Wire rope flaw detector
A flaw detection device and steel cable technology, applied in the direction of material magnetic variables, etc., can solve problems such as failure to detect steel cable damage, and achieve the effect of avoiding skin effect and high-precision damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
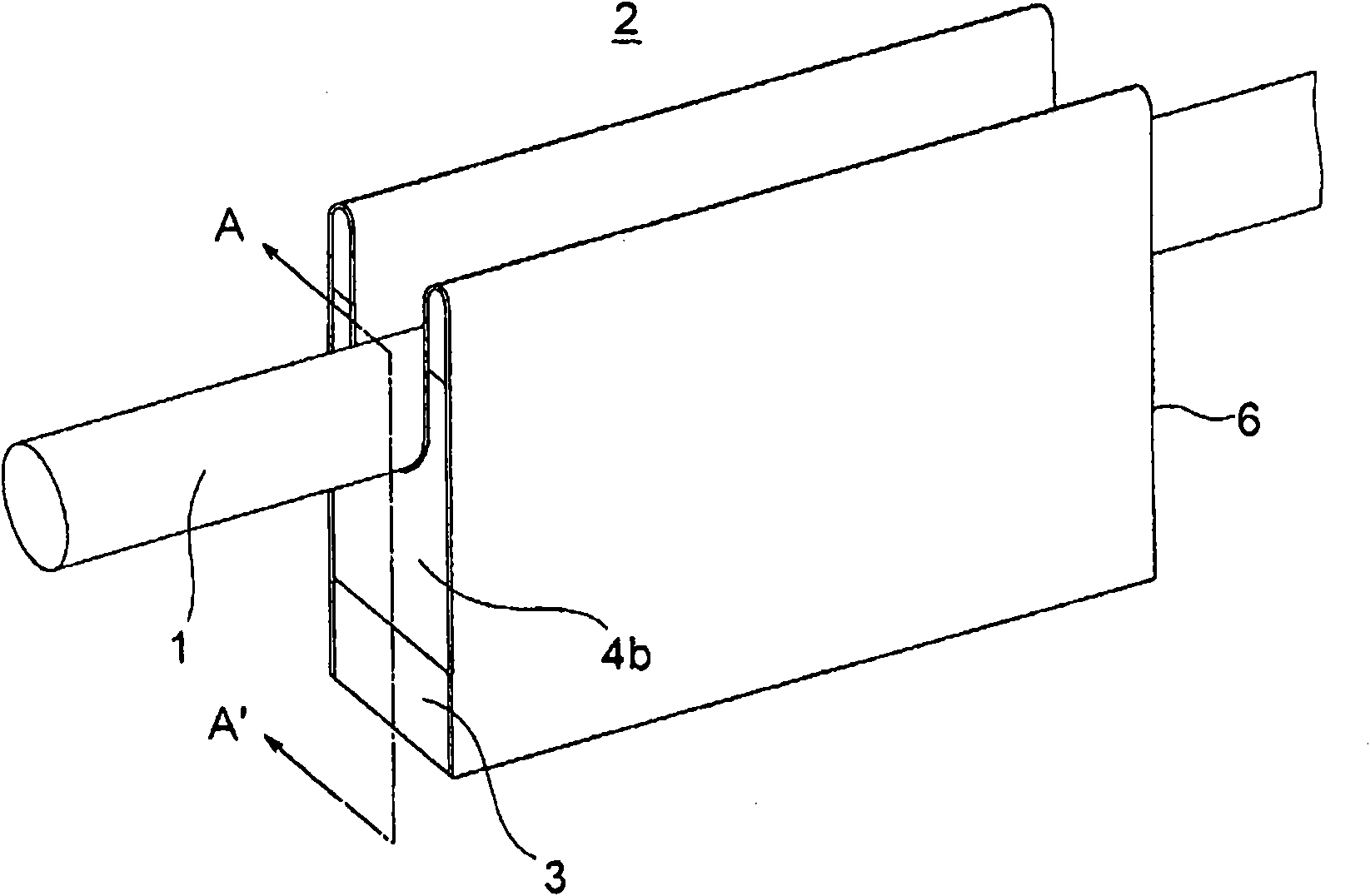
[0028] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 8 A wire cable flaw detection device according to Example 1 of the present invention will be described. figure 1 It is a perspective view showing the appearance of the wire rope flaw detection device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. In addition, in each figure from now on, the same code|symbol represents the same or a corresponding part.
[0029] exist figure 1 The middle table shows the steel cable 1 and the steel cable flaw detection device 2 . In addition, the back yoke 3, the permanent magnet 4b for a field, and the protection plate 6 are shown.
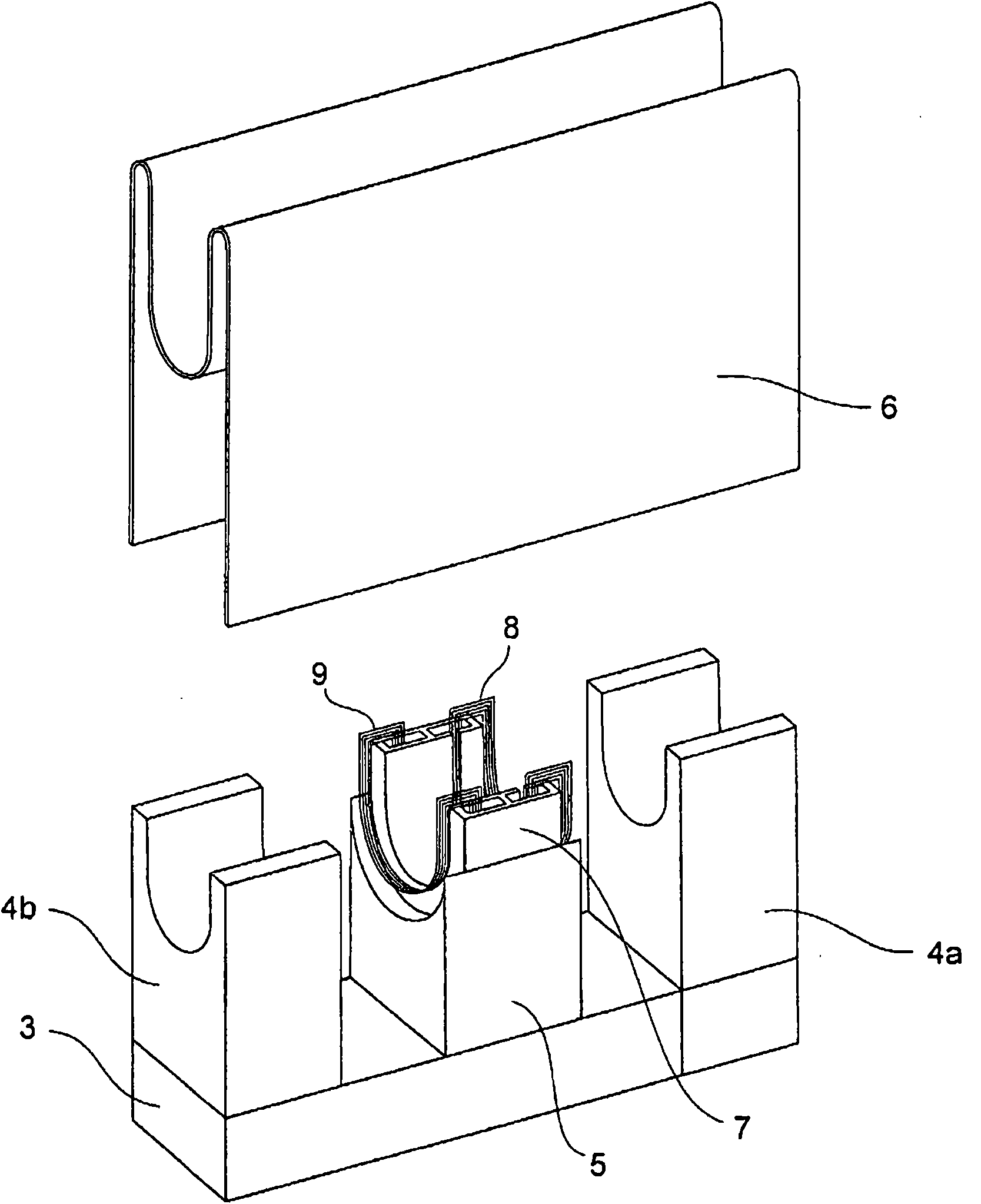
[0030] figure 2 yes means figure 1 A perspective view of the appearance of the wireline flaw detection device with the protective plate removed.
[0031] figure 2 The back yoke 3, the permanent magnets 4a and 4b for excitation, the support stand 5, the protection plate 6 removed from the wire rope flaw detection device, the magnetic circuit member 7, the dete...
Embodiment 2
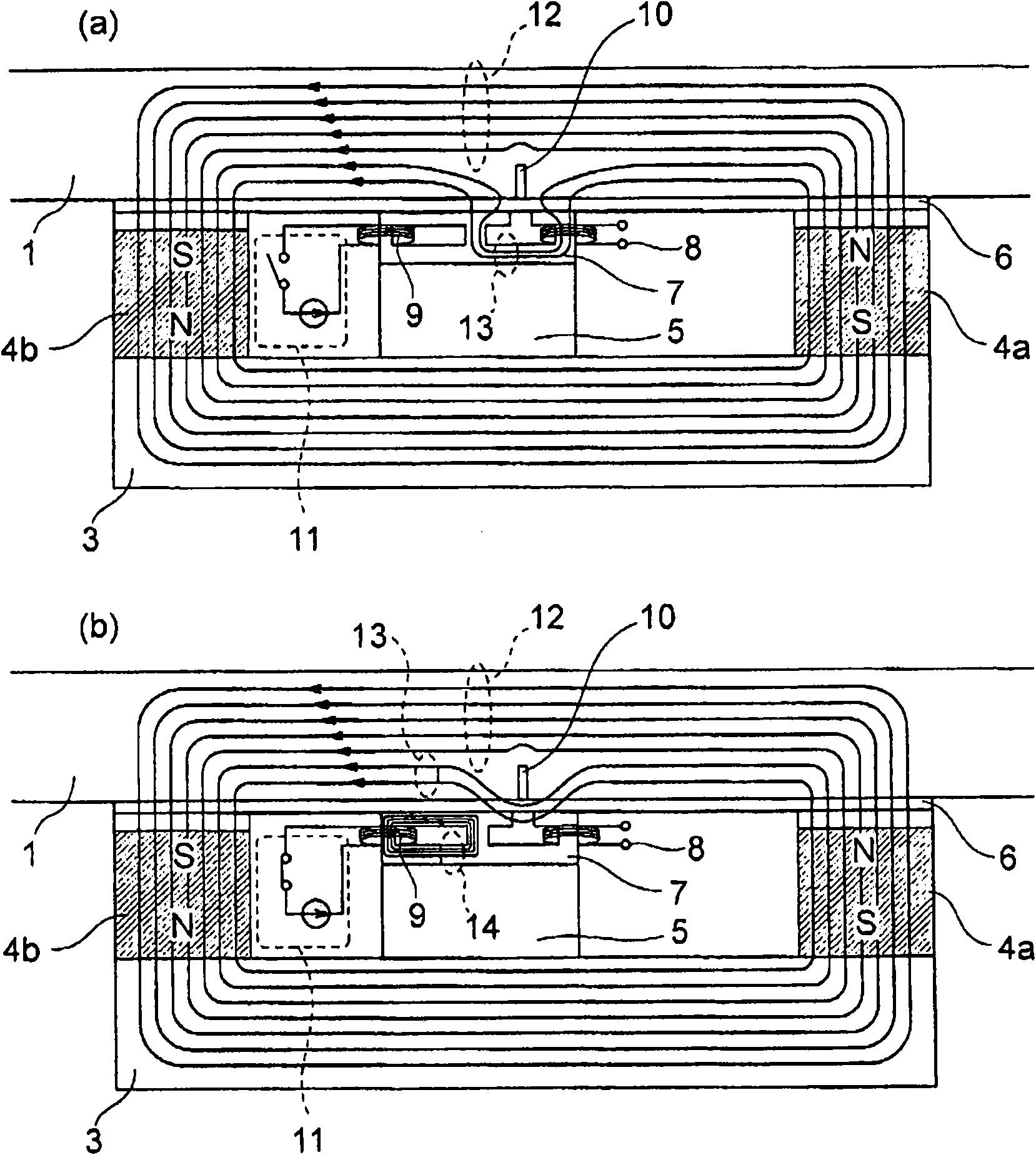
[0051] refer to Figure 9 to Figure 11 A wire cable flaw detection device according to Example 2 of the present invention will be described. Figure 9 It is a diagram showing a partial configuration of a wire rope flaw detection device according to Example 2 of the present invention.
[0052] Should Figure 9 and image 3 Similarly, it means from figure 1 A cross-sectional view of the steel cable flaw detection device of Example 2 viewed along the line A-A'. Should Figure 9 It is a cross-sectional view taken along a plane including the central axis of the wire rope 1, and shows the flow of magnetic flux in the vicinity of the damaged portion of the wire rope. In addition, (a) shows a case where no current flows through the exciting coil, and (b) shows a case where a current flows through the exciting coil.
[0053] exist Figure 9 In the figure, the steel cable 1, the back yoke 3, the permanent magnets 4a and 4b for excitation, the supporting platform 5, the magnetic c...
Embodiment 3
[0062] refer to Figure 12 to Figure 14 A wire cable flaw detection device according to Example 3 of the present invention will be described. Figure 12 It is a diagram showing a partial configuration of a wire rope flaw detection device according to Example 3 of the present invention.
[0063] Should Figure 12 and image 3 Similarly, it means from figure 1A cross-sectional view of the steel cable flaw detection device of Example 3 viewed along the line A-A'. Should Figure 12 It is a cross-sectional view taken along a plane including the central axis of the wire rope 1, and shows the flow of magnetic flux in the vicinity of the damaged portion of the wire rope. In addition, (a) shows a case where no current flows through the exciting coil, and (b) shows a case where a current flows through the exciting coil.
[0064] exist Figure 12 In the figure, the steel cable 1, the back yoke 3, the permanent magnets 4a, 4b for excitation, the supporting platform 5, the magnetic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com