Method, device and system for timing execution of synchronization
A technology for synchronizing systems and synchronizing information, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems that the server cannot know in advance, cannot formulate and modify data synchronization operations, and synchronize data periodically on the client terminal, so as to achieve the effect of reducing requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
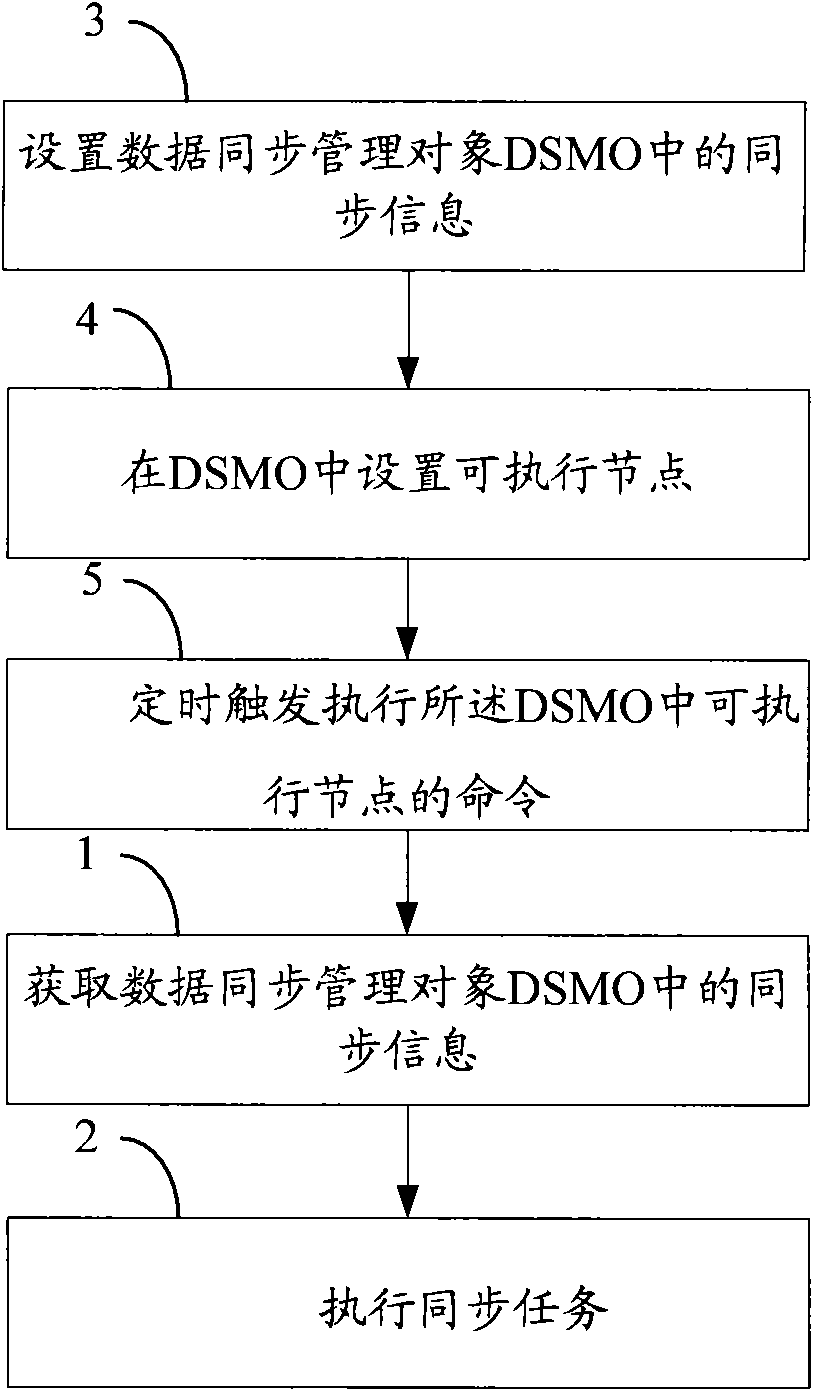
[0059] Embodiment 1. A method for timing synchronization, see figure 2 ,include:
[0060] Step A1, the terminal sets synchronization information in DSMO, and sets server identification ID information, synchronization type information and synchronization content information in DSMO.
[0061] Wherein, setting the DSMO can be done by the terminal, or can be done by the server remotely setting the DSMO. The existing DSMO is mainly used to configure the business parameters of the data synchronization DS, and save the configured parameters in the terminal, such as authentication mode information, etc., and the server initially configures these parameters through the device management DM (Device Management) protocol. Or get and modify these parameters.
[0062] In Embodiment 1 of the present invention, the terminal sets synchronization information in the DSMO, and the synchronization information includes information such as synchronization content, server identification ID, and sy...
Embodiment 2
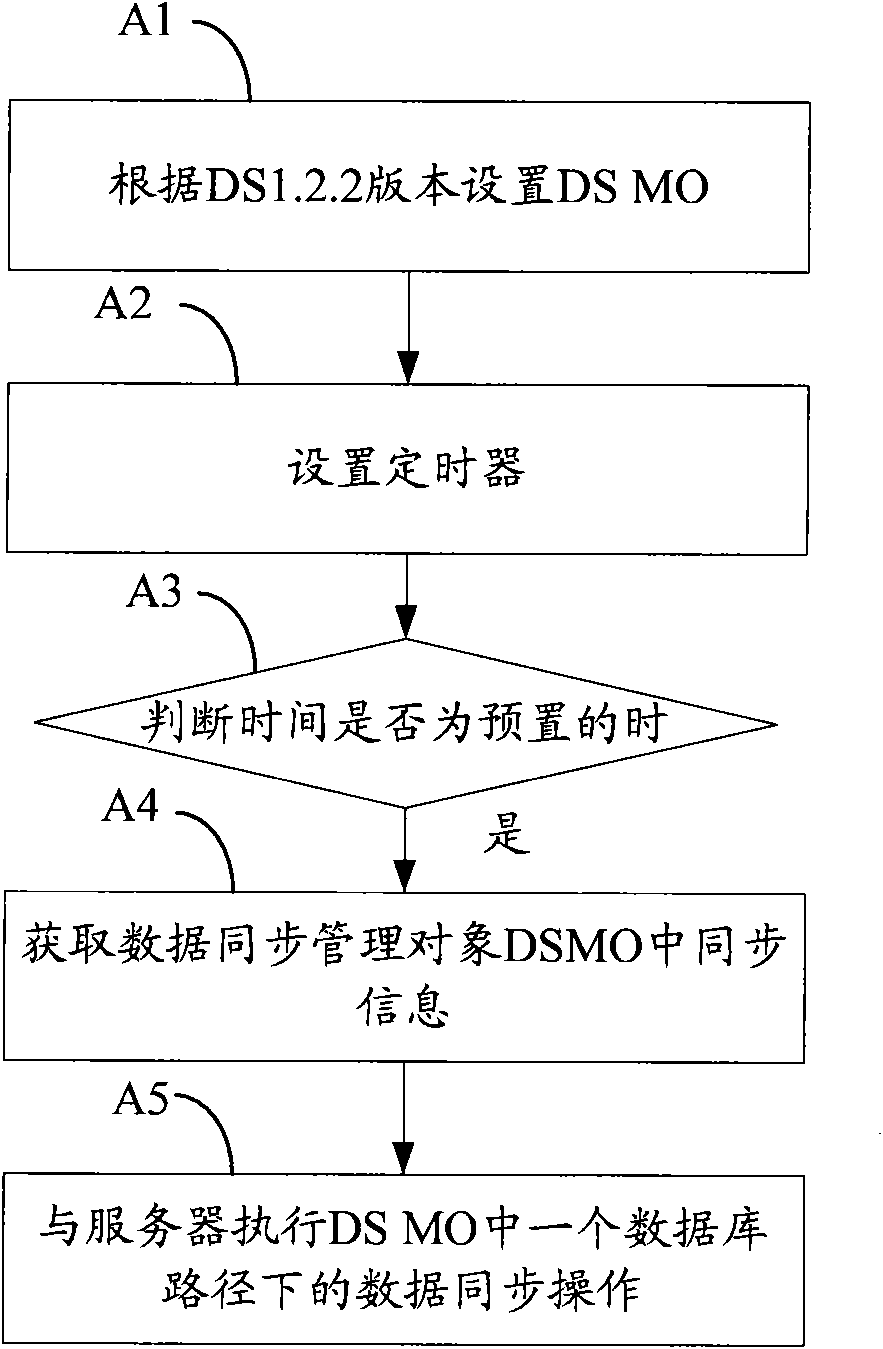
[0080] Embodiment 2, a method for performing synchronization at regular intervals, see Figure 5 shown, including:
[0081] Step B1, the terminal sets synchronization information in DSMO, and sets server identification ID information, synchronization type information and synchronization content information in DSMO.
[0082] Wherein, step B1 is similar to step A1 in the first embodiment, the difference is that in step B1, DSMO is set as follows: a synchronization direction node and a synchronization behavior node are added under the Sync Type node in DSMO, see Figure 6 As shown, it is information included in a DSMO defined in the method provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0083] In order to facilitate the understanding of the difference between Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 of the present invention, it is necessary to explain DS1.2.2 and DS2.0. DS1.2.2 and DS2.0 are two different versions of the OMA DS for Open Mobile Application Data Synchronizati...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Embodiment 3, a method for performing synchronization at regular intervals, see Figure 7 As shown, the method includes:
[0095] Step F1, setting DSMO in the terminal.
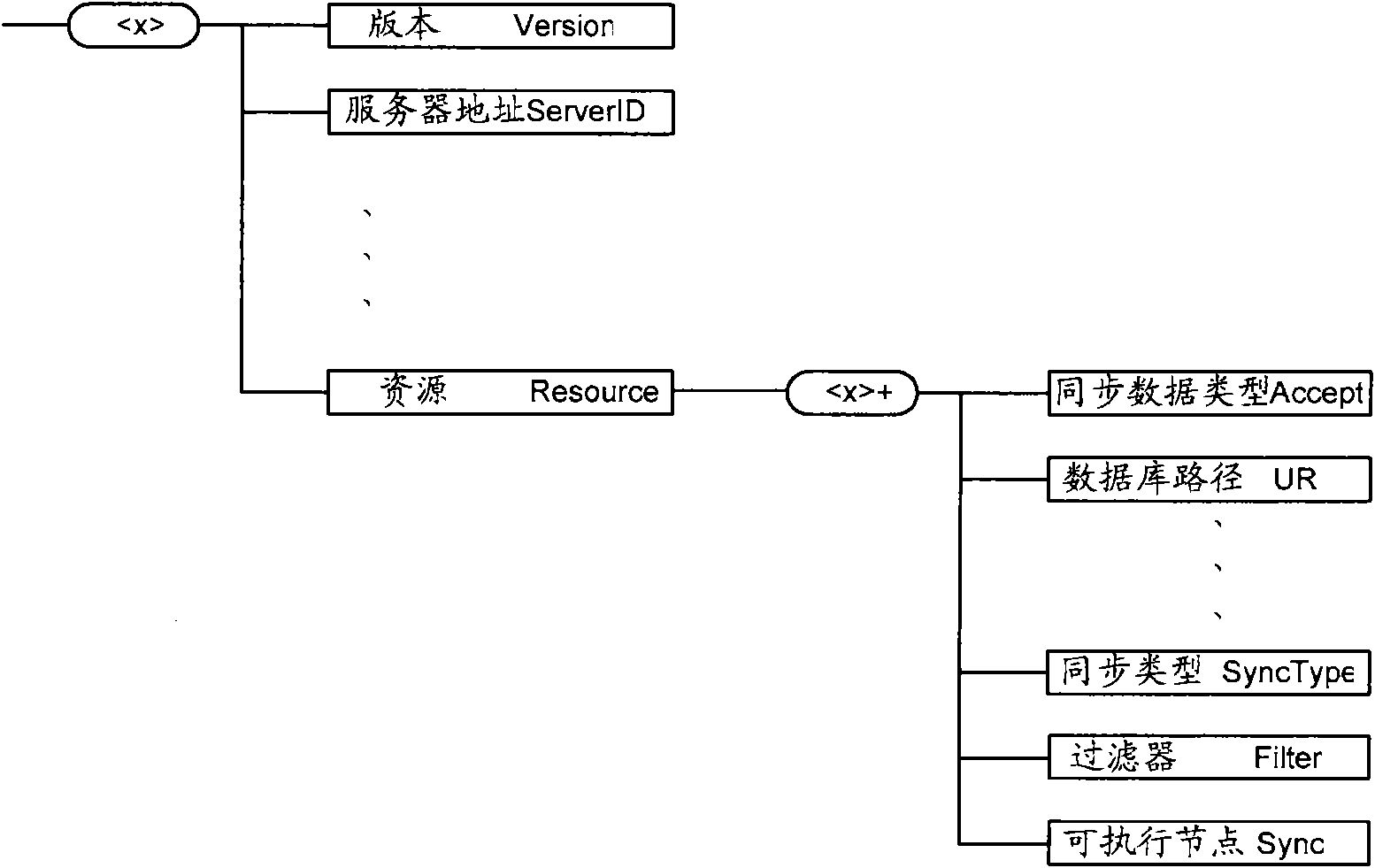
[0096] For the definition of DSMO, see Figure 8 and Figure 9 As shown, an intermediate node, namely the Sync node, is added under the root directory of DSMO. Include multiple child nodes under the Sync node, use * Group the child nodes under the Sync node, *The nodes included in each extended node are similar, and can include database datastore nodes, synchronization type Sync Type nodes and executable Exec nodes; multiple database path URI nodes can be set under the datastore node for recording synchronization content information , each database path is in a +The value in the URI child node of the expansion node. Wherein, the Accept node is similar to the definition of Accept in the prior art.
[0097] It should be noted, Figure 8 and Figure 9 The difference lies in the sett...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com