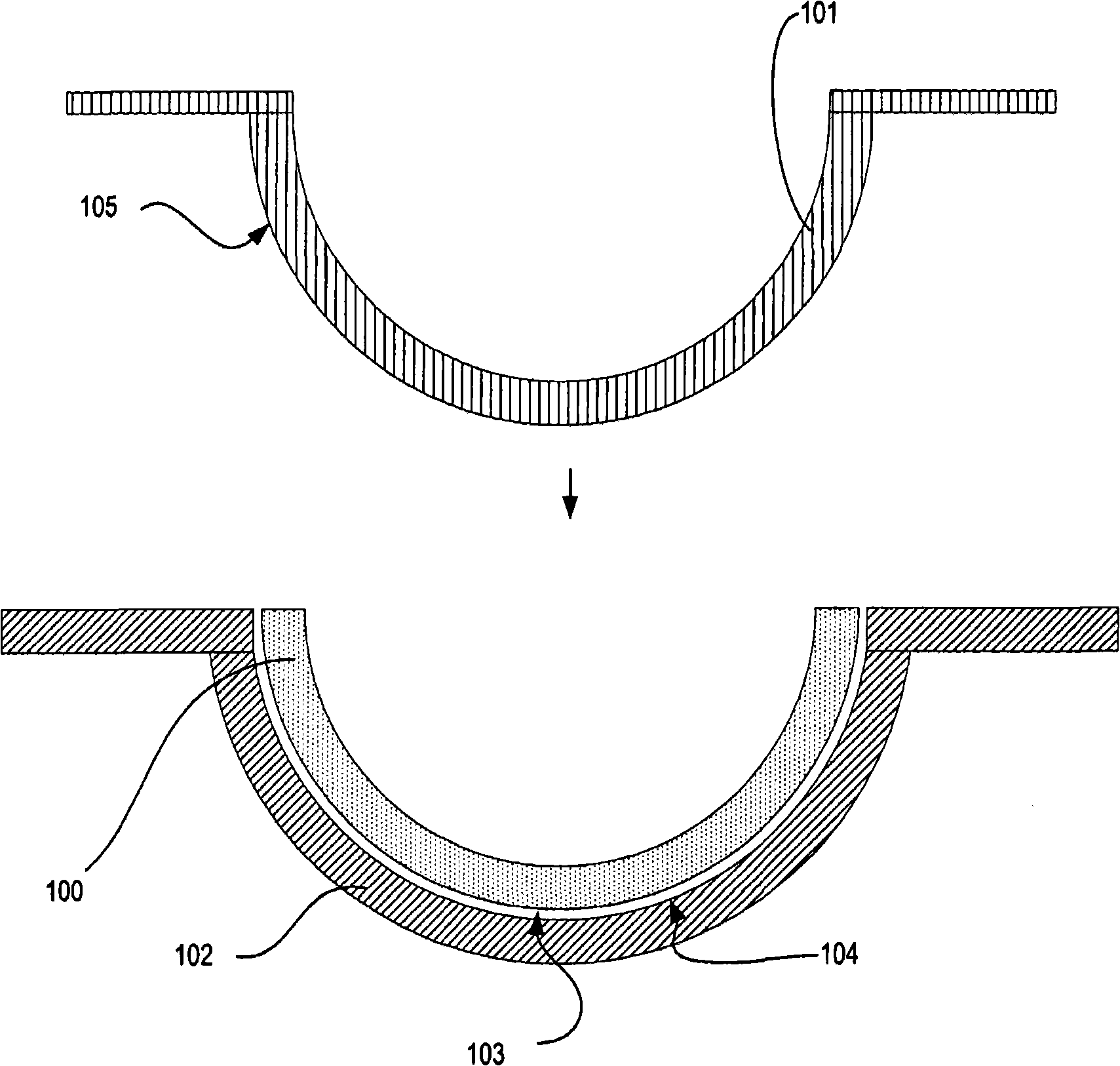
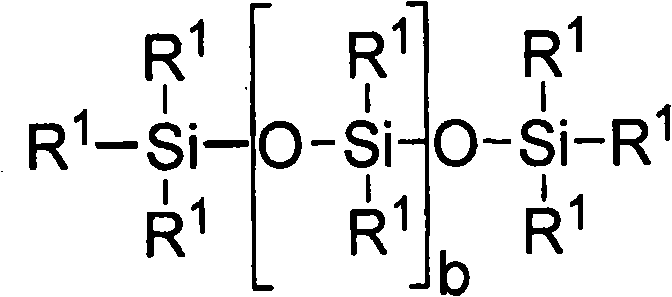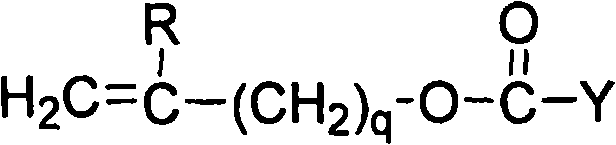Process for forming clear, wettable silicone hydrogel articles
A silicone, hydrophilic polymer technology used in the field of forming molded articles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-11
[0163]A reaction mixture was prepared consisting of 80% by weight monomer component (amounts listed in Table 1) and 20% by weight diluent (listed in Table 1). The reaction mixture was degassed at about 600-700 mmHg for about 30 minutes at ambient temperature. The reaction mixture was then placed in a thermoplastic contact lens mold (front curve made from Zeonor, back curve made from polypropylene) at 55±5°C at 1.2-1.8 mW / cm under a nitrogen atmosphere. 2 , irradiated with Philips TL20W / 03T fluorescent lamp for 25 minutes. The resulting lenses were manually demolded and released by immersing the lenses in a front curve (FC) mold in DI water at 90(±10)°C for about 2 minutes. If the lens fails to release from the FC mold within 2 minutes, the lens is kept in DI water at 90(±5)°C, using a disposable straw, sprayed with the same DI water. If the lens still does not release from the FC, manually wipe the lens from the FC. The lenses are then transferred to jars and undergo two "c...
Embodiment 12-21
[0178] A reaction mixture was prepared consisting of 55% by weight monomer component (amounts listed in Table 1) and 45% by weight diluent (mixture of 55% TPME and 45% co-diluent listed in Table 3). The reaction mixture was degassed at about 600-700 mmHg for about 30 minutes at ambient temperature. The reaction mixture was then placed in a thermoplastic contact lens mold (front curve made from Zeonor, back curve made from polypropylene) at 55±5°C at 1.2-1.8 mW / cm under a nitrogen atmosphere. 2 , irradiated with Philips TL 20W / 03T fluorescent lamp for 25 minutes. The resulting lenses were manually demolded and released by immersing the lenses in a front curve (FC) mold in DI water at 90(±10)°C for about 5 minutes. If the lens fails to release from the FC mold within 5 minutes, keep the lens in DI water at 90(±5)°C, using a disposable straw, spray with the same DI water. If the lens still does not release from the FC, manually wipe the lens from the FC. The lenses are then tr...
Embodiment 22
[0183] Lenses were prepared as in Example 13, except that the release was done in the packaging solution. That is, the resulting lenses were manually demolded and released by immersing the lenses in a front-curve (FC) mold in a packaging solution at 90 (±10)° C. for about 5 minutes. If the lens fails to release from the FC mold within 5 minutes, keep the lens in the packaging solution at 90(±5)°C, and spray it with the same packaging solution using a disposable pipette. If the lens still does not release from the FC, manually wipe the lens from the FC. The lenses are then transferred to the jar and go through two "change-out" steps - step 1) holding the packaging solution at 25(±5)°C for a minimum of 30 minutes, and step 2) holding the packaging solution at 25(±5)°C Minimum 30 minutes. The lenses are then tested in the packaging solution. Lenses were packaged into vials containing 5-7 mL of borate buffered saline solution, capped, and sterilized at 120°C for 30 minutes. Dy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com