High-efficiency single-end available bandwidth measuring method
A single-ended, bandwidth technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of large link intrusion and long measurement time, and achieve low intrusion, strong robustness, and fast measurement speed. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
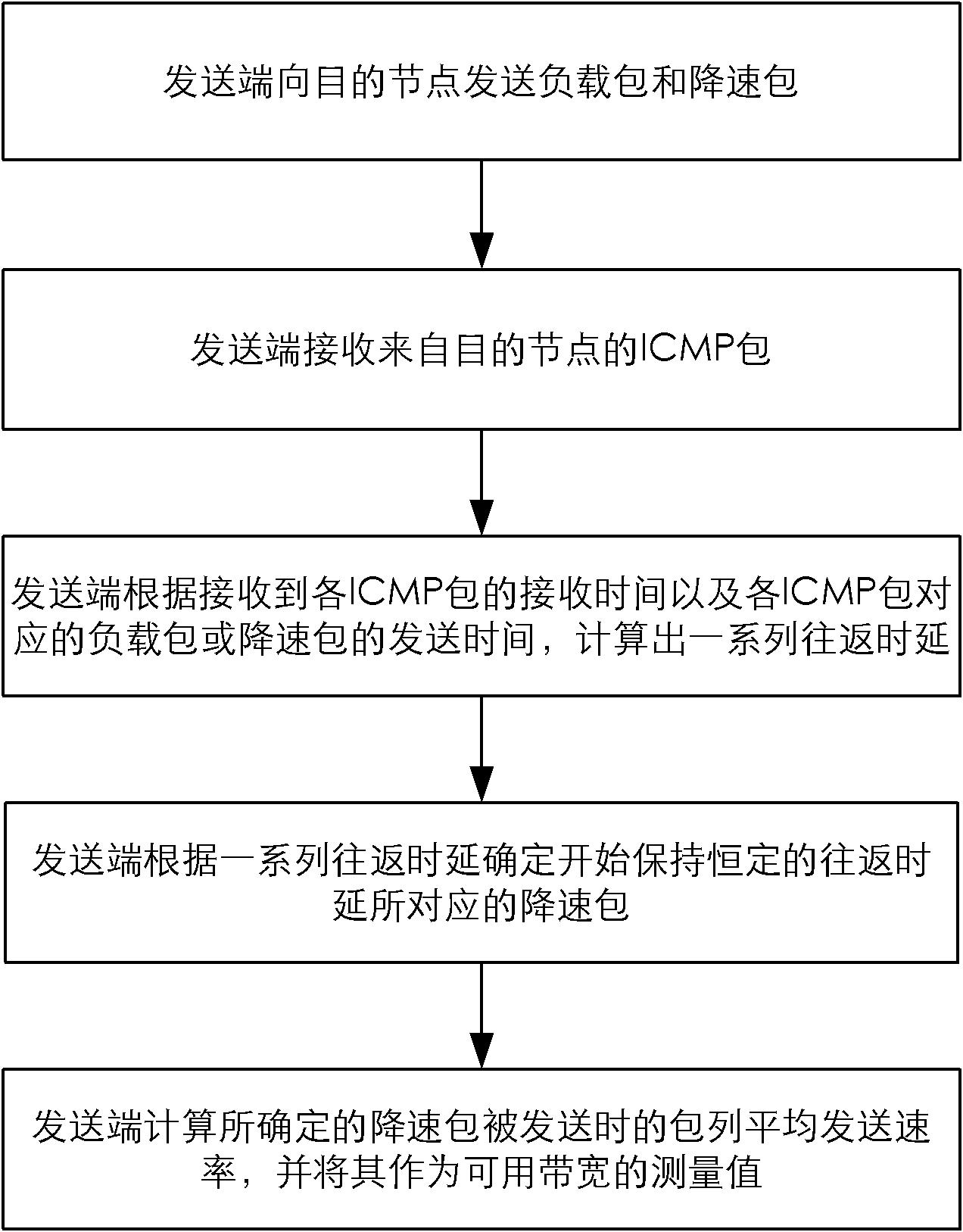
[0027] see figure 1 , the single-ended usable bandwidth measuring method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
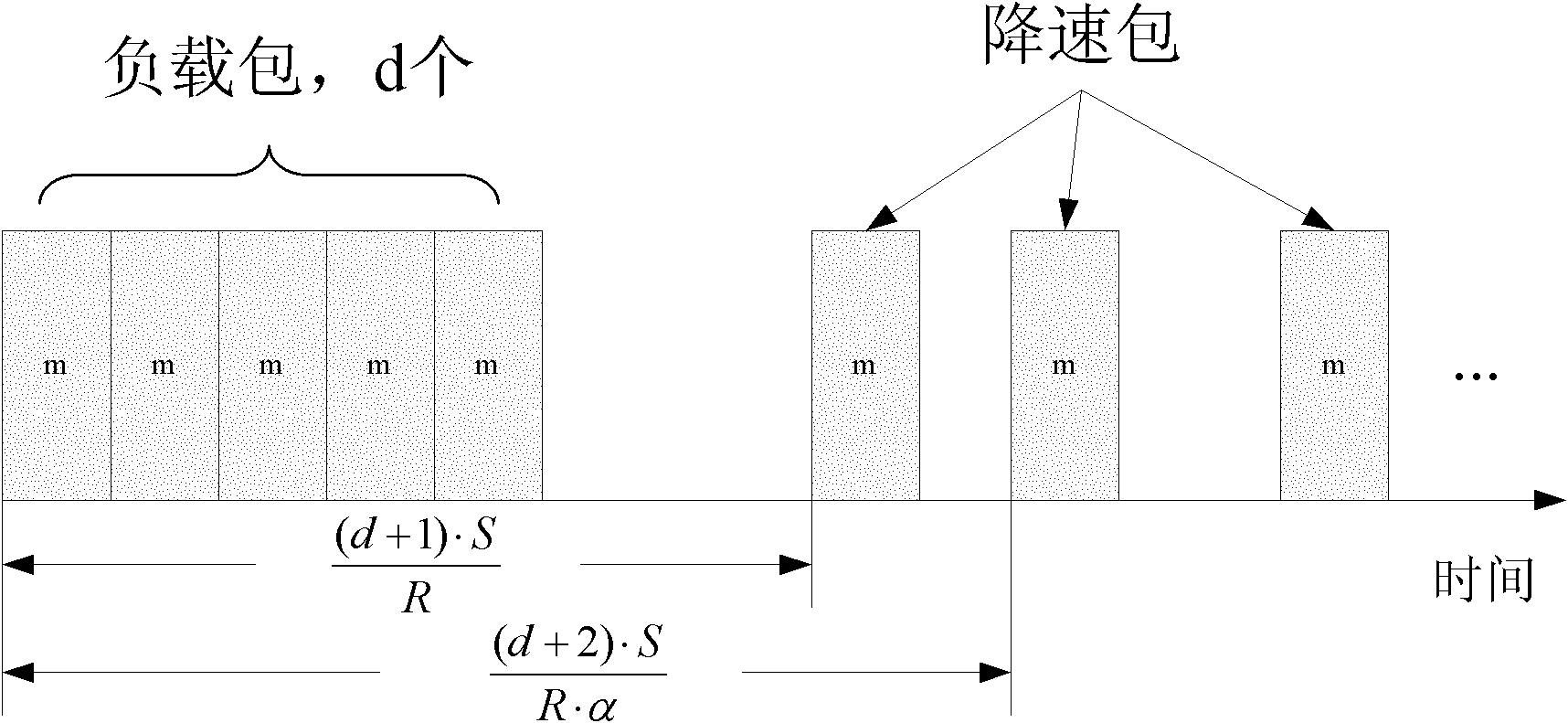
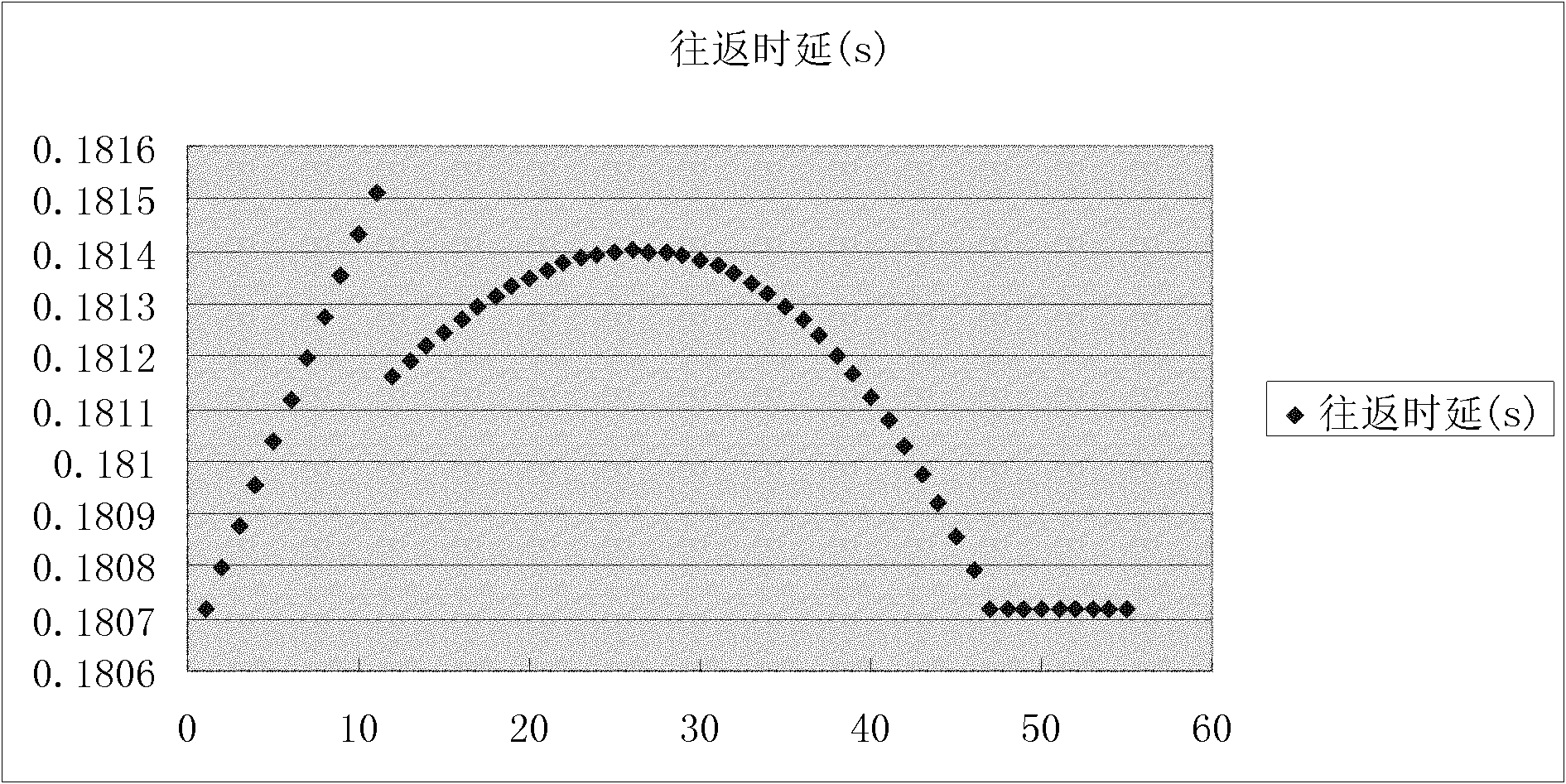
[0028] First, the sending end continuously sends multiple load packets to the destination node in a back-to-back manner, and then continuously sends multiple speed-down packets to the destination node at a gradually decreasing rate. is an unreachable port. see you again figure 2 , which is a schematic diagram of the packets sent by the sender to the destination node, that is, the sender first sends d load packets back-to-back, and then sends multiple deceleration packets to fully congest the network path, and the sender can gradually reduce in exponential form The average sending rate of the packet column, and other speed reduction methods can also be used to send speed reduction packets. If the exponential form is used, the average sending rate R of the packet column when the sender sends the i-th deceleration packet i is the average sending ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] First measure the path length of the path from the sender to the destination node. The sender can send a list of IP packets whose TTL domains gradually increase from 1 to the destination node. Then, in the absence of packet loss, the number of ICMP time-exceeded (TE) packets received by the sender is the path length .
[0041] The detection packet in the packet column is an IP packet, the destination IP is the IP address of the destination node, and the TTL field of the packet is set to the path length of the path from the sender to the destination node. In this way, after the detection packet reaches the destination node, it is discarded because the TTL is reduced to 0, and the destination node sends a TE packet to the sender. The sender first sends d detection packets back-to-back (the d detection packets are called load packets, and the subsequent detection packets are called slowdown packets) to fully congest the network path, and then gradually reduce the average ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com