Carrier management method in multi-carrier system and evolved node B (eNB)
An evolved base station and carrier management technology, which is applied in the field of wireless communication and can solve problems such as wasteful occupation of public resources, impact on public resource allocation, and system capacity impact.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
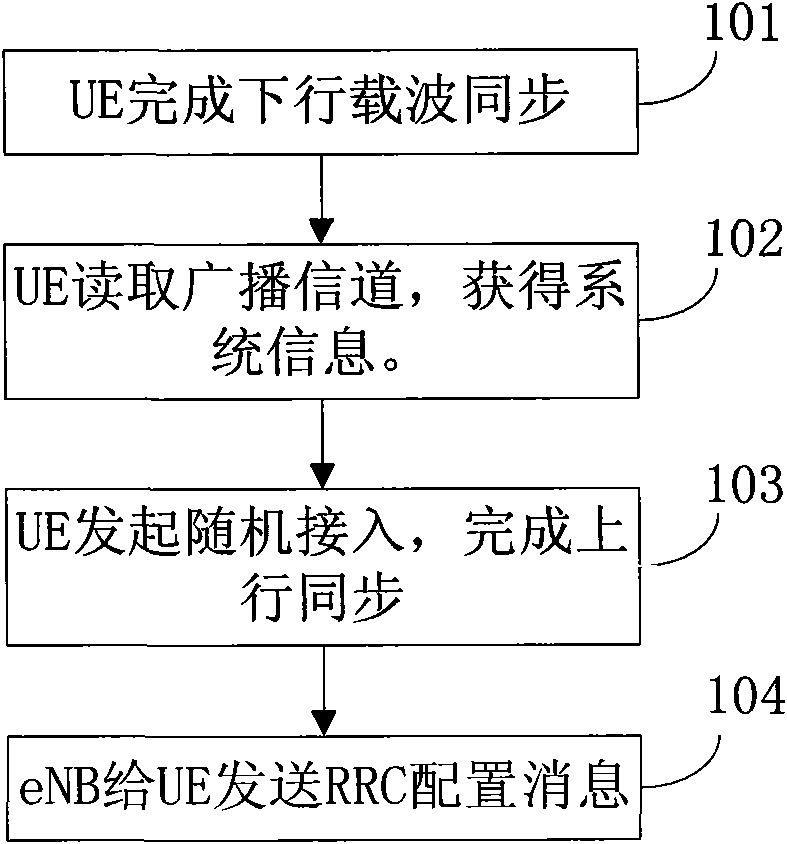
[0212] Assume that the UE and eNB have established an RRC connection, and the eNB configures two pairs of uplink and downlink carriers for the UE. The downlink carriers are DL CC1 (Downlink Component Carrier, downlink component carrier) and DLCC2, and the corresponding uplink carriers are UL CC1 (Uplink Component Carrier, uplink component carrier) and UL CC2.
[0213] It is assumed that the eNB needs to add a pair of uplink and downlink carriers for the UE due to the increase of traffic demanded by the UE, which are DL CC3 and UL CC3. DL CC3 is not synchronized with DL CC1 and DL CC2. UE needs to initiate random access on UL CC3 to obtain uplink synchronization. This information is included in the dedicated parameter configuration of DL CC3 and UL CC3.
[0214] The carrier management in this embodiment adopts the carrier management method 1 described in the summary of the invention, and the process of adding a carrier for the UE in this embodiment is as follows figure 2 As s...
Embodiment 2
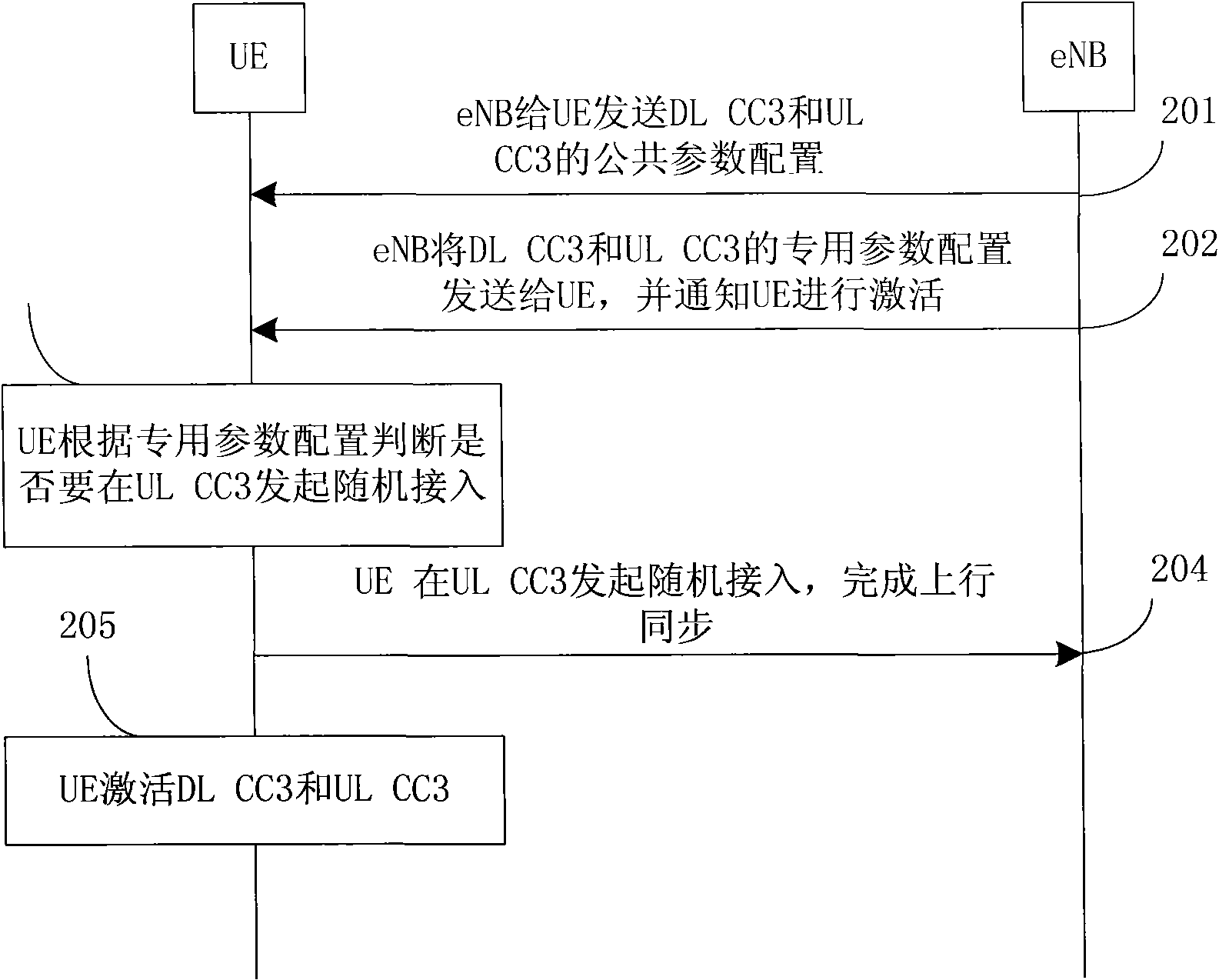
[0221] It is assumed that the UE and the eNB have established an RRC connection, and the eNB configures two pairs of uplink and downlink carriers for the UE. The downlink carriers are DL CC1 and DL CC2, and the corresponding uplink carriers are UL CC1 and UL CC2 respectively.
[0222] Assuming that the eNB needs to add a pair of uplink and downlink carriers for the UE due to the heavy load of the existing carrier, let them be DL CC3 and UL CC3. DL CC3 and DL CC1 are synchronized, and this information is included in the dedicated parameter configuration of DL CC3 and UL CC3.
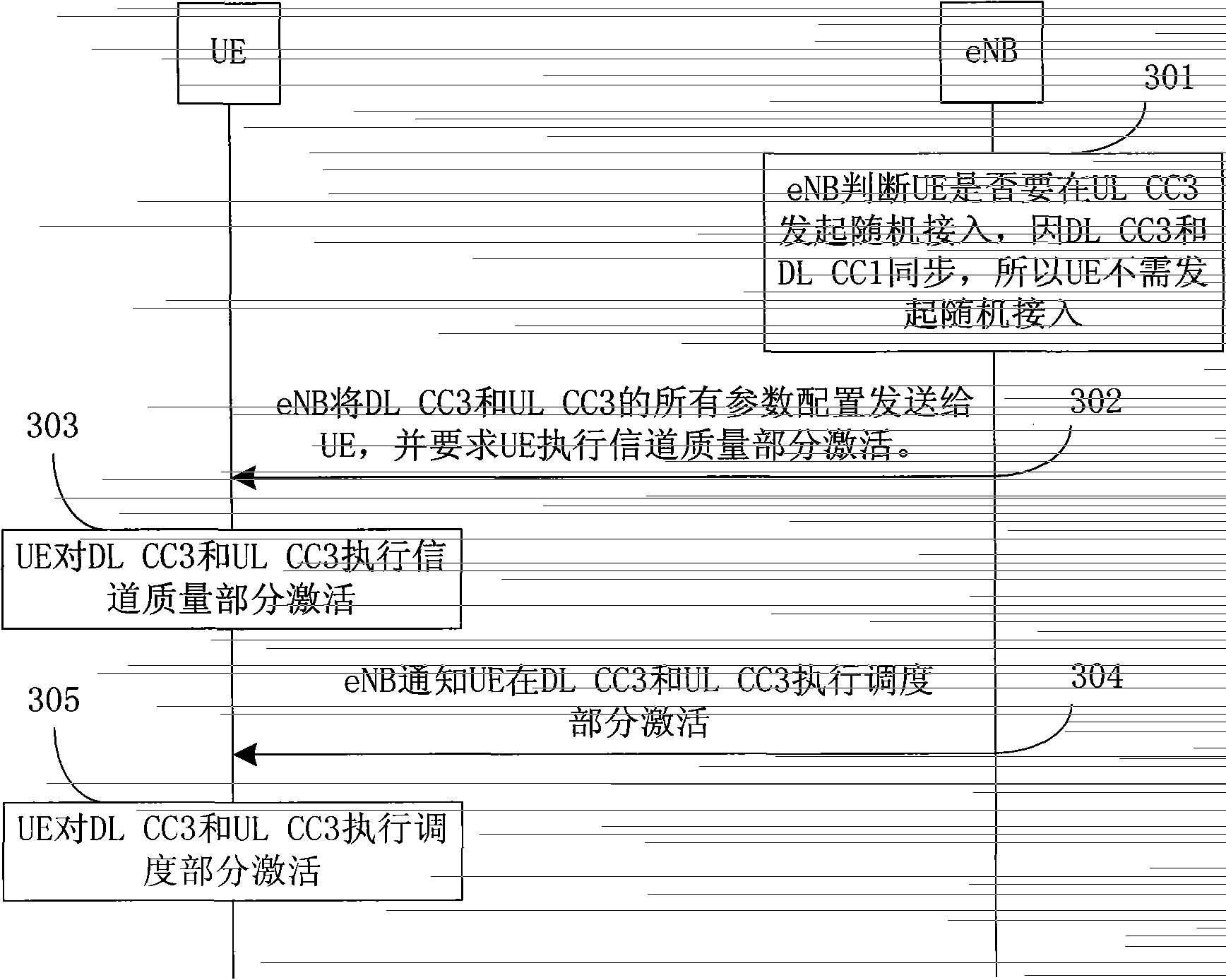
[0223] The carrier management in this embodiment adopts the carrier management method 2 described in the summary of the invention, and the process of adding a carrier for the UE in this embodiment is as follows image 3 As shown, the steps are detailed as follows:
[0224] Step 301: The eNB judges whether the UE will initiate random access on UL CC3, because DL CC3 and DL CC1 are synchronized, so the UE ...
Embodiment 3
[0230] It is assumed that the UE and the eNB have established an RRC connection, and the eNB configures two pairs of uplink and downlink carriers for the UE. The downlink carriers are DL CC1 and DL CC2, and the corresponding uplink carriers are UL CC1 and UL CC2 respectively.
[0231] This embodiment gives an example of the eNB adjusting the activation and deactivation of the carrier in real time according to the change of the UE traffic. In this embodiment, the parameters are not released, so that when the eNB needs to use the target carrier again, the carrier can be reactivated quickly, which greatly reduces the scheduling delay and signaling overhead. This is a part of the carrier management method described in the present invention. An example of flexible use. There are similar applications in other embodiments.
[0232] Assume that the eNB needs to reduce a pair of uplink and downlink carriers for the UE due to the decrease in the traffic demand of the UE, which are DL C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com