Method of reducing enzymatic digestion rates of starch granules in food and food products produced therefrom
A starch granule and enzymatic digestion technology, which can be used in baked food, food preparation, food ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as food systems that have not been studied in detail
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
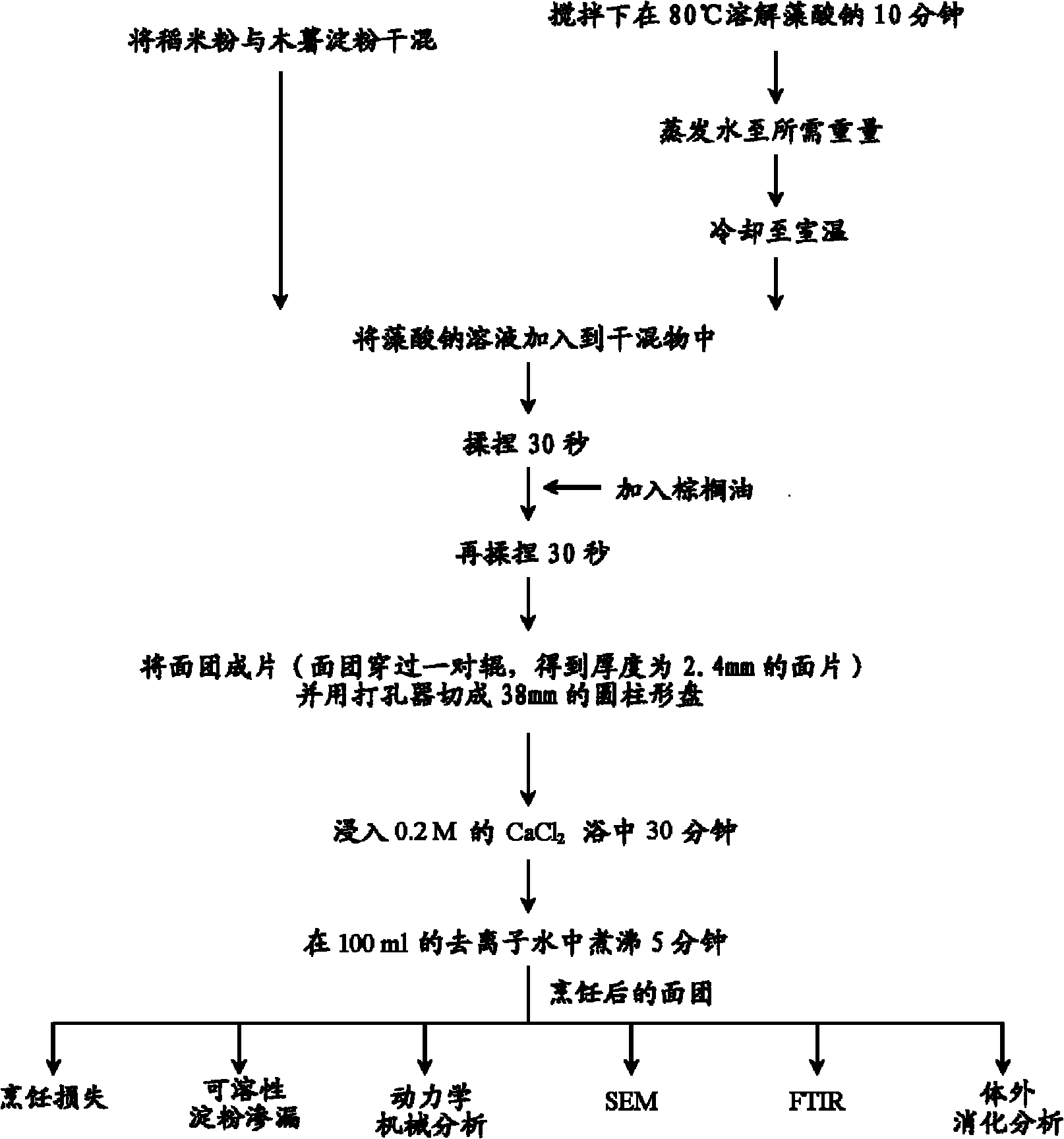
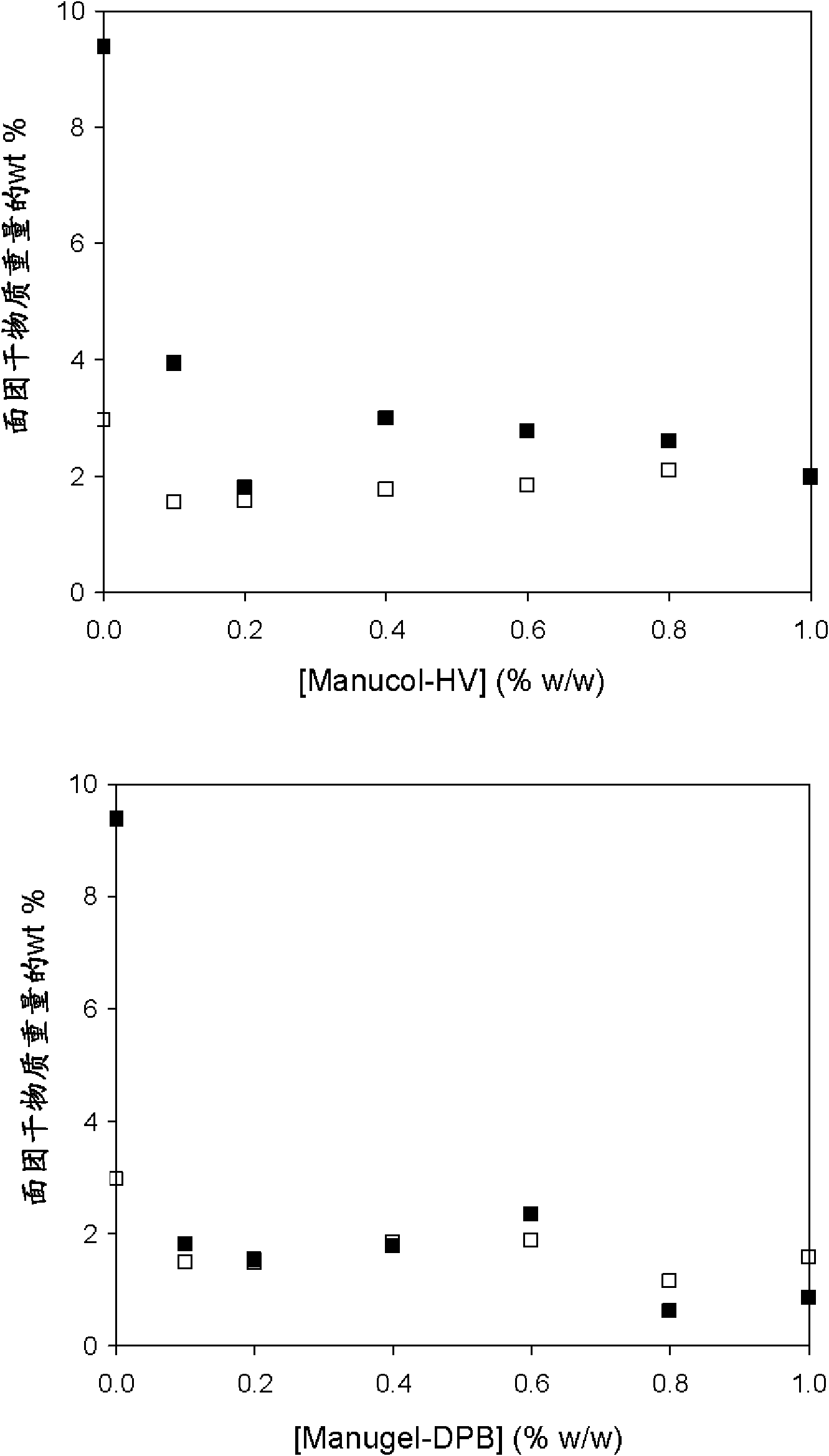
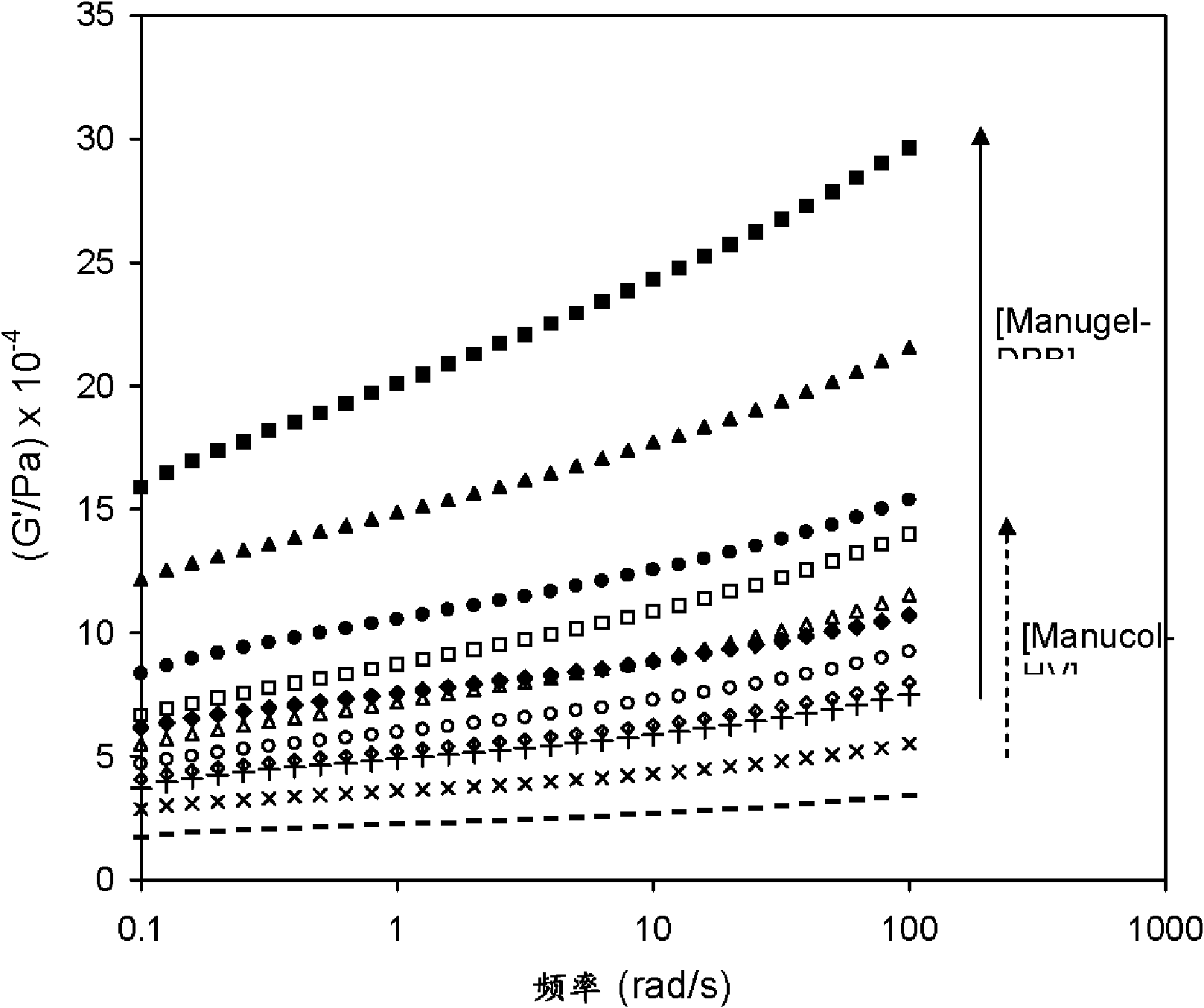
[0050] A dry blend was first prepared by mixing 48.0% rice flour and 9.0% tapioca starch. The alginate was dissolved in deionized water by stirring at 95 °C for 10 minutes. The solution was then cooled to 25°C and added to the above dry blend at a concentration of 0.2%. Palm oil is then added and kneaded with palm oil. Sheet the dough through a pair of rollers with a 2.5mm gap and cut into 38.0mm diameter cylindrical discs with a hole punch. Immerse these discs in 50ml of 0.2M CaCl at ambient temperature 2 solution for 30 minutes, then boiled in 100ml deionized water for 5 minutes.
[0051] The above experimental protocol was repeated with 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% and 1.0% alginate solutions.
[0052] Basic dough without alginate for comparative experiments
[0053] A base dough recipe consisting of 48.0% rice flour, 9.0% tapioca starch, 2.0% palm oil and 41% deionized water was prepared as a model system for commercially available instant soup rice noodles.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com