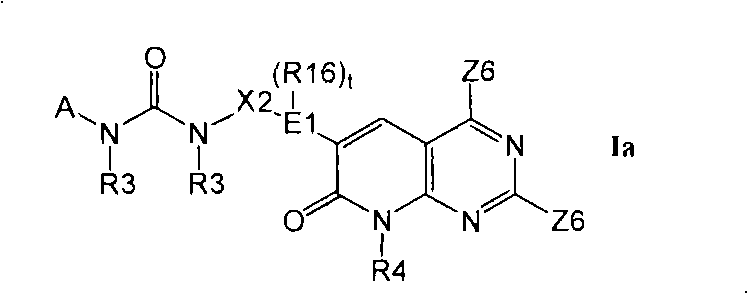
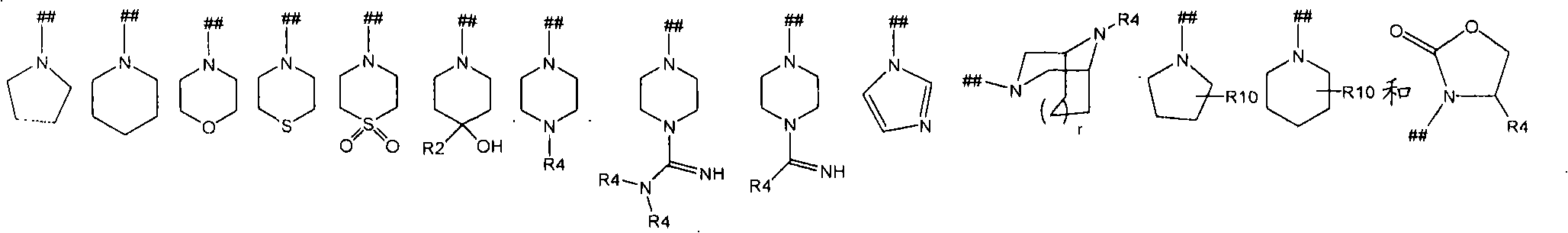
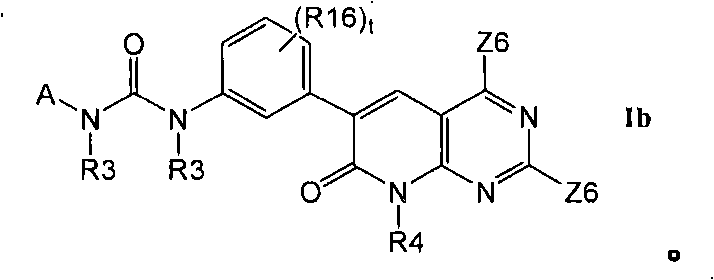
Kinase inhibitors useful for the treatment of proliferative diseases
A technology selected from, pyrimidinyl, applied in the field of kinase inhibitors for the treatment of proliferative diseases, which can solve the problem of uncontrolled signal transduction pathways
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A1
[0509] Example A1: To the CH of Example A3 (6.0g, 19mmol) 2 Cl 2 (50 mL) was added m-chloroperbenzoic acid (mCPBA, 6.5 g, 38 mmol) in one portion. After stirring at room temperature for 2 h, saturated NaHCO 3 Aqueous solution and NaHSO 3 aqueous solution and continued stirring for a few minutes. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in DMSO (5 mL) and ammonia in dioxane (2M, 200 mL, 400 mmol) was added. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was purified by reverse phase prep-HPLC to give 2-amino-6-(3-amino-4-fluorophenyl)-8-methylpyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine- 7(8H)-Kone (1.9 g, 35% yield). 1 H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-d 6 ), δ8.63(s, 1H), 7.80(s, 1H), 7.39(br s, 2H), 7.12(d, J=6.0Hz, 1H), 7.03(t, J=12.0Hz, 1H), 6.80 (m, 1H), 3.53 (s, 3H); MS (ESI) m / z: 286.2 (M+H + ).
Embodiment A2
[0510] Example A2: Using a method similar to Example A1, Example A9 (3.50g, 10.6mmol) was oxidized with mCPBA (2.87g, 11.7mmol, 70%wt) to obtain intermediate 6-(3-amino-4-fluorophenyl )-8-Ethyl-2-(methylsulfinyl)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one (2.35 g, 61% yield). The intermediate (1.40 g, 3.86 mmol) and 0.5 M ammonia in dioxane (15.5 mL, 2 equiv) were combined and purified by silica gel column chromatography to give 2-amino-6-(3-amino-4-fluorobenzene yl)-8-ethylpyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one (0.65 g, 56% yield). 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ8.63(s, 1H), 7.79(s, 1H), 7.27(s, 1H), 7.10(dd, J=2.4, 8.8Hz, 1H), 7.00(dd, J=8.8, 11.6Hz, 1H), 6.75(m, 1H), 5.14(s, 2H), 4.31(q, J=6.8Hz, 2H), 1.18(t, J=6.8Hz, 3H); LC-MS(EI) m / z : 300.0(M+H + ).
Embodiment A3
[0511] Example A3 : Example C1 (15g, 82mmol), ethyl 2-(3-amino-4-fluorophenyl)acetate (19.4g, 98mmol; described by Kuse et al. Tetrahedron (2005), 61,5754-5762 method) and K 2 CO 3 (34.0 g, 246 mmol) in DMF (100 mL) was heated at 110 °C overnight. The mixture was poured into water and the product was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 x 200 mL). The combined organics were washed with brine, dried (Na 2 SO 4 ) and concentrated in vacuo. Purification by silica gel chromatography gave 6-(3-amino-4-fluorophenyl)-8-methyl-2-(methylthio)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one (13.0 g, 50% yield). 1 H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-d 6 ), δ8.91(s, 1H), 7.99(s, 1H), 7.15(dd, J=8.7, 2.1Hz, 1H), 7.04(dd, J=11.4, 8.4, 1H), 6.80(m, 1H ), 5.21 (br s, 2H), 3.65 (s, 3H), 2.60 (s, 3H); MS (ESI) m / z: 317.2 (M+H + ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com