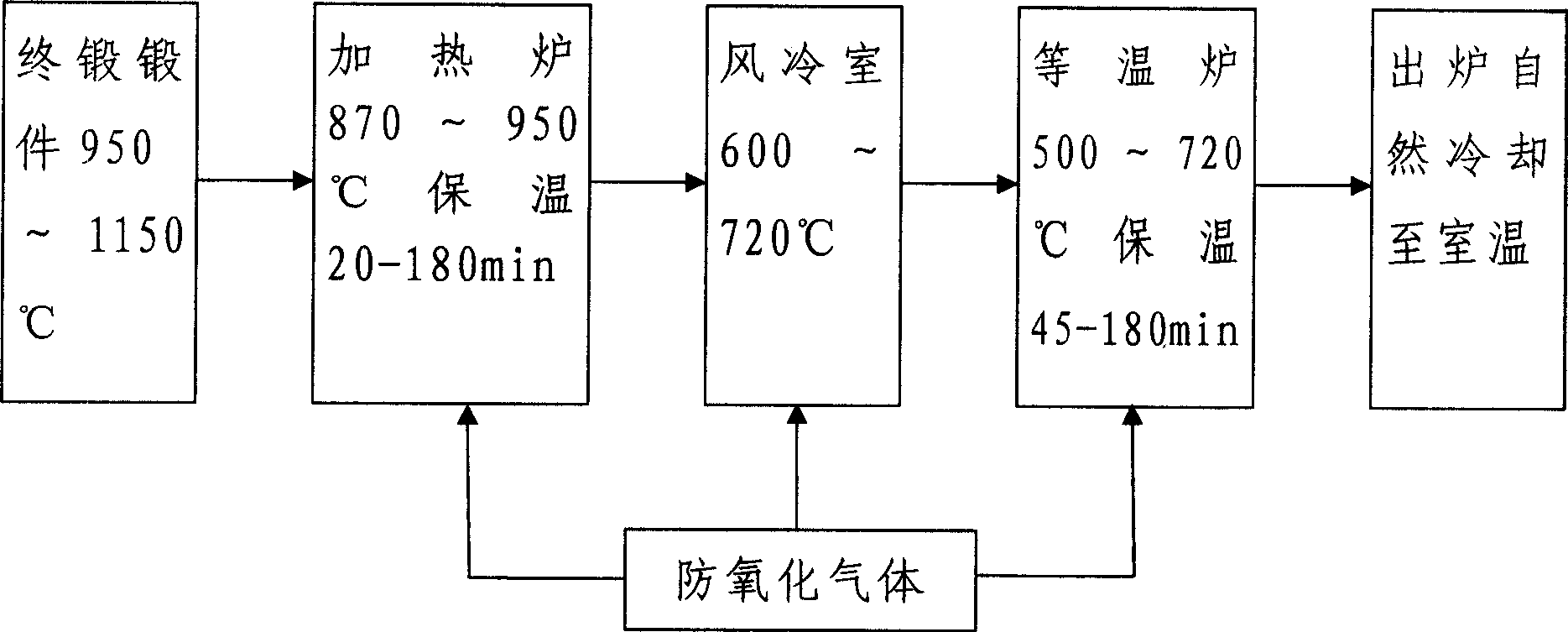
[0018] The isothermal normalizing treatment process is carried out by using the waste heat of forging forging, which is the process of carrying out normalizing treatment after the final forging of forgings. The forging in this embodiment is a car differential gear forged by precision hot die forging. The final forged forgings are sequentially sent to the heating furnace through the conveyor belt, and methanol is dripped into the heating furnace. The temperature of the heating furnace is controlled at 940±10°C. Under this temperature condition, the dripped methanol becomes gaseous methanol and fills the heating furnace. After the forging is kept warm for 160±20min, the forging is sent to the air-cooled room by the conveyor belt, and the forging is air-cooled to 610±10°C with nitrogen. After the forging is air-cooled, it is sent to the isothermal furnace filled with nitrogen by the conveyor belt. Keep warm for 170±10min at a furnace temperature of ±10°C, and then take it out of ...
Embodiment 2
[0020] The forging in this embodiment is the connecting gear of the automobile gearbox, and its material is the same as that in Embodiment 1, except that its structural size and volume are relatively smaller. The steps of the isothermal normalizing process using the residual heat of forging are the same as those in Example 1, but the values of some process parameters are different. For example, the forgings enter the heating furnace at 860±10°C and are kept warm for 30±10min under the protection of methanol gas, and then sent to the air-cooled room by the conveyor belt, and the forgings are air-cooled to 710±10°C with nitrogen, and the forgings are air-cooled. The conveyor belt is sent into an isothermal furnace filled with nitrogen, and the forgings are kept at a furnace temperature of 710±10°C for 50±5min, and then cooled naturally after being released from the furnace. The technical effect of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and it can fully guarantee ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com