Pneumatic tire for two-wheeled vehicle
A technology for pneumatic tires and two-wheeled vehicles, which is applied to the reinforcement layer of pneumatic tires, motorcycle tires, tire parts, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
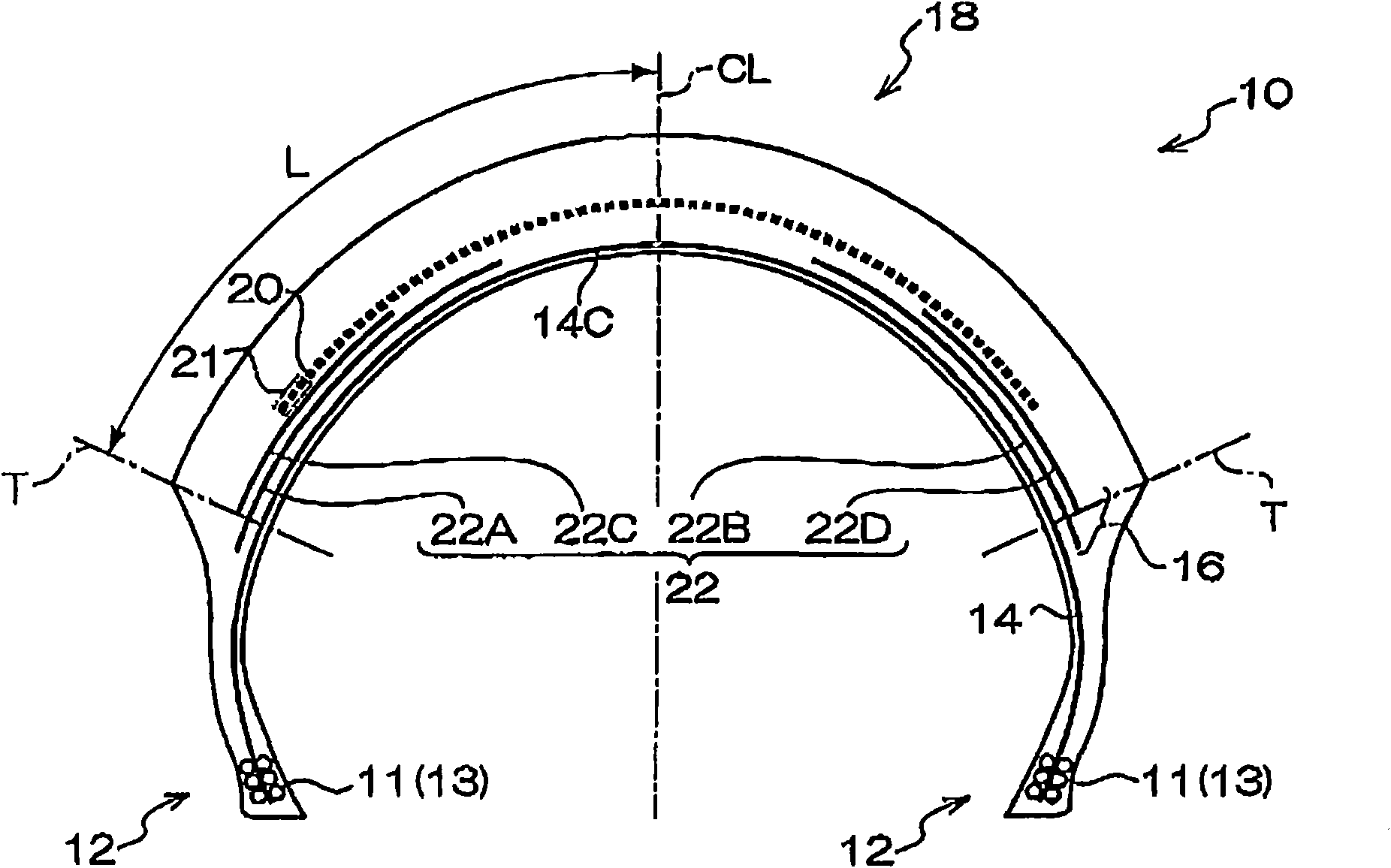
[0089] Example 1 is as figure 1 In the pneumatic tire for motorcycles constructed as shown, the width of the spiral belt layer 20 is 0.75 times the entire tread width 2L, which is 180 mm (the width on one side from the tire equator plane is 90 mm). The spiral belt layer 20 is formed by spirally winding steel cords obtained by twisting steel single wires with a diameter of 0.18 mm in a 1×3 pattern at a weft density interval of 60 cords / 50 mm.
[0090] In addition, two pairs of cross belt layers 22A to D (cross belt layers 22A and 22C are a pair and cross belt layers 22B and 22D are a pair) exist in the inner side of the spiral belt layer 20 . The width of the first intersecting belt layers 22A and 22B is 80 mm, and the outer end in the tire width direction protrudes 5 mm from the tread end T toward the tire outer side. The width of the second intersecting belt layers 22C and 22D is 50 mm, and the outer end in the tire width direction is at the same position as the tread end T...
Embodiment 2
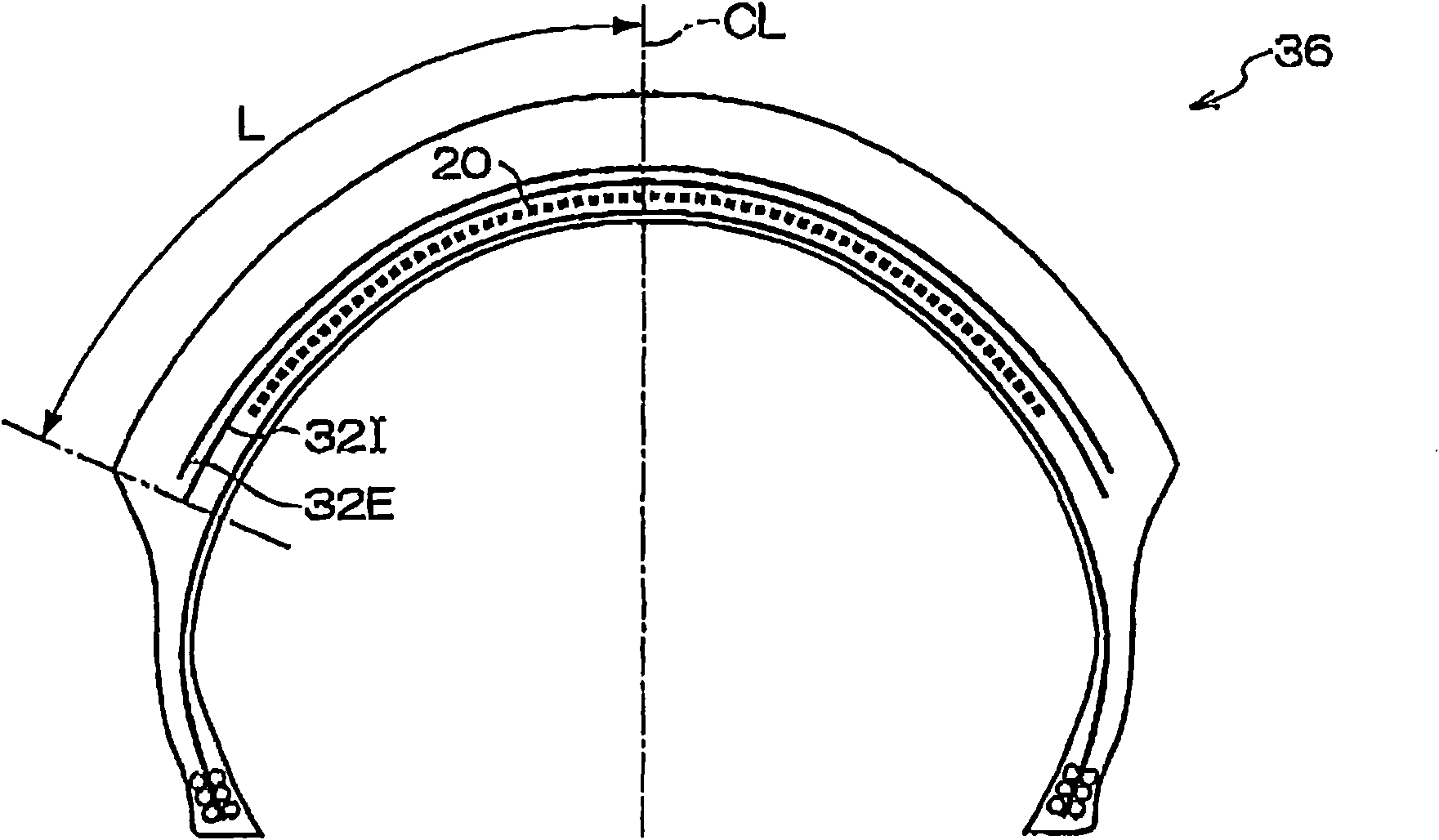
[0093] Embodiment 2 is in embodiment 1 (with reference to figure 1 ) on the outer side of the spiral belt layer 20 in the radial direction, a reinforcing belt layer (the same as the reinforcing belt layer 34 used in Example 3 described later) is added with an angle of 90 degrees relative to the tire circumferential direction. structure. The width of the additional reinforcing belt layer is 240mm, and the material of the belt layer is aramid. The material of the reinforcing belt layer is the same as that of the cross belt layers 82I and 82E of the conventional example, and the weft density and cord diameter are also the same, but the cord angle is 90 degrees, which is different from the conventional example.
Embodiment 3
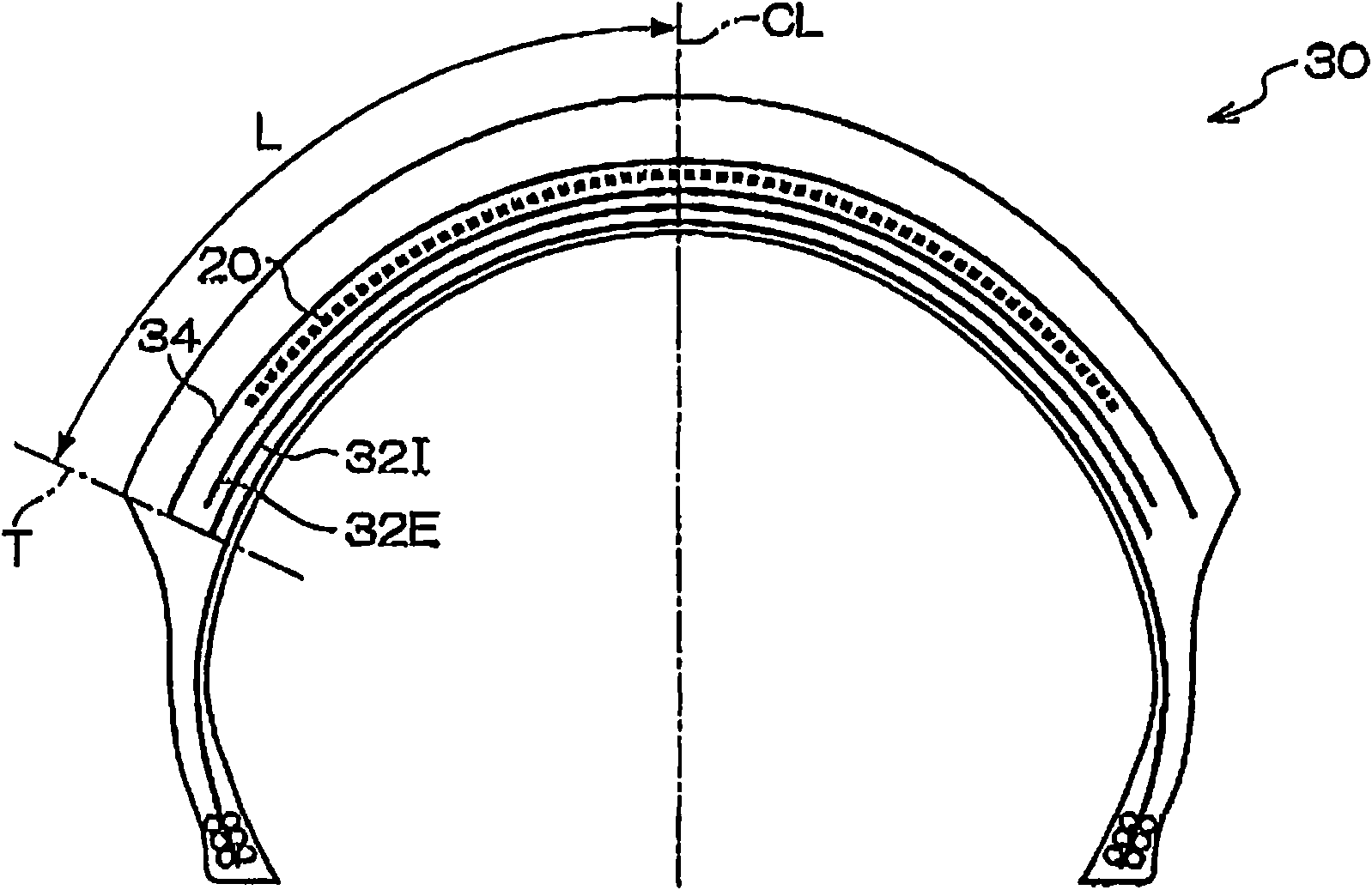
[0095] Example 3 is as figure 2 A pneumatic tire 30 for a two-wheeled vehicle configured as shown. Example 3 has the spiral belt layer 20 and the same cross belt layers 32I and 32E as the conventional example. That is, the first intersecting belt layer 32I has a width of 240 mm, and the second intersecting belt layer 32E has a width of 230 mm, and the cord angles thereof are crossed at 65 degrees with respect to the tire circumferential direction. The width of the spiral belt layer 20 is 180 mm as in other examples, which is different from the width of the spiral belt layer 80 employed in the conventional example. In addition, on the outer side of the spiral belt layer 20 in the radial direction, there is a reinforcing belt layer 34 having a cord angle of 90 degrees as in Example 2. As shown in FIG. The width of the reinforcing belt layer 34 is 240 mm as in Example 2, and the cord material constituting the reinforcing belt layer 34 is aramid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com