Method for distinguishing failure and tripping of high-voltage short-distance double-circuit chain-type power network
A double-circuit line and power network technology, applied to electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of unguaranteed removal of busbar faults, complex operation and maintenance, loss of reliability and flexibility of power supply in double-circuit parallel series network And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
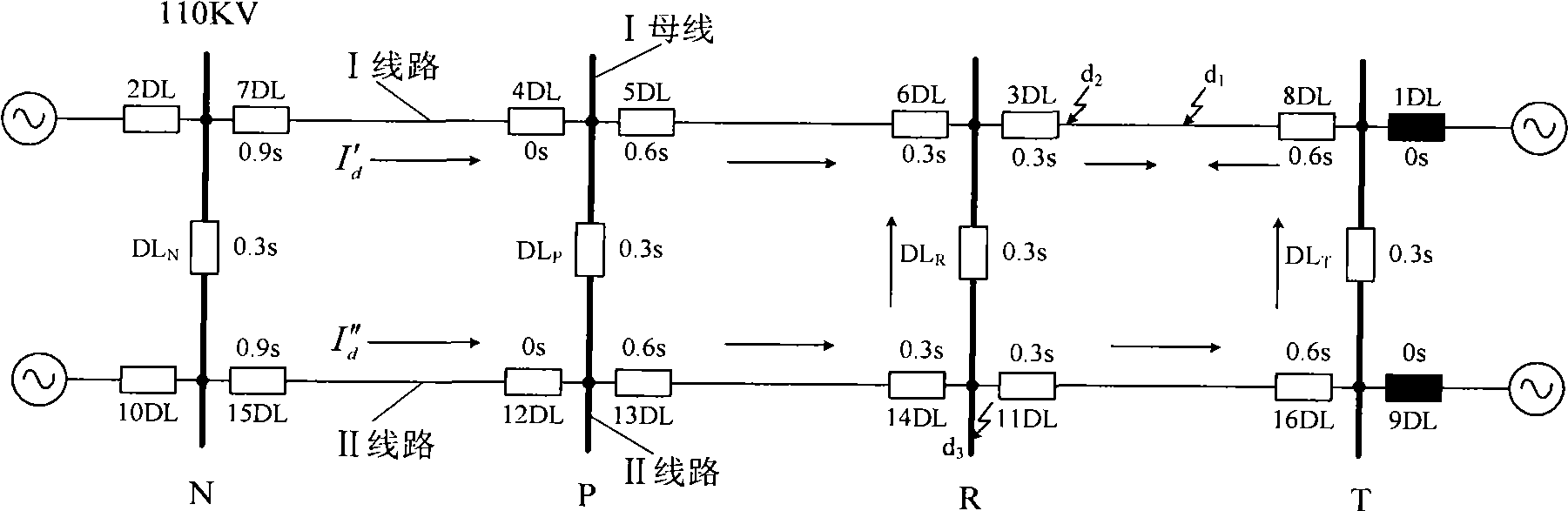
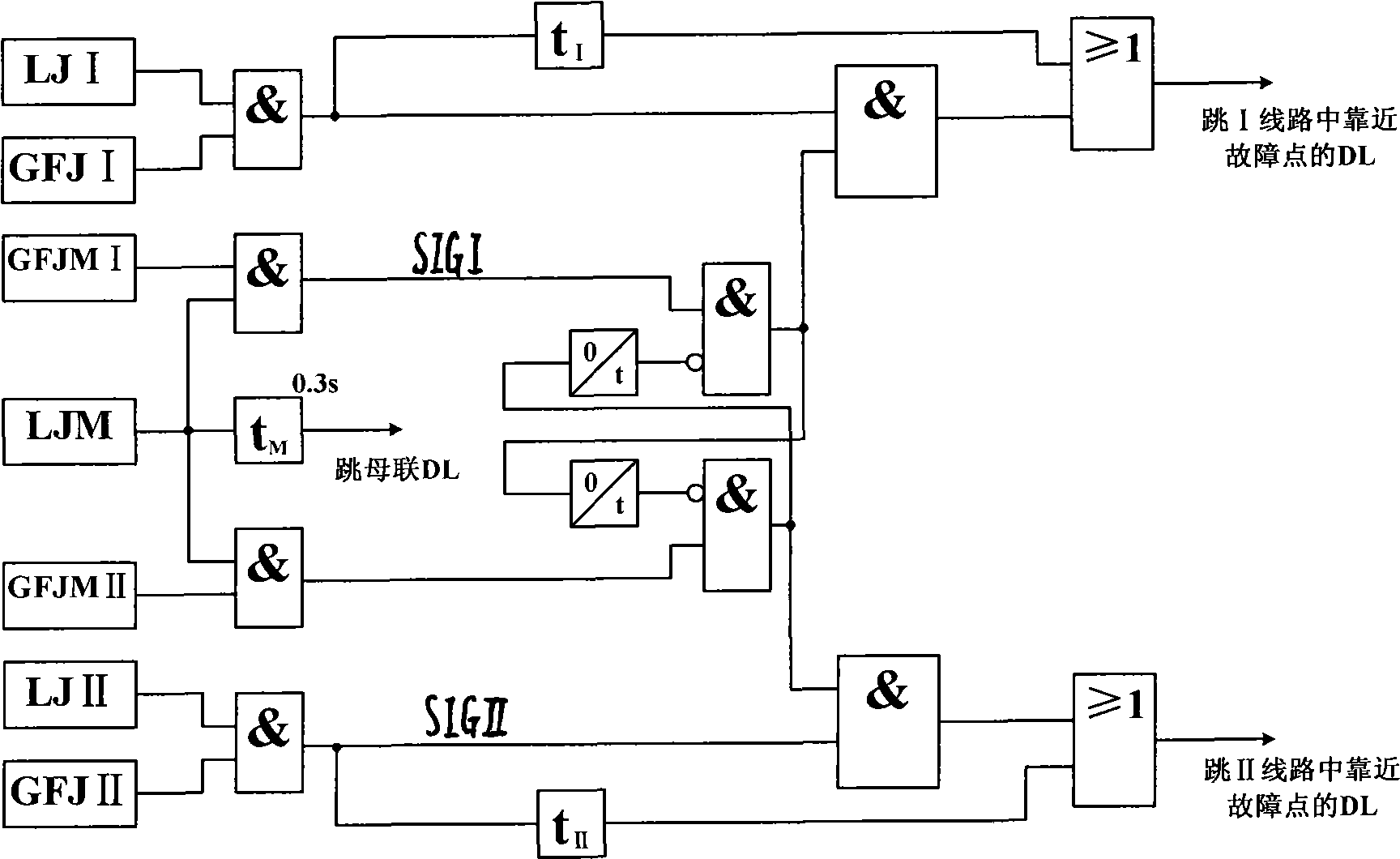
[0021] figure 1 Although the medium and high voltage short-distance double-circuit chained power network is a double-sided power supply or a ring network, almost all of the time in actual operation is de-looped somewhere in the network, and it becomes a short-distance double-circuit line with two single-sided power supplies chain network. Therefore, in the analysis of the action behavior of protection with figure 1 The mode of operation of the 1DL and 9DL solution in the ring and according to the present invention image 3 The general block diagram of the protection shown is discussed. Assume figure 1 The power supply network is de-looped at T substation (1DL and 9DL are disconnected), when d 1 When the point-to-phase short circuit occurs, the flow path and direction of the short circuit current are as shown in the figure I′ d , I" d indicated by the arrow.
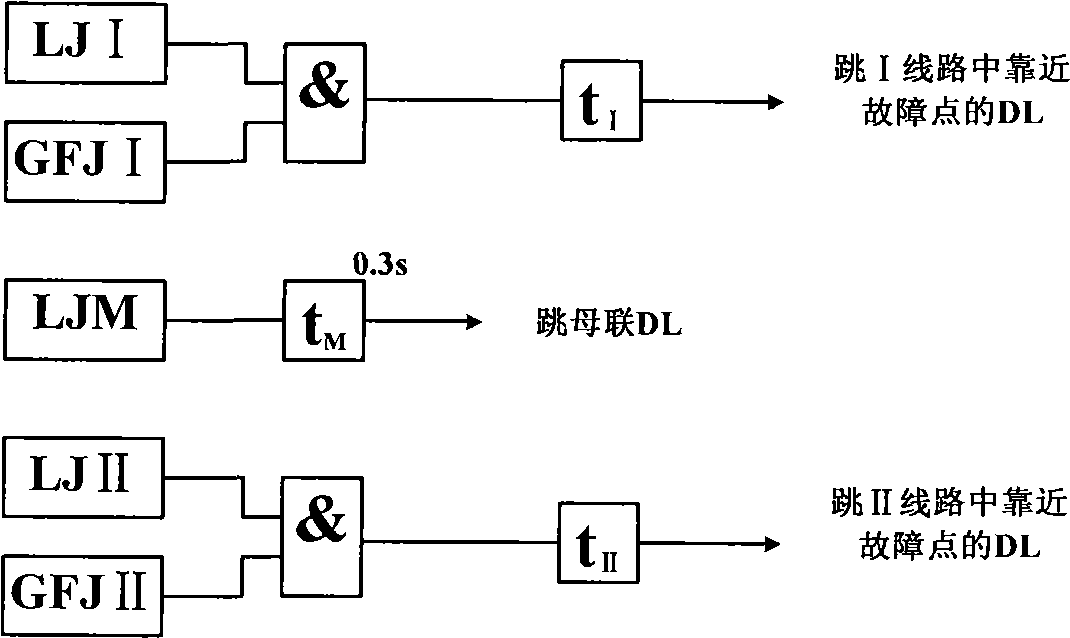
[0022] image 3 The protection of each bus-tie branch in the system adopts two power direction criteria: GFJM I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com