True three-dimensional modeling method for complicated faults
A three-dimensional modeling and fault technology, applied in the field of geological surveying and mapping, can solve the problems of non-negligible thickness, limited scope of application, and inability to integrate expert knowledge, so as to simplify the difficulty and ensure the correctness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
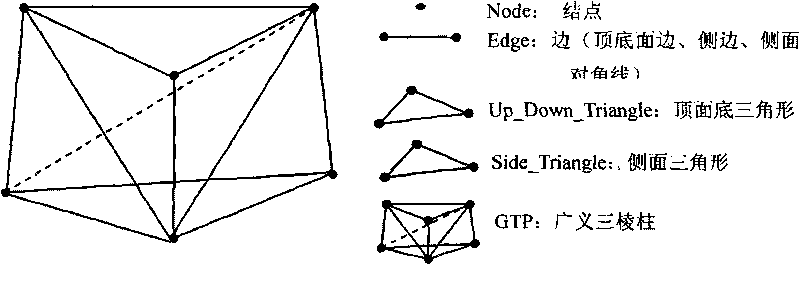
[0022] Such as figure 1 Shown: GTP is surrounded by two triangles whose top and bottom are not necessarily parallel, and three side space quadrilaterals. The geometric elements include nodes, edges, top and bottom triangles, side triangles, and GTP. This paper stipulates that all GTP voxels (including voxels formed after various degenerates) contain top and bottom triangular elements. The topological relationship between GTP voxels and their modeling elements can be inferred from the top and bottom triangle nodes and their corresponding relationships. Therefore, the determination of the top and bottom triangles determines the GTP voxel itself, and the top and bottom triangles are also one of the important reference factors for the 3D interactive modeling method of faults in this paper.
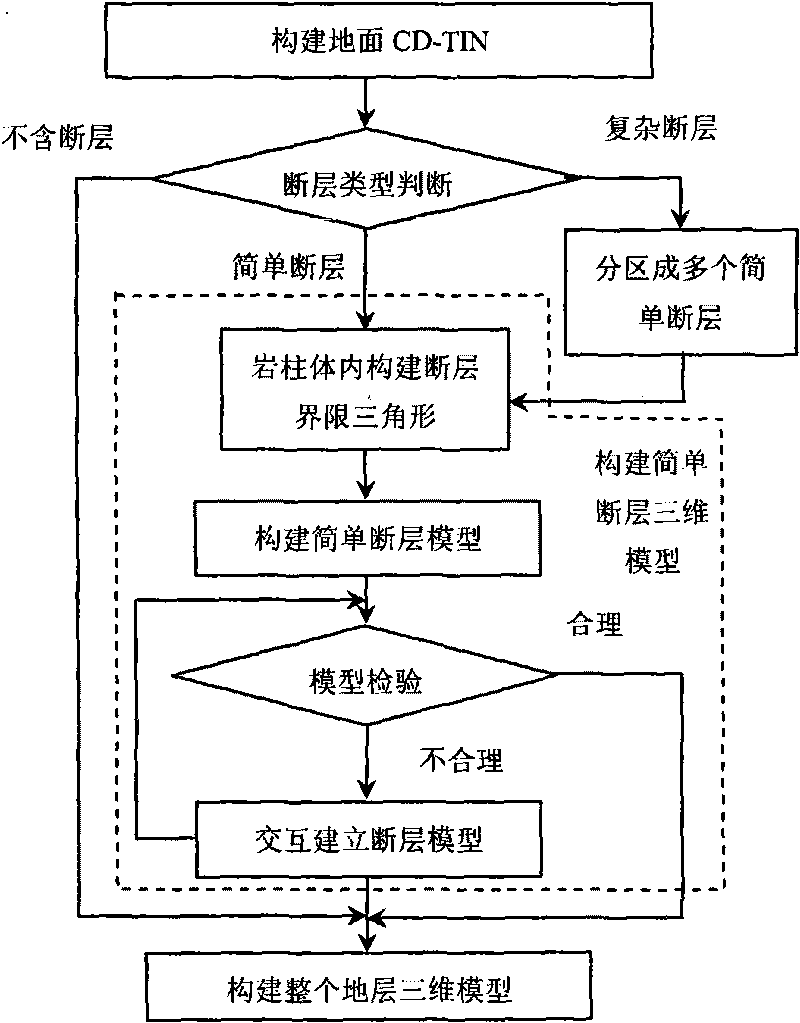
[0023] Such as figure 2 Shown: Using the RPBP method, the complex fault system is converted into multiple simple fault systems, and then the method of building a simple fault system model i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com