Method for fabricating nitride semiconductor light-emitting device
A technology for nitride semiconductors and light-emitting devices, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor lasers, lasers, etc., can solve problems such as uneven Al composition, and achieve the effects of inhibiting lateral growth, inhibiting rapid growth, and preventing the occurrence of cracks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0056] This embodiment relates to a method for manufacturing a nitride semiconductor light-emitting device, including the steps of: forming a recessed region in a nitride semiconductor substrate having a non-polar surface or a semi-polar surface; Nitride semiconductor thin film of p-type nitride semiconductor thin film, active layer and Al-containing p-type nitride semiconductor thin film. The p-type nitride semiconductor thin film is grown at a growth temperature higher than or equal to 700°C and lower than 900°C. A specific description will be given below.
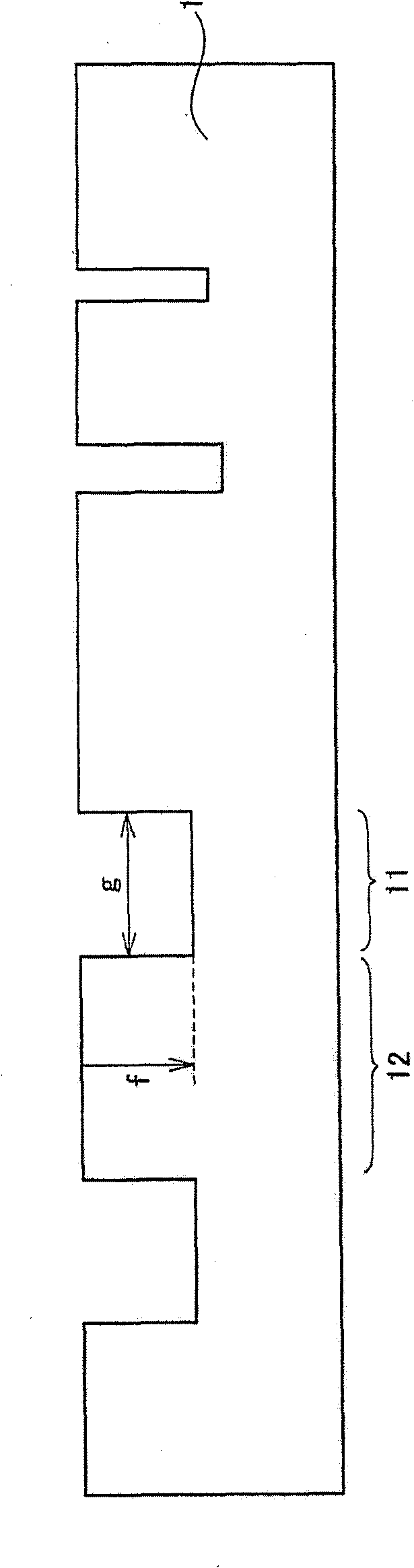
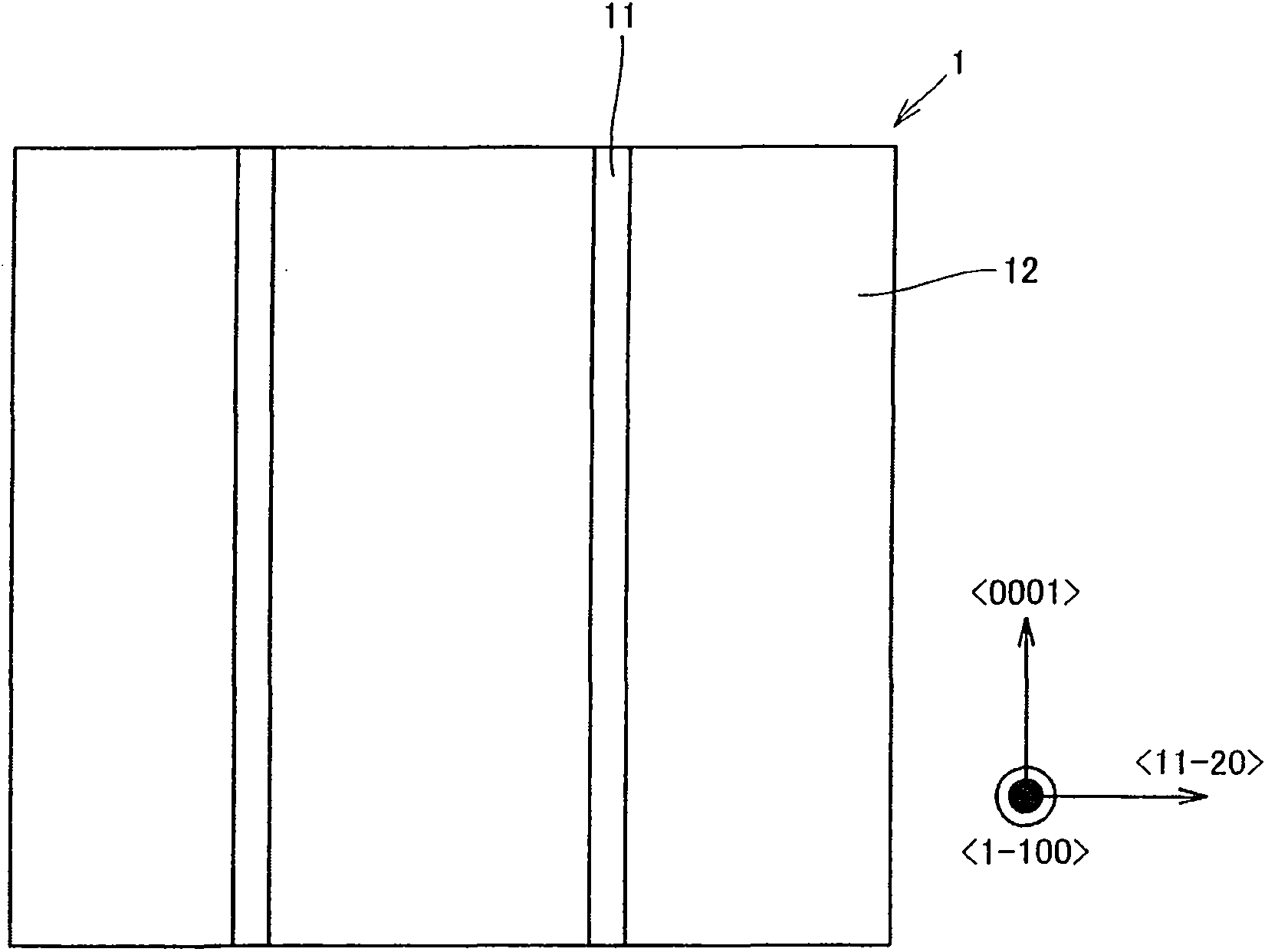
[0057] see figure 2 and 4 A case where a nitride semiconductor thin film is directly grown on a nitride semiconductor substrate will be described. According to this embodiment, Figure 4 The nitride semiconductor thin film shown in ( Figure 4 31 to 39) were grown by MOCVD in the figure 2 The shown strip shape forms the recessed region 11 on the surface of the nitride semiconductor substrate 1, thereby fabricatin...
no. 2 example
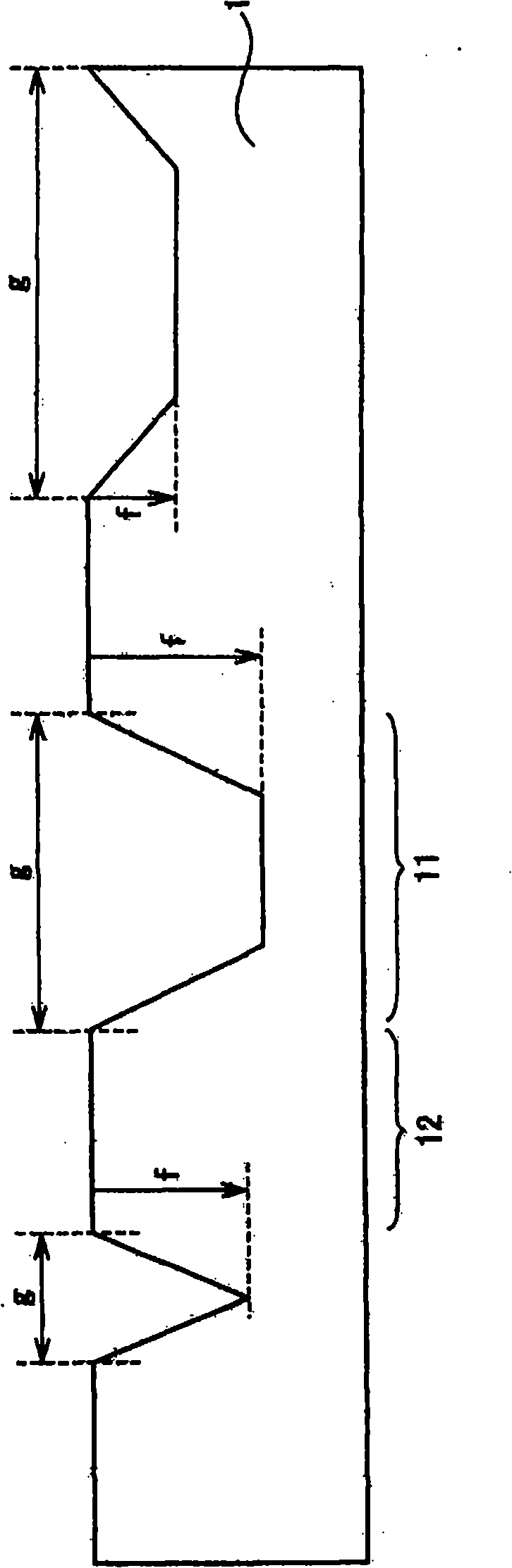
[0090] This embodiment relates to a method of manufacturing a nitride semiconductor light emitting device, except for Figures 10A to 10C As shown, a growth inhibiting film 5 to be described later is provided in a recessed region of a nitride semiconductor substrate and a nitride semiconductor thin film is subsequently provided outside the nitride semiconductor substrate, and the manufacturing method of this nitride semiconductor light-emitting device is similar to in the first embodiment. Figure 8C The nitride semiconductor light-emitting device obtained by this example is shown. Although the effects of the present invention can be achieved by the first embodiment, providing the growth inhibiting film as in this embodiment can further slow down the growth rate of the nitride semiconductor film (particularly, the p-type nitride semiconductor film) on the recessed region.
[0091] Setup of Growth Inhibitory Membrane
[0092] will now refer to Figures 9A to 9F An example of...
no. 3 example
[0114] This embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, except that the substrate adopts a GaN substrate with an A-face {11-20}, and its GaN substrate has a strip shape formed in the direction by vapor phase etching. A recessed region with a width of 5 μm, a depth of 3 μm, and a period of 400 μm. No growth inhibitory film was provided. This embodiment can achieve effects similar to those of the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com