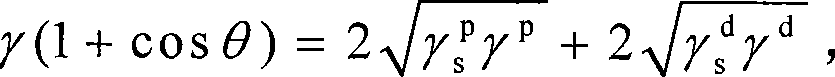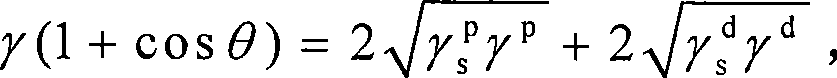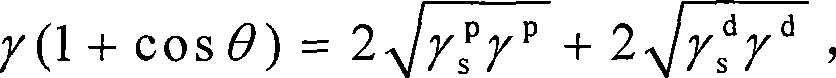Carbon fibre surface energy measurement method
A measurement method, carbon fiber technology, applied in the direction of surface tension analysis, etc., can solve the problems of large capillary effect of bundle filaments, low accuracy of test results, and inability to truly reflect the surface energy of carbon fibers, etc., to achieve accurate carbon fiber surface energy and accuracy High, precise test results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0012] Specific Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, the surface energy of carbon fiber is measured according to the following steps: 1. Dry the carbon fiber; The carbon fiber monofilaments are parallel to each other, the distance between adjacent carbon fiber monofilaments is greater than 5mm and less than 10mm, and the length of the carbon fiber exposed to the fixture is X, 8mm≤X≤10mm; 3. Use a surface tension meter to obtain carbon fiber and water and The contact angle of diiodomethane, the surface energy of the test liquid, the polar component of the test liquid surface energy and the dispersion component of the test liquid surface energy, wherein the detection limit of the surface tensiometer is 0.08mg, and the carbon fiber monofilament is inserted into water and diiodine The depth in methane is 5mm, the surface infiltration speed is 0.1mm / s, and the forward and backward infiltration speeds are both 0.008mm / s; 4. Substitute the data measured in step 3 into formula (1) and for...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0013] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the dispersion component of the surface energy of water is 22.1mJ / m 2 , the polar component of the surface energy of water is 50.7mJ / m 2 , the surface energy of water is 72.80mJ / m 2 ; The dispersion component of the surface energy of diiodomethane is 50.8mJ / m 2 , the polar component of the surface energy of diiodomethane is 0mJ / m 2 , the surface energy of diiodomethane is 50.8mJ / m 2 . Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0014] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the length of the clamp in step 2 is 4 times the length of the fiber clamp. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
[0015] In step 2 of this embodiment, except for the length, other structures and structures of the clamp are the same as those of the existing fiber clamp (monofilament fiber clamp).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com