A method of detecting cryptosporidium
A Cryptosporidium, consistent technology, applied in the field of hybrid analysis probes, can solve the problems of lack of sensitivity or specificity, labor-intensive and time-consuming microscopic analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0159] Example 1: Sample source and DNA purification
[0160] Cryptosporidium DNA was obtained from purified oocyst samples, either from culture or feces. Fecal-derived oocysts were purified using the QIAamp DNA Stool kit (Qiagen, CA, USA), while culture-derived oocysts were subjected to separate PBS washes. Purified oocysts were suspended in 1x PCR buffer II (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.3, 50 mM KCl) (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA), counted by a hemocytometer or a cytometer, and subjected to five freeze-thaw cycles. cycle. The samples were then centrifuged at 10,000 xg for 5 min and the supernatant was transferred to a new microcentrifuge tube. Oocyst samples were then serially diluted (1:2) to the desired concentration ranging from 10,000 to 1 equivalent of oocysts per sample.
[0161] Cryptosporidium species or genotypes previously identified by other molecular techniques used in this study were: Cryptosporidium hominis isolates 6149, 6189, H270, H271, H273 (unpublished); Cryptos...
Embodiment 2
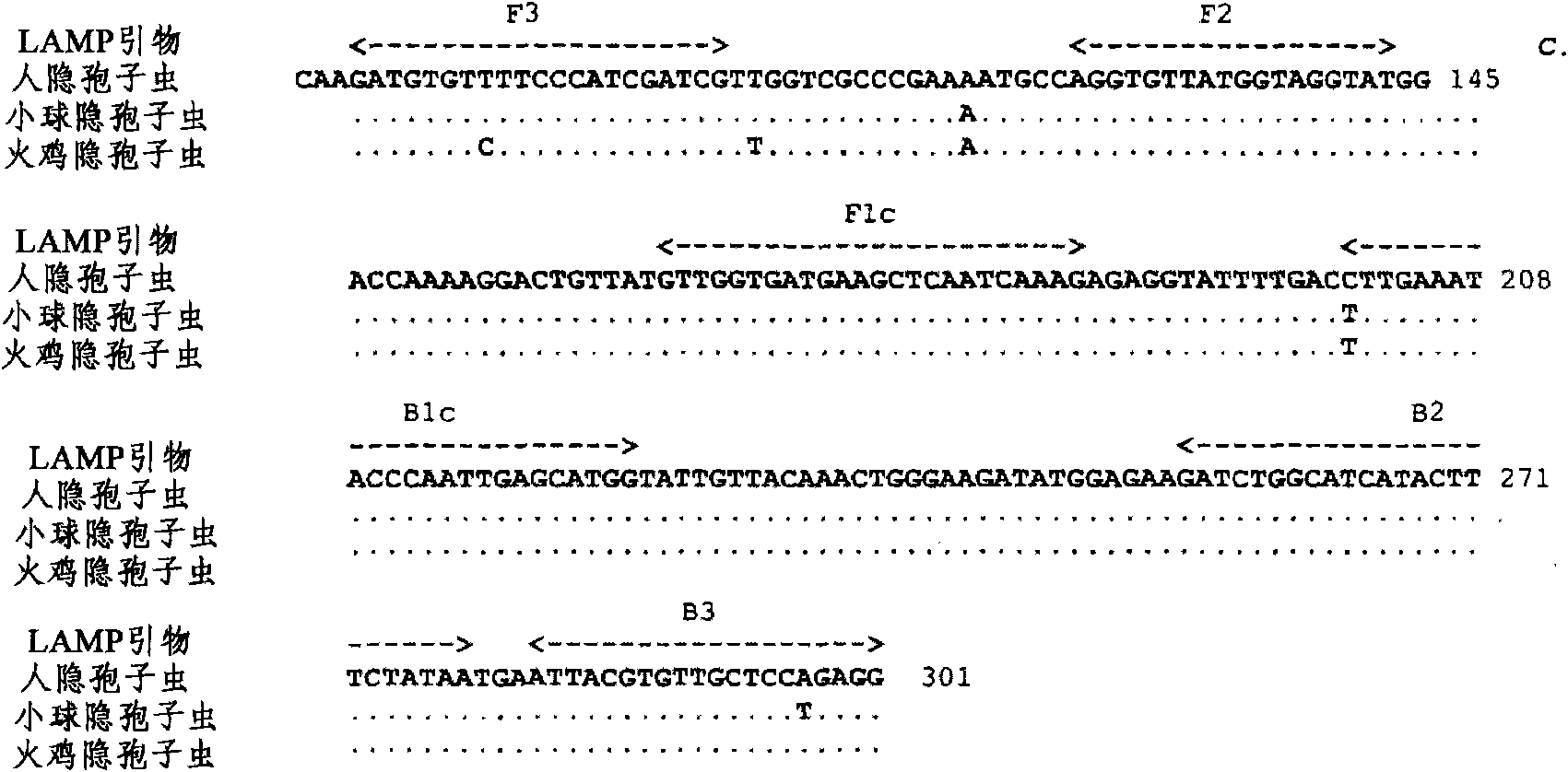
[0163] Example 2: LAMP primers
[0164] The LAMP primers were designed to be specific for the Cryptosporidium actin gene. The previously published sequences (Sulaiman et al., 2002) were aligned with BioEdit Version 7.0.5.2 (Hall, 1999), and compared with Eiken PrimerExplorer Version 3 ( http: / / primerexplorer.jp / e / ) with the aid of manually designing a set of LAMP primers. Primers were commercially synthesized by Sigma-Proligo (NSW, Australia).
[0165] Table 1: Nucleotide sequences of four LAMP primers targeting Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium hominis genes
[0166]
[0167] Nucleotide position numbering is based on the Cryptosporidium human TU502 actin sequence, GenBankXM 661095 (Xu et al., 2004). Note that each FIP and BIP constituting only one primer consists of two separate nucleotide regions: F1c and F2, and B1c and B2, respectively.
Embodiment 3
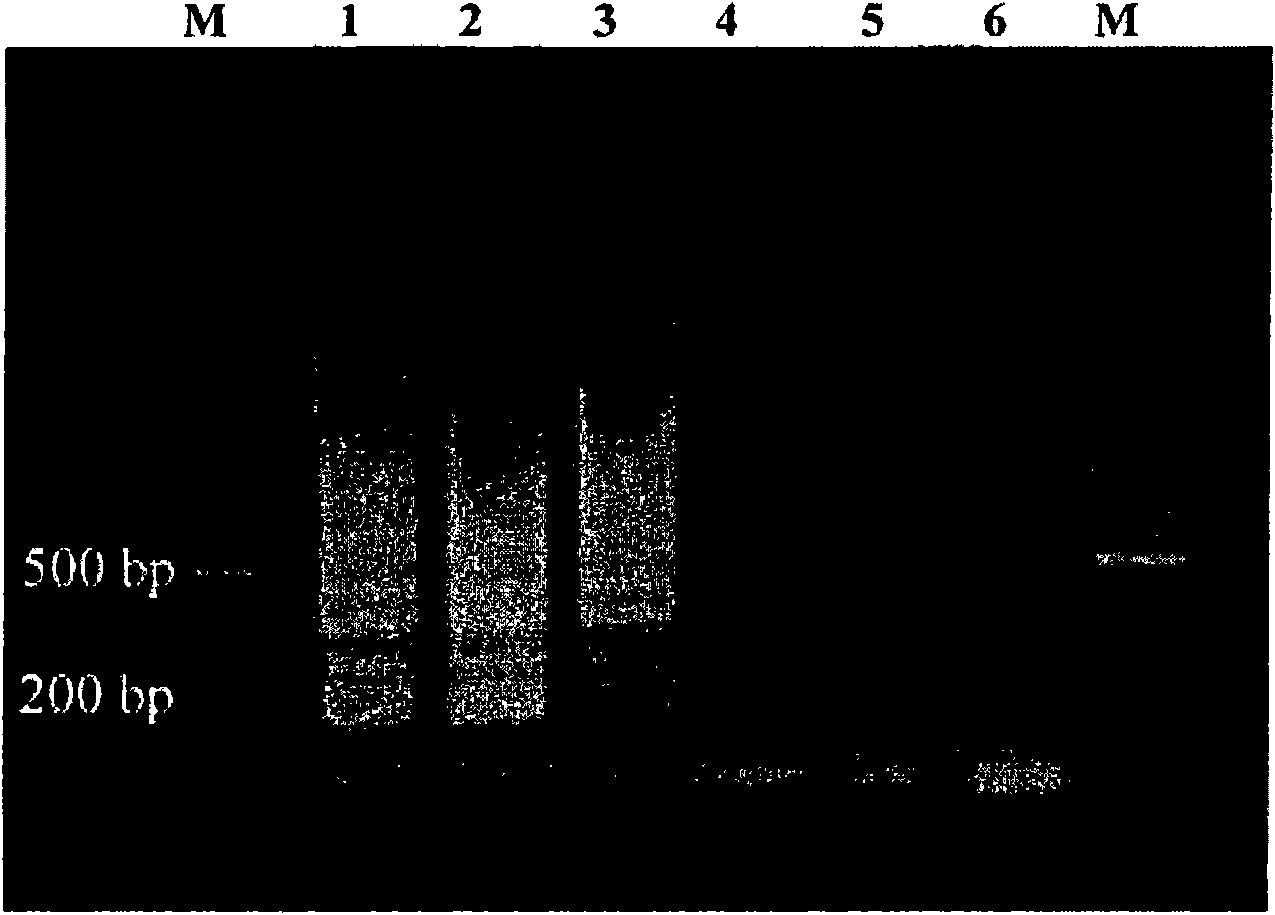
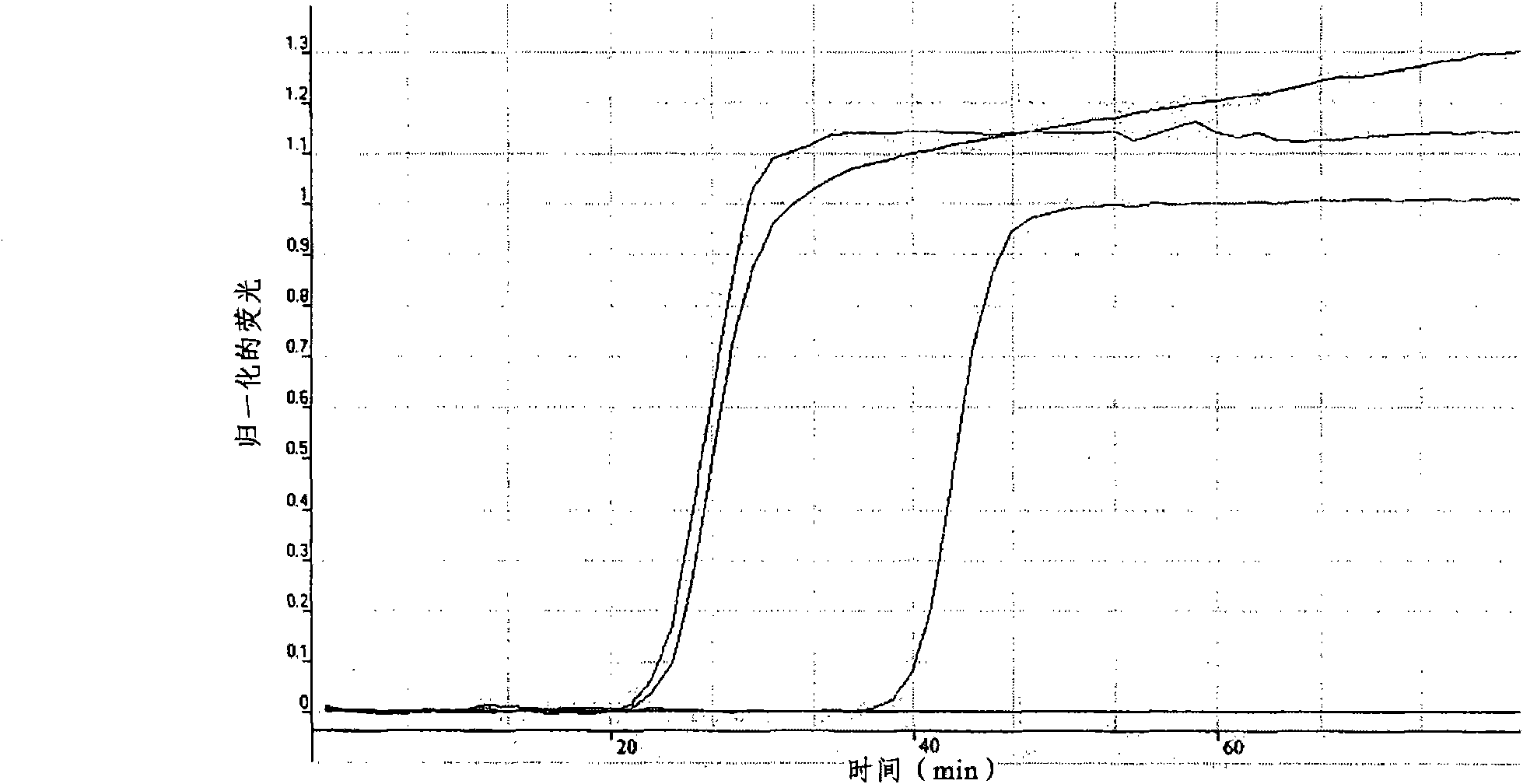
[0168] Example 3: LAMP reaction
[0169]25 μl of the LAMP reaction mixture consisted of the following components: 1.6 μM each of FIP and BIP inner primers, 0.8 μM each of F3 and B3 outer primers, 8 U of Bst enzyme (New England Biolabs, MA USA), 1× ThermoPol reaction buffer (New England Biolabs), 200 μM dNTP mixture (Fisher-Biotech, Western Australia), 0.8 M Betaine (Sigma-Aldrich, CA, USA), 3.34 μM SYTO9 (Molecular Probes, OR USA) and 1 μl of heat-denatured DNA template (95°C, 5 minutes). The reaction mixture was loaded into a RotorGene 3000 (Corbett Research, NSW Australia) and run at 60° C. for 60 min on the FAM channel (excitation at 470 nm, detection at 510 nm) with 30 seconds per minute fluorescence data acquisition. For fluorescence data acquisition, three gain settings (1, 2 and 4 or 5) are included. Then, the reaction was terminated by incubation at 80°C for 5 min.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com