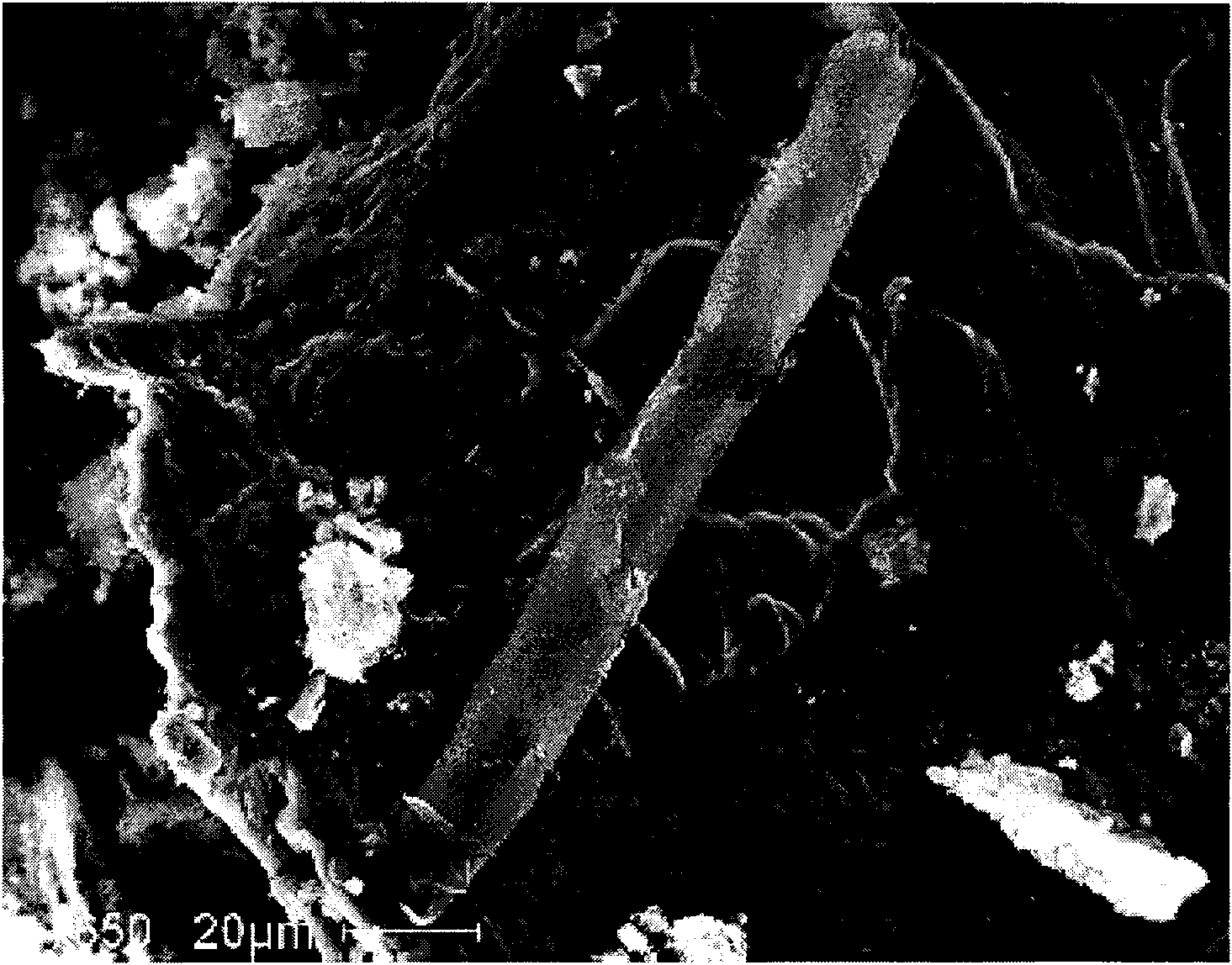
Method adopting neutral salt electrolyte to electrolytically extract tiny impurities from steel
An electrolytic extraction and electrolyte technology, which is applied in the field of metal physics research, can solve the problems of high cost, high requirements for the electrolytic environment, and large sample quality, and achieve the effect of intact composition and shape, simple and convenient operation, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment one: first configure electrolyte, formula is as follows: (wt%)
[0023] Sodium citrate: 0.2%, sodium chloride: 1%, ferrous sulfate: 3%, ammonium chloride: 2%, deionized water: 93.8%
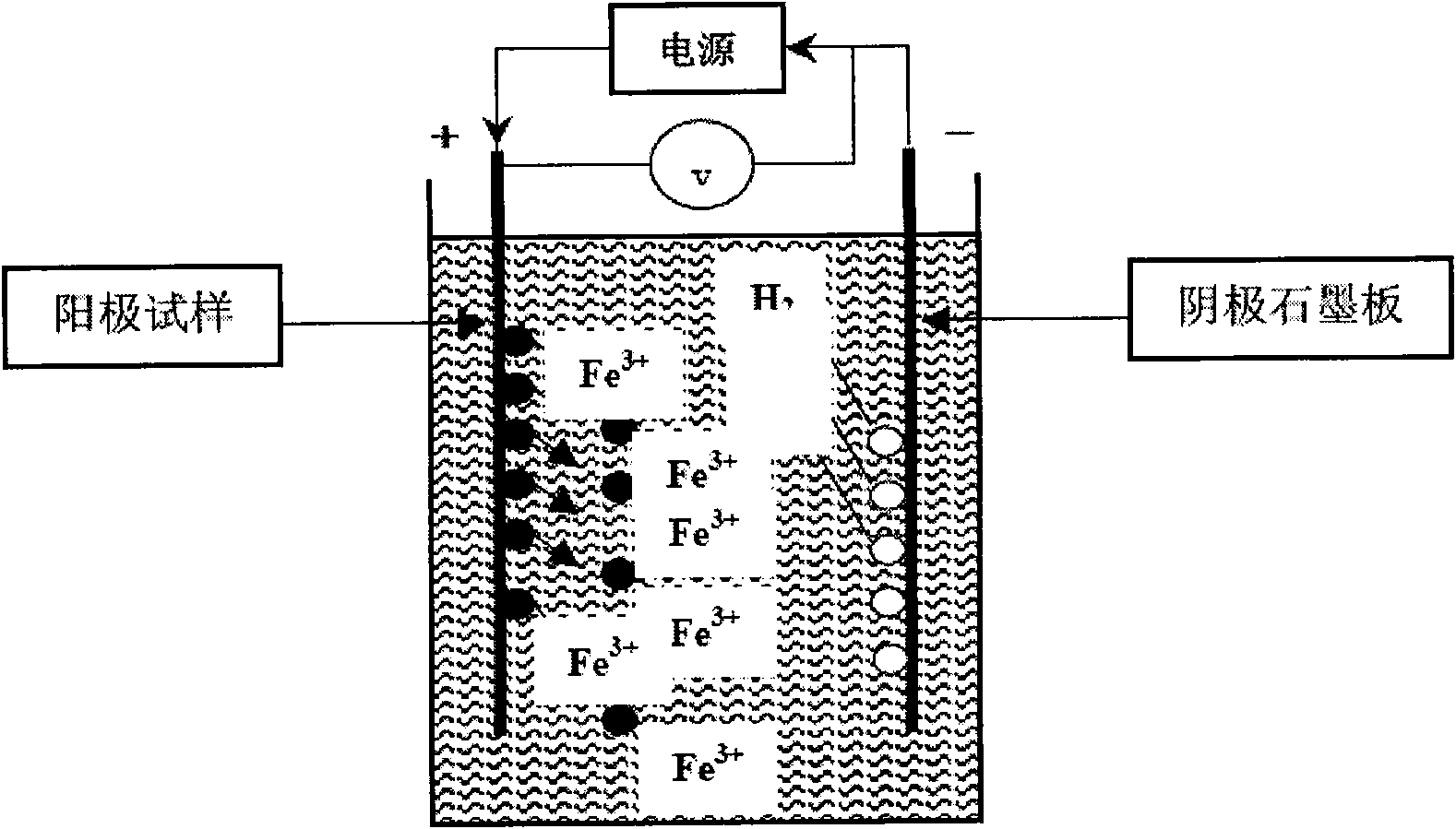
[0024] Put the above electrolytic solution into the electrolytic cell, use the graphite electrode as the electrolysis cathode, and use the pipeline steel X70 steel sample containing inclusions as the anode. When starting electrolysis, adjust the electrolysis potential to 3-10V, and the cathode current density to 0.02-0.1A / cm 2 . Electrolyze until the anode sample is completely dissolved.
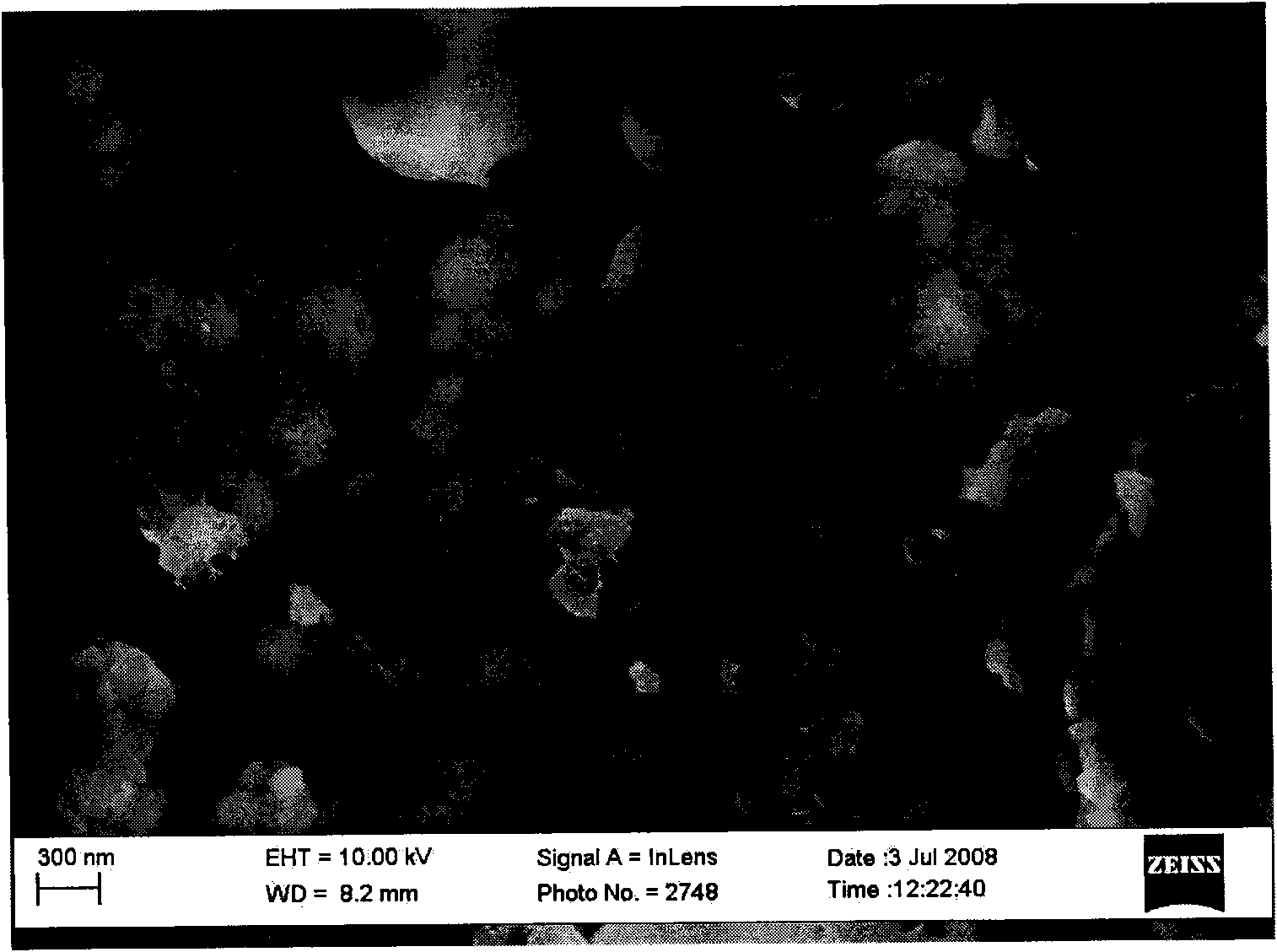
[0025] After the solution obtained by electrolysis is centrifuged with a centrifuge, the precipitate is added to a saturated ammonium salt (such as ammonium nitrate) solution, reacted and dissolved in a water bath, and centrifuged and dissolved repeatedly until no ammonia gas is released. The precipitated matter is added to deionized water, and repeatedly centrifuged and clarified in a cent...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment two: first configure electrolyte, formula is as follows: (wt%)
[0027] Sodium Citrate: 0.1%, Sodium Chloride: 4%, Ferrous Sulfate: 1%, Ammonium Chloride: 2%, Deionized Water: 92.9%
[0028] In this embodiment, the above electrolytic solution is put into an electrolytic cell, a graphite electrode is used as an electrolysis cathode, and a semi-process electrical steel sample containing inclusions is used as an anode. When starting electrolysis, adjust the electrolysis potential to 3-10V, and the cathode current density to 0.02-0.1A / cm 2 . Electrolyze until the anode sample is completely dissolved.
[0029] After the solution obtained by electrolysis is centrifuged with a centrifuge, the precipitate is added to a saturated ammonium salt (such as ammonium nitrate) solution, reacted and dissolved in a water bath, and centrifuged and dissolved repeatedly until no ammonia gas is released. The precipitated matter is added to deionized water, centrifuged and clari...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment three: first configure electrolyte, formula is as follows: (wt%)
[0032] Sodium citrate: 0.4%, sodium chloride: 1%, ferrous sulfate: 4%, ammonium chloride: 5%, deionized water: 89.6%;
[0033] In this embodiment, the above-mentioned electrolyte solution is put into an electrolytic cell, a graphite electrode is used as an electrolysis cathode, and a pipeline steel X80 steel sample containing inclusions is used as an anode. When starting electrolysis, adjust the electrolysis potential to 3-10V, and the cathode current density to 0.02-0.1A / cm 2 . Electrolyze until the anode sample is completely dissolved.
[0034] After the solution obtained by electrolysis is centrifuged with a centrifuge, the precipitate is added to a saturated ammonium salt (such as ammonium nitrate) solution, reacted and dissolved in a water bath, and centrifuged and dissolved repeatedly until no ammonia gas is released. The precipitated matter is added to deionized water, centrifuged an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com