Method for preparing polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)/polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) composite hollow fiber film
A fiber membrane and hollow technology, applied in the field of pervaporation membrane separation, can solve the problems of large footprint of membrane modules, difficulty in industrial application, low mechanical strength, etc., and achieve low production cost, not easy to be polluted, and good mechanical strength.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
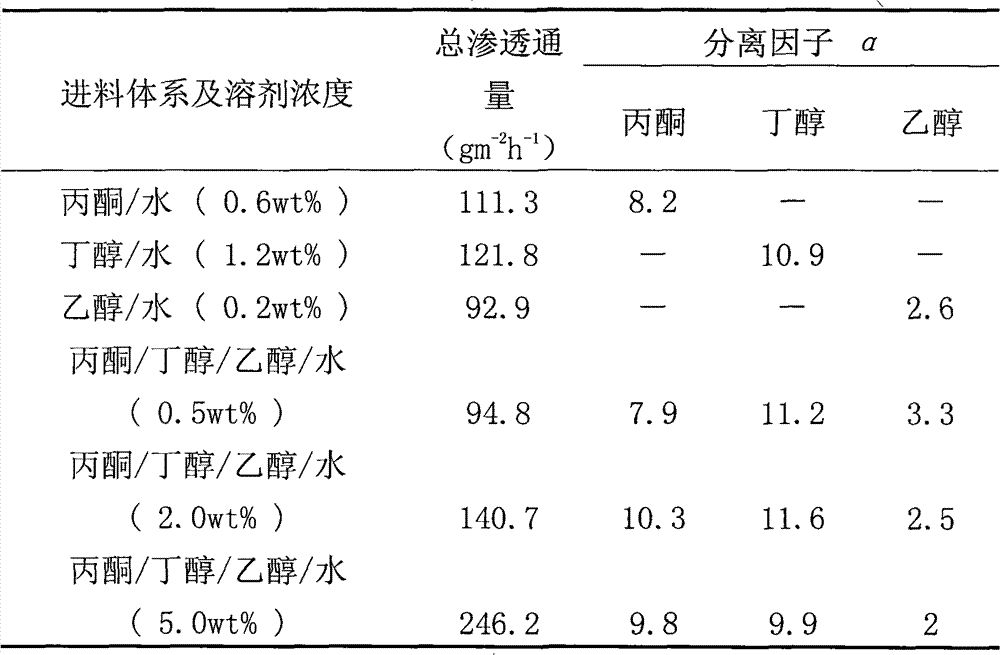
[0014] Dissolve 10g of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) in 100g of n-hexane, add 0.6g of cross-linking agent ethyl orthosilicate, mix and stir at room temperature for 0.5 hours, then add 0.1g of catalyst dibutyltin dilaurate, add n-hexane alkane until the concentration of polydimethylsiloxane in the mixed solution is 5 wt%, and after sealing, stir at room temperature for 8 hours, and the obtained solution is centrifuged and defoamed to make a film-making solution. Rinse the polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) hollow fiber membrane with distilled water until neutral, dry it at room temperature, and use it as the base membrane. The treated basement membrane is immersed in the membrane-forming solution for 2 to 3 seconds, taken out, and dried at room temperature. The coating was repeated 3 times, and then placed in a vacuum oven at 110°C for 10 hours to be vacuum-dried until completely cross-linked to obtain a PDMS / PVDF composite hollow fiber membrane. The outer layer of the obtained comp...
Embodiment 2
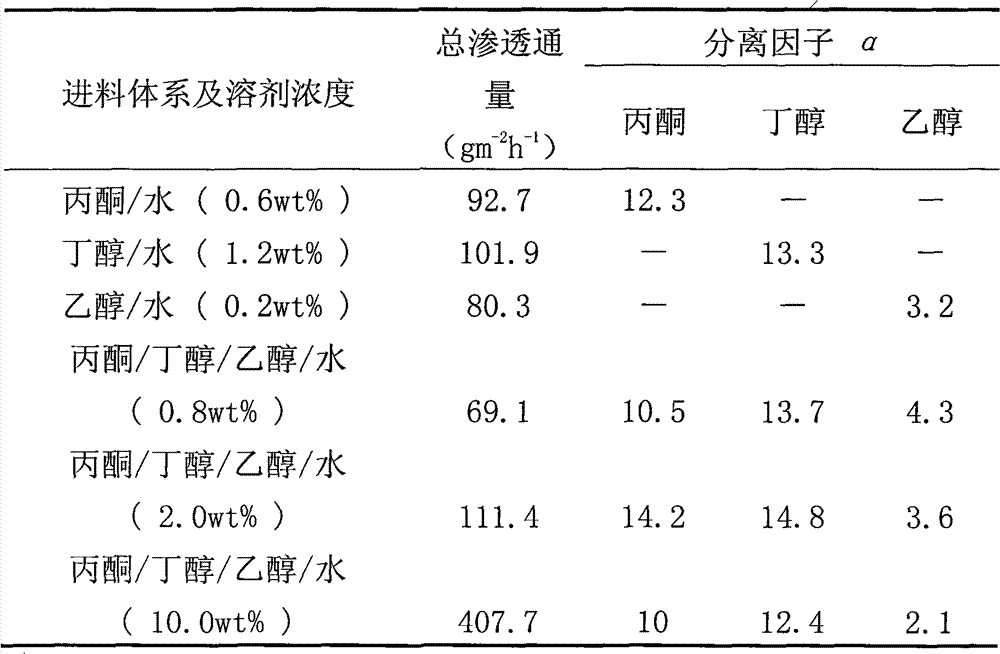
[0019] Dissolve 10g of polydimethylsiloxane in 50g of n-hexane, add 1.0g of crosslinking agent ethyl orthosilicate, mix and stir at room temperature for 1 hour, then add 0.5g of catalyst dibutyltin dilaurate, add n-hexane to mix The concentration of polydimethylsiloxane in the liquid is 15 wt%, and after sealing, it is stirred at room temperature for 12 hours, and the obtained solution is centrifuged and defoamed to prepare a film-forming liquid. Rinse the PVDF hollow fiber membrane with distilled water until neutral, dry it at room temperature, and use it as the base membrane. The treated basement membrane is immersed in the membrane-forming solution for 2 to 3 seconds, taken out, and dried at room temperature. The coating was repeated 3 times, and then placed in a vacuum oven at 30°C for 10 hours to be vacuum-dried until completely cross-linked to obtain a PDMS / PVDF composite hollow fiber membrane. The outer layer of the obtained composite hollow fiber membrane is a dense P...
Embodiment 3
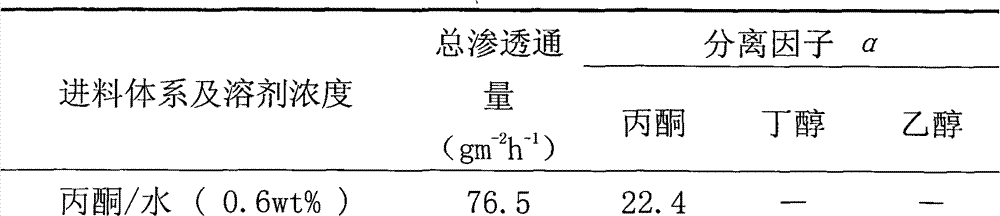
[0024] Dissolve 20g of polydimethylsiloxane in 50g of n-hexane, add 1.6g of crosslinking agent ethyl orthosilicate, mix and stir at room temperature for 2 hours, then add 0.6g of catalyst dibutyltin dilaurate, add n-hexane until mixed The concentration of polydimethylsiloxane in the liquid is 30 wt%, and after being sealed, it is stirred at room temperature for 16 hours, and the obtained solution is centrifuged and defoamed to make a film-forming liquid. Rinse the PVDF hollow fiber membrane with distilled water until neutral, dry it at room temperature, and use it as the base membrane. The treated basement membrane is immersed in the membrane-forming solution for 2 to 3 seconds, taken out, and dried at room temperature. The coating was repeated twice, and then placed in a vacuum oven at 80°C for 10 hours to be vacuum-dried until completely cross-linked to obtain a PDMS / PVDF composite hollow fiber membrane. The outer layer of the obtained composite hollow fiber membrane is a d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| separation factor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| separation factor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com