Method for preparing battery-level ferrous oxalate
A ferrous oxalate, battery-grade technology is applied in the field of energy storage materials to achieve the effects of eliminating pollution, high purity and reducing raw material costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
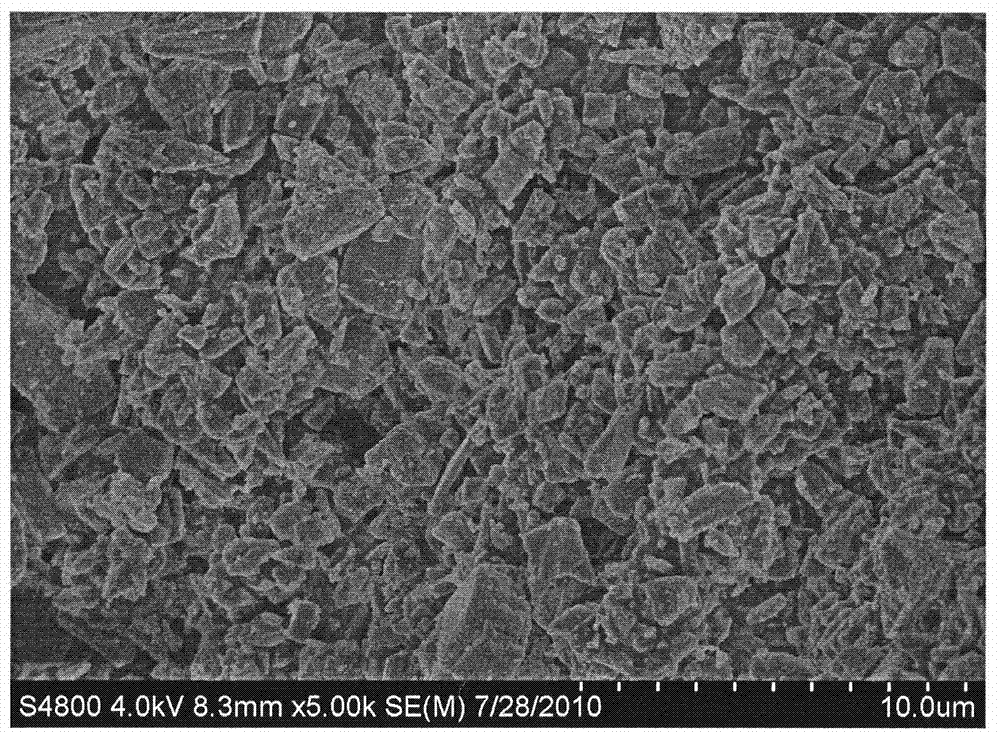
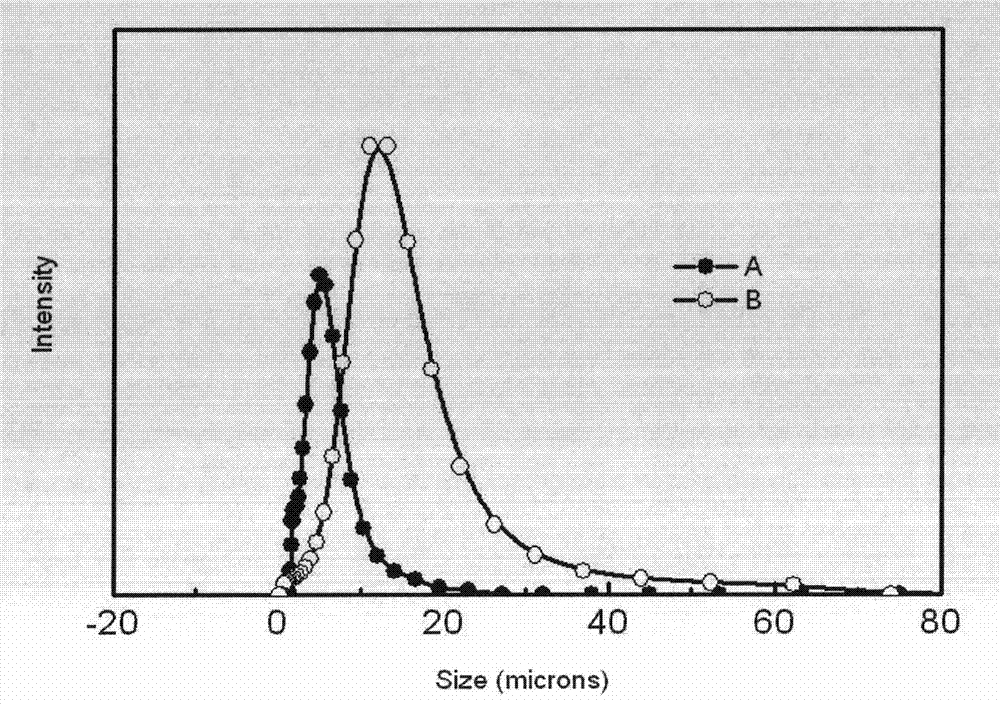
[0024] Dissolve 2 kg of titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate in 4 liters of deionized water, add 20 grams of reduced iron powder at a stirring rate of 600 rpm, heat at 50°C for 3 hours, and then filter to obtain the purified ferrous sulfate transparent filtrate , adjust this solution pH=3, heating system and keeping temperature are 30 ℃, adding concentration is 1200 grams of the polyethylene glycol 20000 solution of 1.5wt% in the ferrous sulfate filtrate, stir rapidly after 10 minutes under the stirring rate of 600rpm 1100 g of oxalic acid solution with a concentration of 50 wt % was added, and after the addition was completed, it was incubated at 30° C. for 30 minutes to form a pale yellow ferrous oxalate crystal precipitate. The precipitated product is filtered, washed and dried to obtain battery grade ferrous oxalate. The battery-grade ferrous oxalate has a purity of 99.5% and an average particle size of 4.2 micrometers as tested by an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Dissolve 1 kg of titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate in 3 liters of deionized water, add 10 grams of reduced iron powder at a stirring rate of 500 rpm, heat at 50°C for 3 hours, and then filter to obtain the purified ferrous sulfate transparent filtrate , adjust the pH of this solution=1, heat the system and keep the temperature at 60°C, add 200 grams of polyethylene glycol 10000 solution with a concentration of 3wt% in the ferrous sulfate filtrate, stir at a stirring rate of 500rpm for 10 minutes and then add Concentration is 970 grams of 50% ammonium oxalate solution, heat preservation for 2 hours after feeding is completed, light yellow ferrous oxalate crystals are generated, then the product is filtered and washed, dried to obtain battery grade ferrous oxalate, and tested by X-ray fluorescence spectrometer and laser particle size analyzer The battery-grade ferrous oxalate has a purity of 99.6% and an average particle size of 4.8 microns.
Embodiment 3
[0028]Dissolve 2 kg of titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate in 4 liters of deionized water, add 20 grams of reduced iron powder at a stirring rate of 800 rpm, heat at 50°C for 3 hours, and then filter to obtain the purified ferrous sulfate transparent filtrate , adjust this solution pH=2, keep system temperature be 10 ℃, add the polyacrylamide 10000000 solution 1000 grams that concentration is 0.5wt% in ferrous sulfate filtrate, add concentration rapidly after stirring 10 minutes under the stirring rate of 800rpm 1500 grams of 50% sodium oxalate solution. After the addition, the system was kept at 10°C for 2.5 hours to form light yellow ferrous oxalate crystals. Then the product was filtered, washed, and dried to obtain battery-grade ferrous oxalate. X-ray fluorescence The battery-grade ferrous oxalate has a purity of 99.5% and an average particle size of 3.4 microns as measured by a spectrometer and a laser particle size analyzer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com