Single-code channel absolute position encoding method
A technology of absolute position and encoding method, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, conversion sensor output, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of irrecoverable, long grating manufacturing process, poor data reliability, etc. The effect of cumulative error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
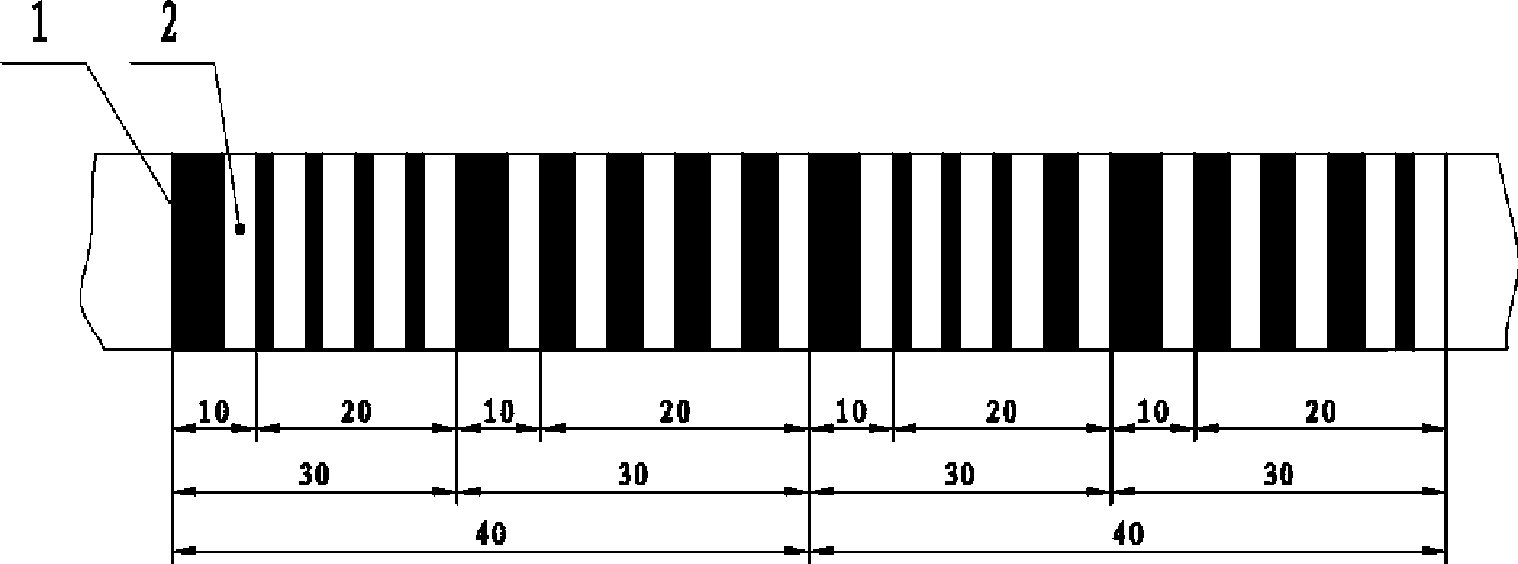
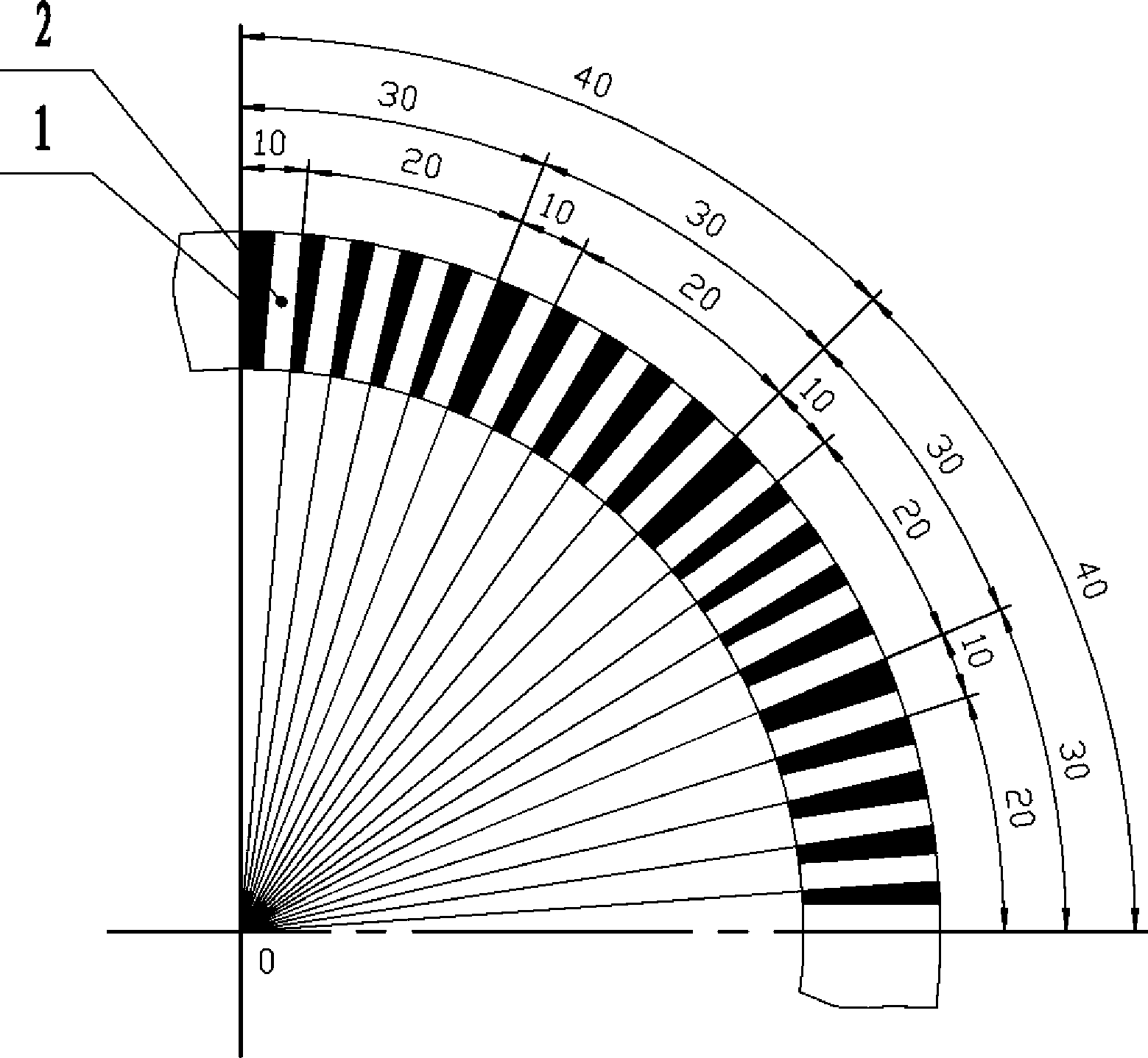
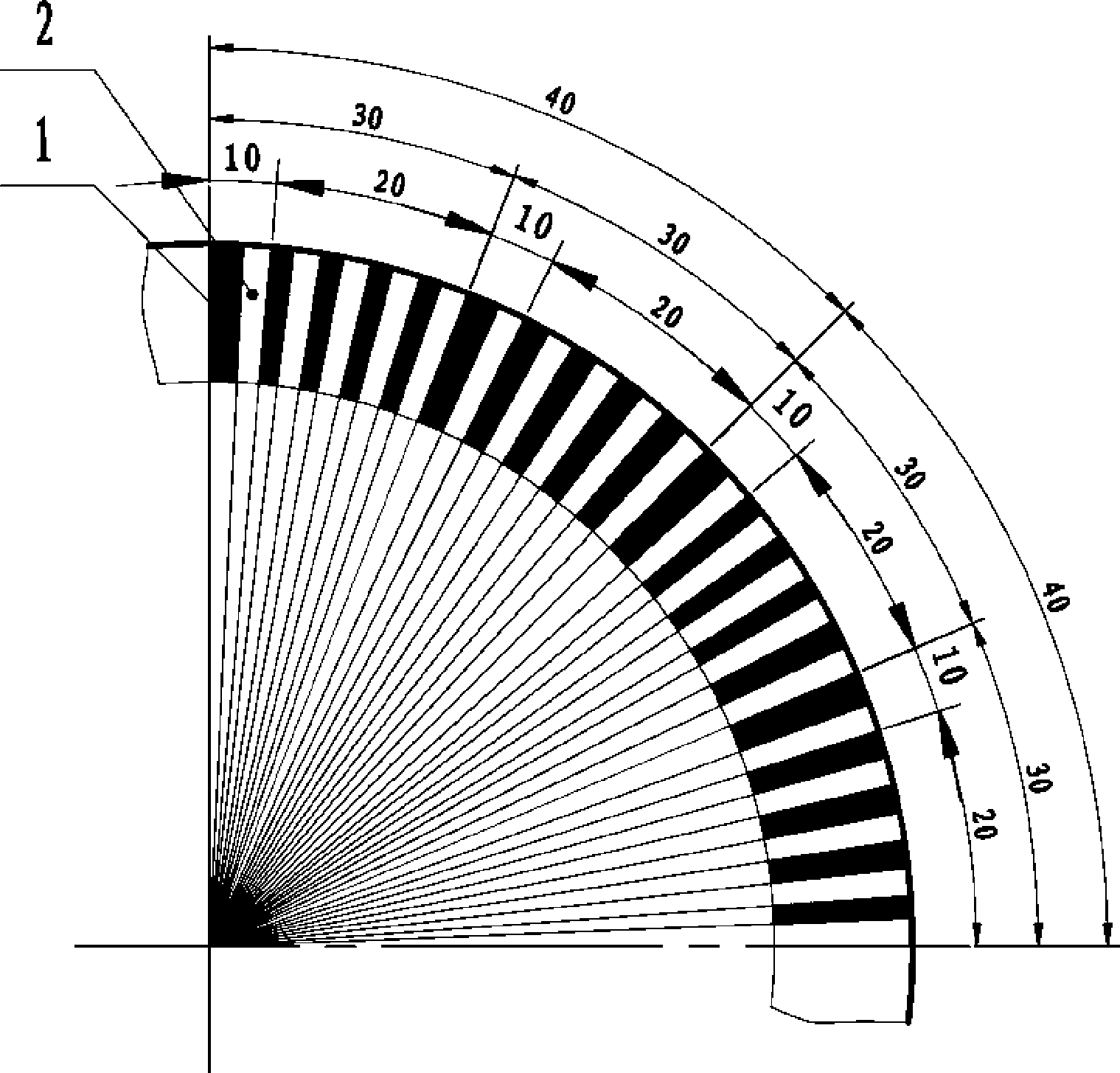
[0020] The single code track absolute position encoding method of this embodiment includes: engraving black stripes and white stripes arranged alternately on the grating; adjacent black stripes and white stripes constitute a coding bit in turn; a coding bit constitutes an identification code , nine coding bits constitute a position code, and the number of coding bits contained in each position code is the same; the number of identification codes and position codes is the same, and the identification codes and position codes are arranged alternately; Any code bit in all position codes, that is: the width of the black stripes that constitute the identification code is different from the width of any black stripe in all position codes; the identification codes are the same, that is: the black stripes in each identification code of the same width. The black stripes with unequal widths are used to distinguish different coded bits.
[0021] There are three types of black stripes en...
Embodiment 2
[0032] See Figure 1-2 , assuming that a black stripe 1 plus a white stripe 2 is used as the identification code 10, that is, each identification code occupies one coding bit, and a 4-bit binary sequence is used as the position code 20, that is, each position code occupies 4 coding bits, then by The first-level code area 30 formed by the identification code 10 and the position code 20 occupies 5 coded bits in total, and the entire code can form (4+1)×2 at most. 4= 80 encoded bits, encoding requires three black stripes and one white stripe.
[0033] Randomly take an identification code 10 and a position code 20 to form the first primary code area 30 of the code, reverse the binary position code of this primary code area bit by bit to obtain a new binary position code, add An identification code constitutes the second two first-level code areas of the code. Merging these two primary code areas forms the first secondary code area 40 of encoding, which includes two identificatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com