Electronic component transporting device
A technology of electronic components and transmission devices, applied in the direction of electrical components, electrical components, circuits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
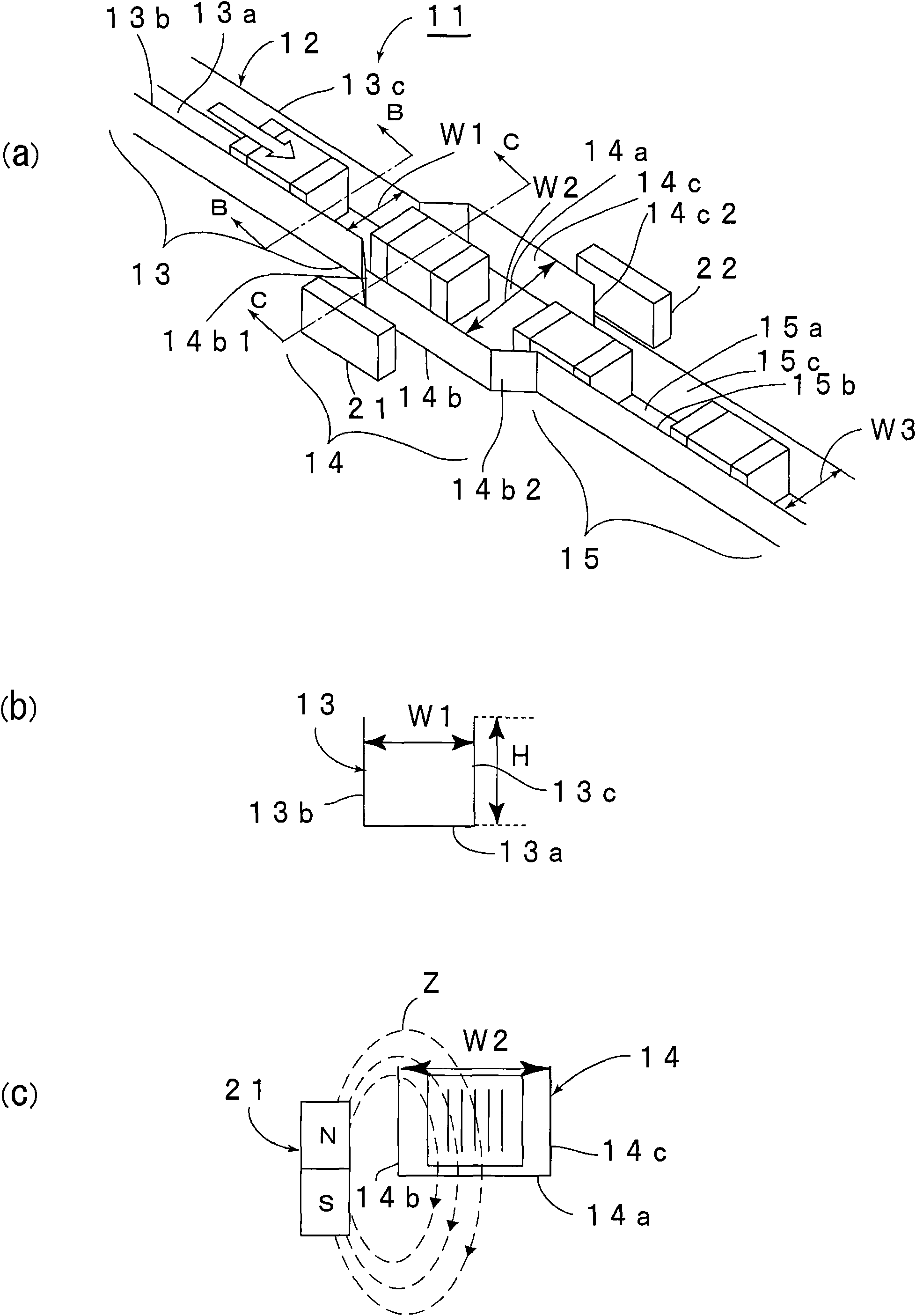
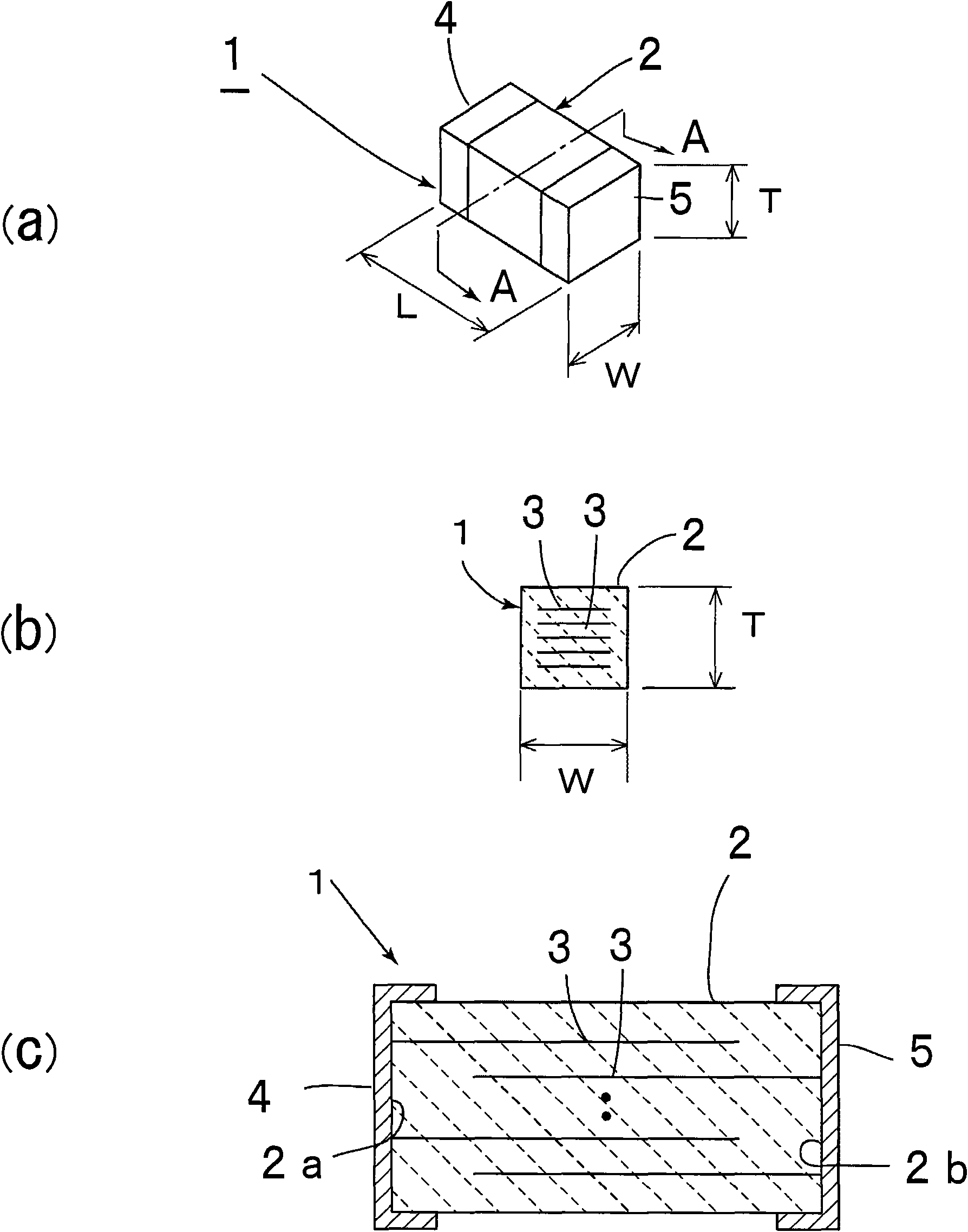
[0057] image 3 (a) is a perspective view of the electronic component conveyed in 1st Embodiment of this invention. The electronic component 1 is a multilayer ceramic capacitor and has a rectangular parallelepiped shape. That is, electronic component 1 has rectangular parallelepiped ceramic sintered body 2 . Such as image 3 As shown in (b) and (c), in the ceramic sintered body 2, a plurality of internal electrodes 3 are laminated via a ceramic layer. In the present embodiment, the internal electrode 3 is mainly composed of nickel and has strong magnetism. The internal electrodes of the electronic component which is the object of the present invention can be made of suitable materials as long as they have strong magnetism.
[0058] The first and second external electrodes are formed so as to cover the first and second end faces 2 a and 2 b of the ceramic sintered body 2 facing each other. The direction connecting the first end face and the second end face 2a, 2b of the el...
no. 2 approach
[0108] In the first embodiment, the first magnet 21 is located outside the guide wall 14b, with the N pole on the upper side and the S pole on the lower side.
[0109] Unlike this, as Figure 5 As shown, in the second embodiment, the first magnet 21A is arranged below the rotation path 14, more specifically, below the second transfer table 14a. The upper surface of the first magnet 21A is an N pole, and the lower surface is an S pole. Therefore, yielding Figure 6 The magnetic lines of force Z shown. Since the magnetic field lines Z extending substantially in the vertical direction are generated on both the guide wall 14b side and the guide wall 14c side, as in the case of the first embodiment, the orientation of the electronic component 1 is aligned so that the surface direction of the internal electrodes 3 is vertically vertical. direction extension.
[0110] Since the first magnet 21A is located below the central position in the width direction of the second transfer ta...
no. 3 approach
[0112] Such as Figure 7 As shown, in the electronic component transfer device of the third embodiment, in addition to the first magnet 21A, another first magnet 21B is provided. That is, in the second embodiment, the first magnet 21A is provided below the second transfer table 14a, and in the third embodiment, the first magnet 21B is provided above it. In this way, the rotation path 14 is pinched by the upper and lower first magnets 21A, 21B.
[0113] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the upper side of the first magnet 21B is the N pole, and the lower side is the S pole.
[0114] In this way, if Figure 8 As shown, the first magnet 21B is arranged above the rotation path 14, and the magnetic lines of force Z from the first magnet 21B also act, so the electronic component 1 can be rotated more reliably and its orientation is consistent.
[0115] By adjusting the position of the first magnet 21B with respect to the position of the first magnet 21A, the arrangement of the lines of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com