VRRP and learning bridge CPE
A technology of virtual network and telecommunication network, applied in the direction of network connection, data exchange network, digital transmission system, etc., which can solve the problems of wasting local loops and gathering network bandwidth, occupation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
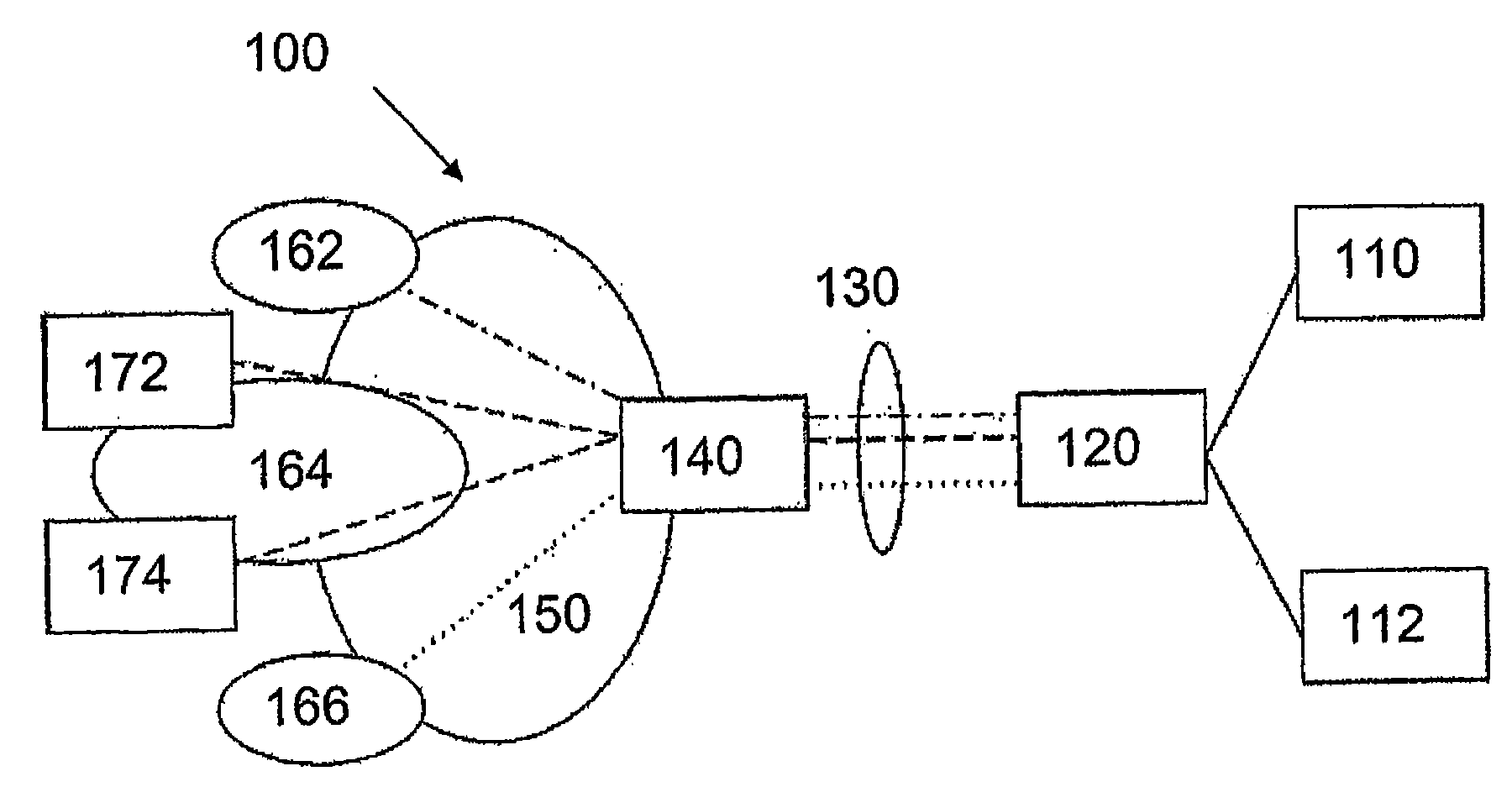
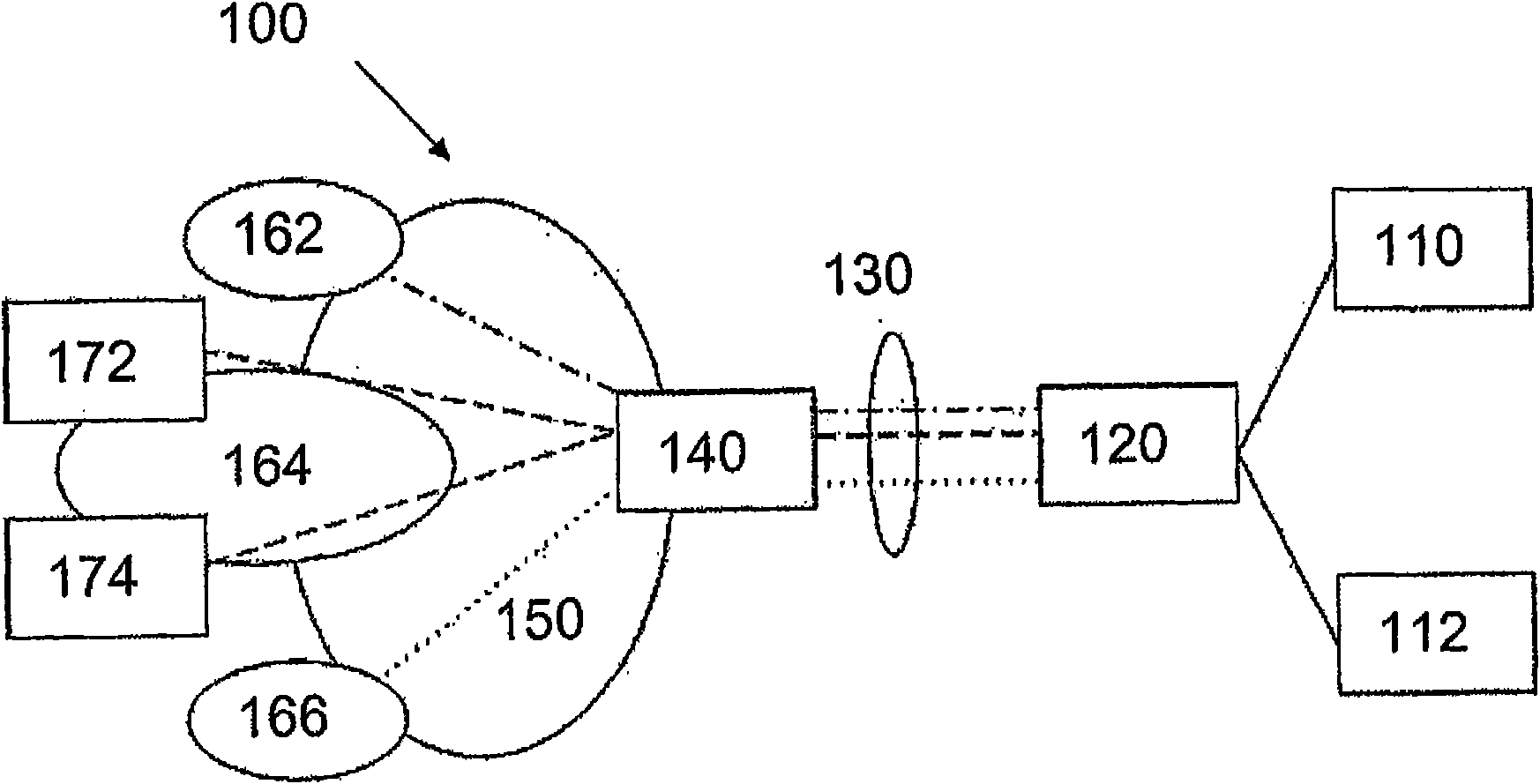
[0048] Figure 1 shows a network infrastructure 100 according to one embodiment of the present invention.
[0049] It should be mentioned here that the network infrastructure 100 in Figure 1 may represent any type of telecommunications network in which data is sent in packets or frames from end user hosts to nodes in the network. Thus, the invention can also be applied in wireless telecommunication networks which are part of the invention.
[0050] Now, the network infrastructure 100 in FIG. 1 comprises a first end user host 110 and a second end user host 112 connected to a learning bridge in case of an Ethernet connection. However, the first and second end-user hosts 110 , 112 may also be connected not to the learning bridge 120 but to an Ethernet switch, hub or some other Ethernet node performing a function equivalent to the learning bridge 120 . It should be mentioned here that the end user hosts 110 and 112 may include mobile terminals or static telecommunication terminals...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com