Differential feed half-wave length antenna with harmonic suppression function
A technology of differential feeding and harmonic suppression, applied to antennas, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to provide sufficient suppression of harmonic bandwidth, reduce antenna gain and efficiency, etc., achieve easy processing, reduce interference, and suppress secondary The effect of harmonics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
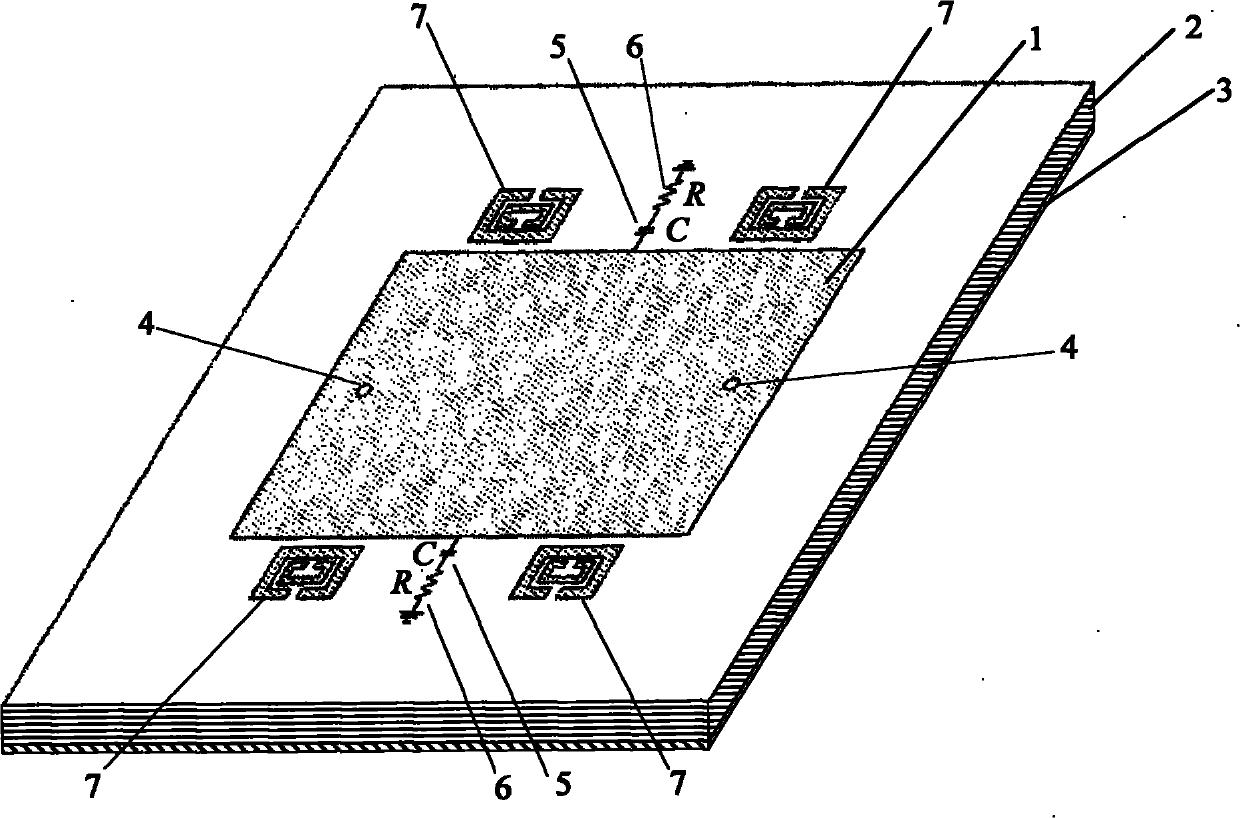
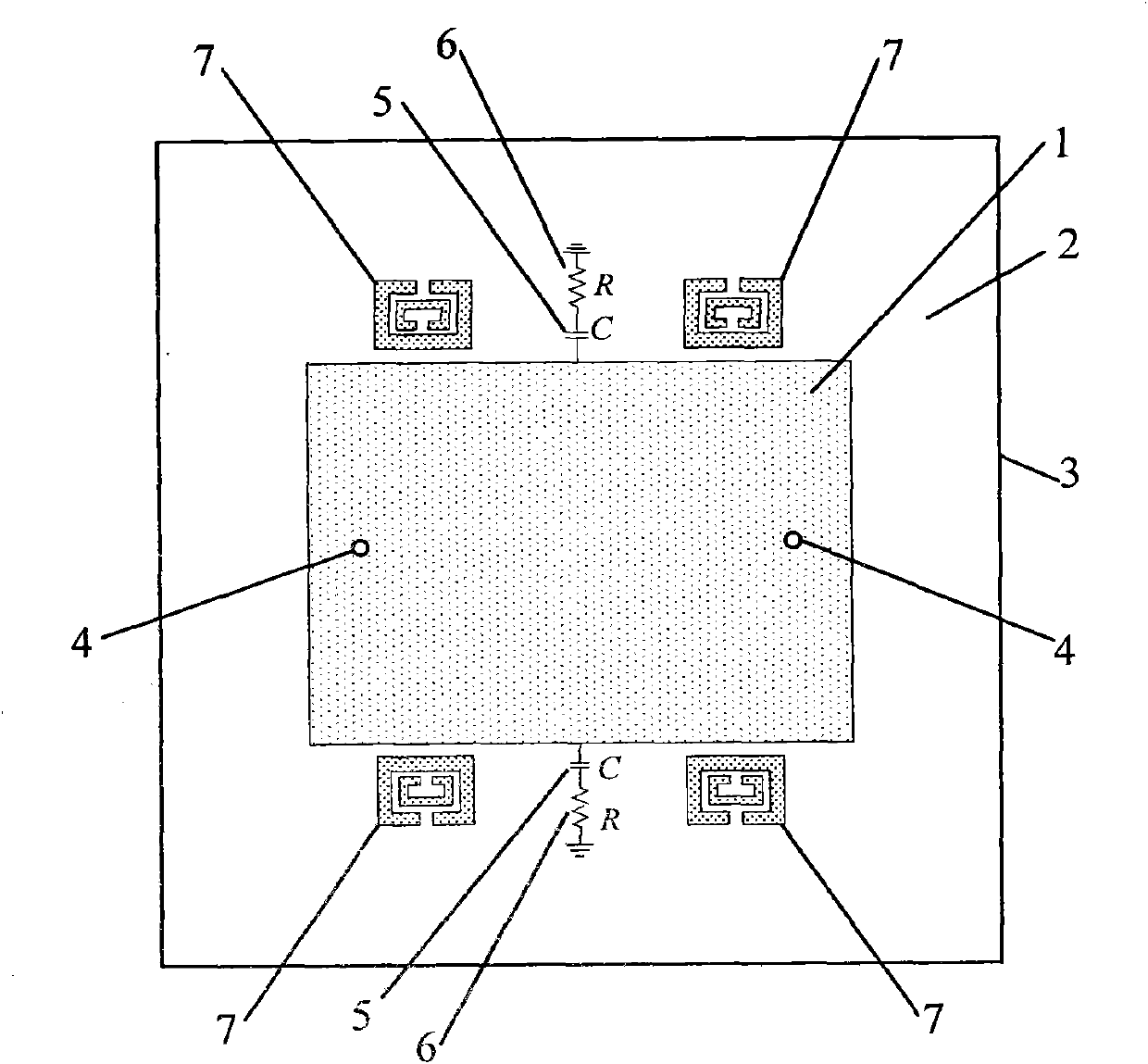
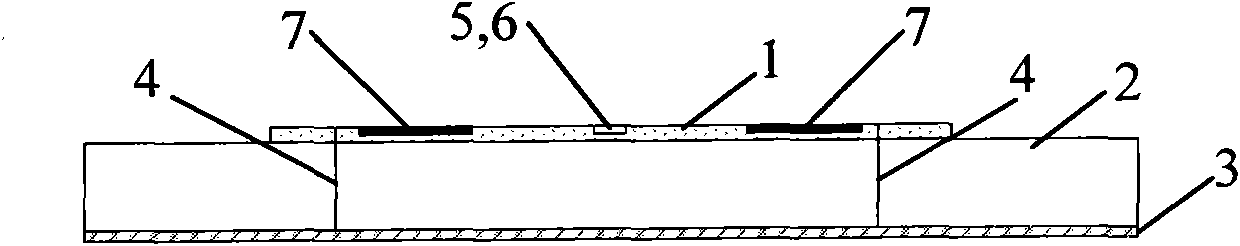
[0025] Such as Figure 1-3As shown, a differentially fed half-wavelength antenna includes an upper radiation patch 1, an intermediate dielectric substrate 2 and a bottom metal floor 3; One end of the electrical probe 4 is connected to the upper radiation patch 1 and the other end is connected to the coaxial feed port of the bottom metal floor 3 through the intermediate dielectric substrate 2 . When the port is matched with the antenna, the signal can be fed into the antenna, and the antenna resonates to radiate the energy. The antenna is fed by a pair of parallel probes 4 . Two matching attenuation networks are respectively connected to the lateral side of the upper radiation patch 1 on the symmetrical line of the two feeding points 4 of the upper radiation patch 1, and the symmetrical line of the two feeding points 4 is the lateral midline. The matching attenuation network includes a capacitor 5 and a resistor 6, the capacitor 5 and the resistor 6 are connected in series, t...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Such as Figure 4-6 As shown, a typical differentially fed half-wavelength antenna with harmonic radiation suppression function includes an upper radiation patch 1, a first dielectric substrate 4, a probe layer 2, a second dielectric substrate 5 and a bottom metal floor 3; A first dielectric substrate 4 is provided between the upper radiation patch 1 and the probe layer 2, and a second dielectric substrate 5 is provided between the probe layer 2 and the bottom metal floor 3; the two probes 4 are located vertically on the second dielectric substrate 5 On the center line of the side, one end of the feed probe 10 is connected to the probe layer 2 to feed the upper radiation patch 1 through coupling, and the other end is connected to the coaxial feed port of the bottom metal floor 3 through the dielectric substrate 5 . When the port is matched with the antenna, the signal can be fed into the antenna, and the antenna resonates to radiate the energy. Two matching attenuatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com