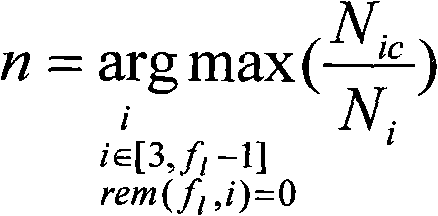Blind identification method of circulation code grouping length
A technology of block length and cyclic code, applied in cyclic code, error correction/detection using block code, error correction/detection using linear code, etc., to achieve the effect of wide application, simple principle, and simple identification process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
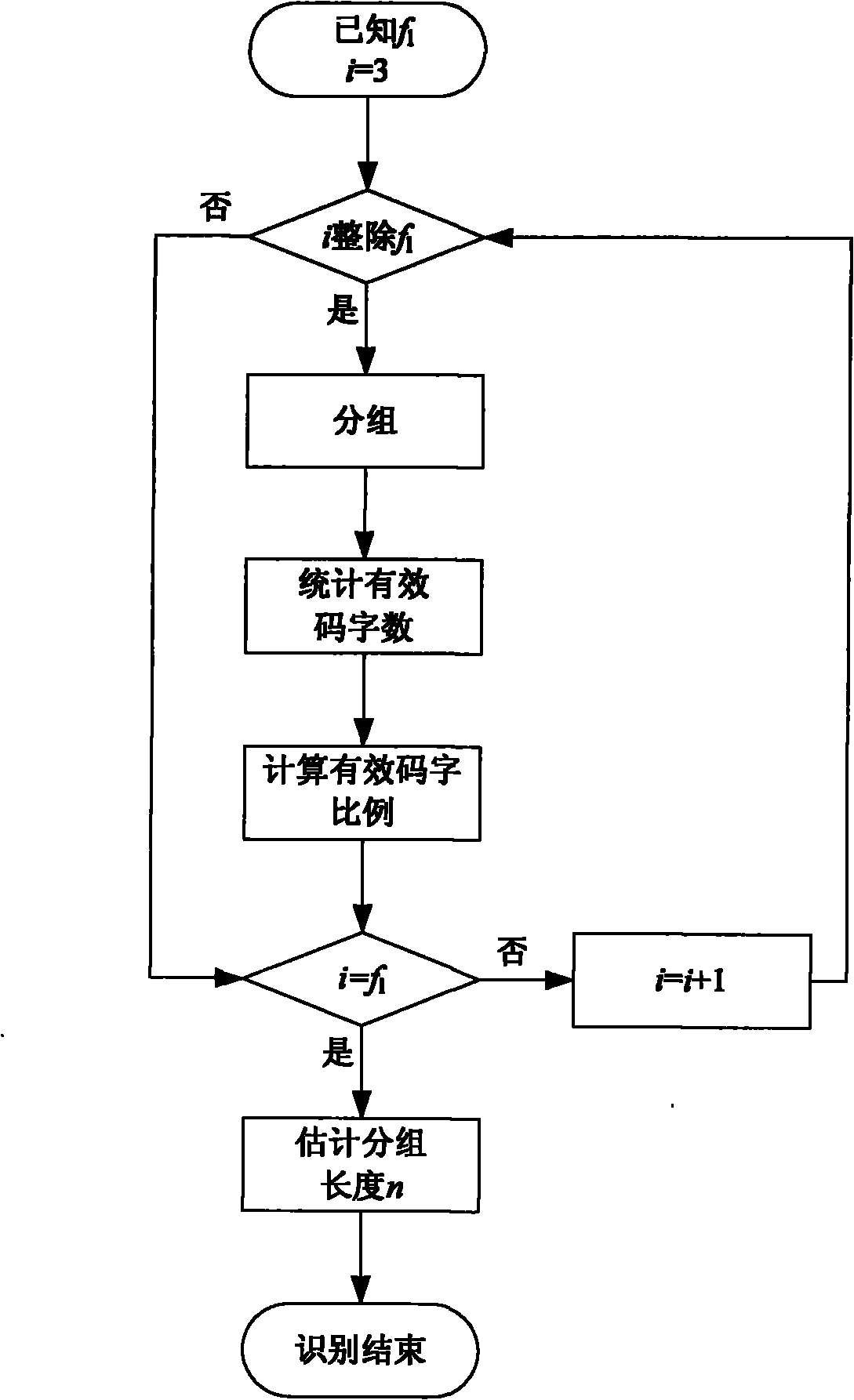
[0040] A blind identification method of the block length of the cyclic code, when identifying the block length n of the (n, k) cyclic code whose message length is k, first determine the frame length of the cyclic code as f l , and in [3, f l ], take the factor i as the grouping length for grouping, and the cyclic code will get N after being grouped i codewords, and then in the obtained N i Determine and count the proportion of valid codewords among the codewords, and the i value with the largest proportion of valid codewords is identified as the packet length n.
[0041] The judgment rules for valid codewords are:
[0042] gcd[c 0 (x),c 1 (x),...,c i-1 (x)]≠1
[0043] where c 0 (x) is the code polynomial corresponding to code word c, c j (x), j=1, 2, ..., i-1, is the code polynomial corresponding to the code word obtained after the code word c is cyclically shifted to the left j times; gcd[] represents seeking the greatest common divisor operation.
[0044] In this pa...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Taking the most commonly used binary BCH code and RS code in cyclic codes as examples, verify the recognition algorithm described in 2.
[0073] 1. (15, 11) binary BCH code
[0074] Knowing that the frame length is 75, its factors are 3, 5, 15, and 25. Counting 100 codewords respectively, the effective codeword ratios obtained are: 0.58, 0.55, 1.00, and 0.58, respectively. Obviously the packet length is 15.
[0075] 2. (15, 11) RS code
[0076] Knowing that the frame length is 75, its factors are 3, 5, 15, and 25. Counting 100 codewords respectively, the effective codeword ratios obtained are: 0.22, 0.24, 1.00, and 0.35, respectively. Obviously the packet length is 15.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com