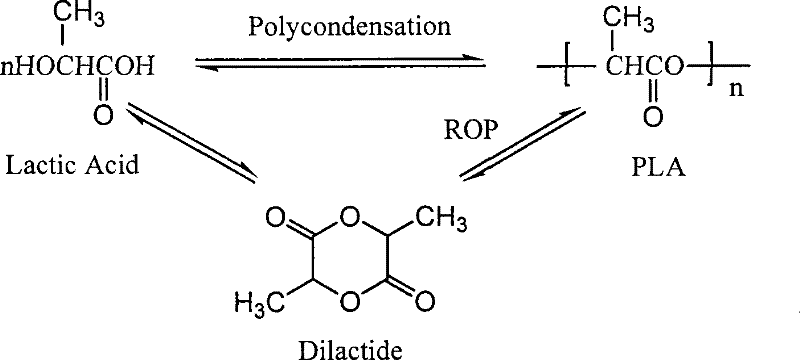
Solid state polymerization method for preparing polylactic acid
A technology of solid phase polymerization and polylactic acid, which is applied in the field of preparation of high molecular weight polylactic acid, can solve the problems of low efficiency, prepolymer powder sticking, low yield, etc., to suppress the formation of lactide and accelerate molecular weight The effect of growth and improvement of reaction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Starting material: polylactic acid prepolymer powder (containing 0.3wt% stannous acetate / 0.2wt% methanesulfonic acid composite catalyst), particle size 150-250um, molecular weight Mw=11,000, crystallinity 15%, melting point Tm = 150°C; glass transition temperature Tg = 45°C.
[0066] Spread 5g of the above polylactic acid powder in a vacuum oven whose temperature is stable at Tq=90°C±0.1°C, turn on the vacuum pump, adjust the pressure at 200±10Pa, and raise the temperature to Tz at a heating rate of 0.2°C / min. = 150°C and solid phase polymerization at Ts = 150°C, 155°C and 160°C for 8 hours each. During the whole process, neither the formation of lactide nor the welding of powder was observed. When the product was taken out, the powder was still in a free state, and no agglomeration and discoloration were observed. The obtained polylactic acid had a weight-average molecular weight Mw of 154,000, a melting point Tm of 170°C, and a yield of 96%.
Embodiment 2
[0068] Starting material: polylactic acid prepolymer powder (containing 0.3wt% stannous acetate / 0.2wt% methanesulfonic acid composite catalyst), particle size 150-250um, molecular weight Mw=11,000, crystallinity 40%, melting point Tm = 152°C; glass transition temperature Tg = 45°C.
[0069] Spread 5g of the above polylactic acid powder in a vacuum oven whose temperature is stable at Tq=110°C±0.1°C, turn on the vacuum pump, adjust the pressure at 200±10Pa, and raise the temperature to Tz at a heating rate of 0.1°C / min. = 158°C and solid state polymerization at Ts = 158°C for 24 hours. During the whole process, neither the formation of lactide nor the welding of powder was observed. When the product was taken out, the powder was still in a free state, and no agglomeration and discoloration were observed. The obtained polylactic acid had a weight average molecular weight Mw of 175,000, a melting point Tm of 171°C, and a yield of 95%.
Embodiment 3
[0071] Starting material: polylactic acid prepolymer powder (containing 0.3wt% stannous acetate / 0.2wt% methanesulfonic acid composite catalyst), particle size 150-250um, molecular weight Mw=11,000, crystallinity 65%, melting point Tm = 158°C; glass transition temperature Tg = 45°C.
[0072] Spread 5g of the above-mentioned polylactic acid powder in a vacuum oven whose temperature is stable at Tq=139°C±0.1°C, turn on the vacuum pump, adjust the pressure at 200±10Pa, and raise the temperature to Tz at a heating rate of 0.05°C / min. = 160°C and solid phase polymerization at Ts = 160°C and 165°C for 8 hours each. During the whole process, neither the formation of lactide nor the welding of powder was observed. When the product was taken out, the powder was still in a free state, and no agglomeration and discoloration were observed. The obtained polylactic acid had a weight average molecular weight Mw of 195,000, a melting point Tm of 171°C, and a yield of 90%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com