Path computing method and unit in optical network
A technology of path calculation and optical network, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem of no ring topology information and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
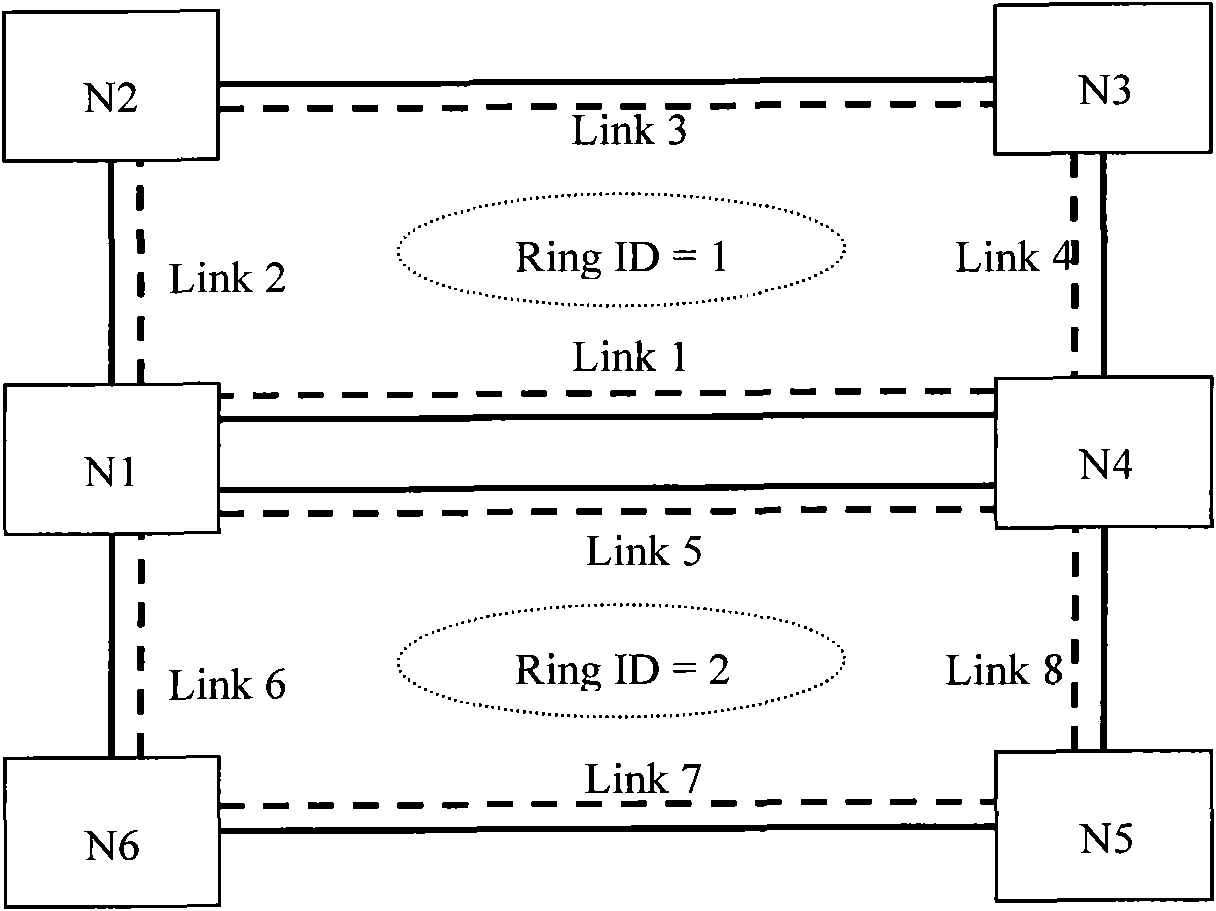
[0104] Example 1: 2-fiber MS-SPRING
[0105] Taking the 2-fiber multiplex section ring in the SDH network as an example, in a pair of optical fibers with opposite directions between adjacent nodes, half of the time slots are used as the working path to transmit bidirectional services; the other half of the time slots are used as the protection path (that is, these The protection type of the timeslot is ring protection), when there is no fault in the ring, additional services that can be preempted can be transmitted; when the ring fails, the services in the working path can preempt the additional services and switch to the protection path for transmission.
[0106] Such as Figure 7 As shown, assuming that the bandwidth of the link is STM-16 (Synchronous Transfer Mode-16, Synchronous Transfer Mode-16), there are two ways to publish link information:
[0107]Solution 1: The working path part of a pair of optical fibers can be bound as one TE link, and the protection path part c...
example 2
[0135] Example 2: 4-fiber MS-SPRING
[0136] The 4-fiber multiplex section ring is similar to the 2-fiber multiplex section ring. The main difference is that between adjacent nodes, the working path and protection path in the same direction are transmitted by two optical fibers instead of the same optical fiber. different time slots to transmit.
[0137] Such as Figure 8 As shown, similar to Example 1, the working path in two directions can be regarded as one TE link; the protection path in two directions can be regarded as another TE link; the four optical fibers can also be regarded as one There are two TE links, and two Link Protection Type Sub-TLVs are used to distinguish the working path and the protection path.
example 3
[0138] Example 3: Multi-ring shared optical fiber
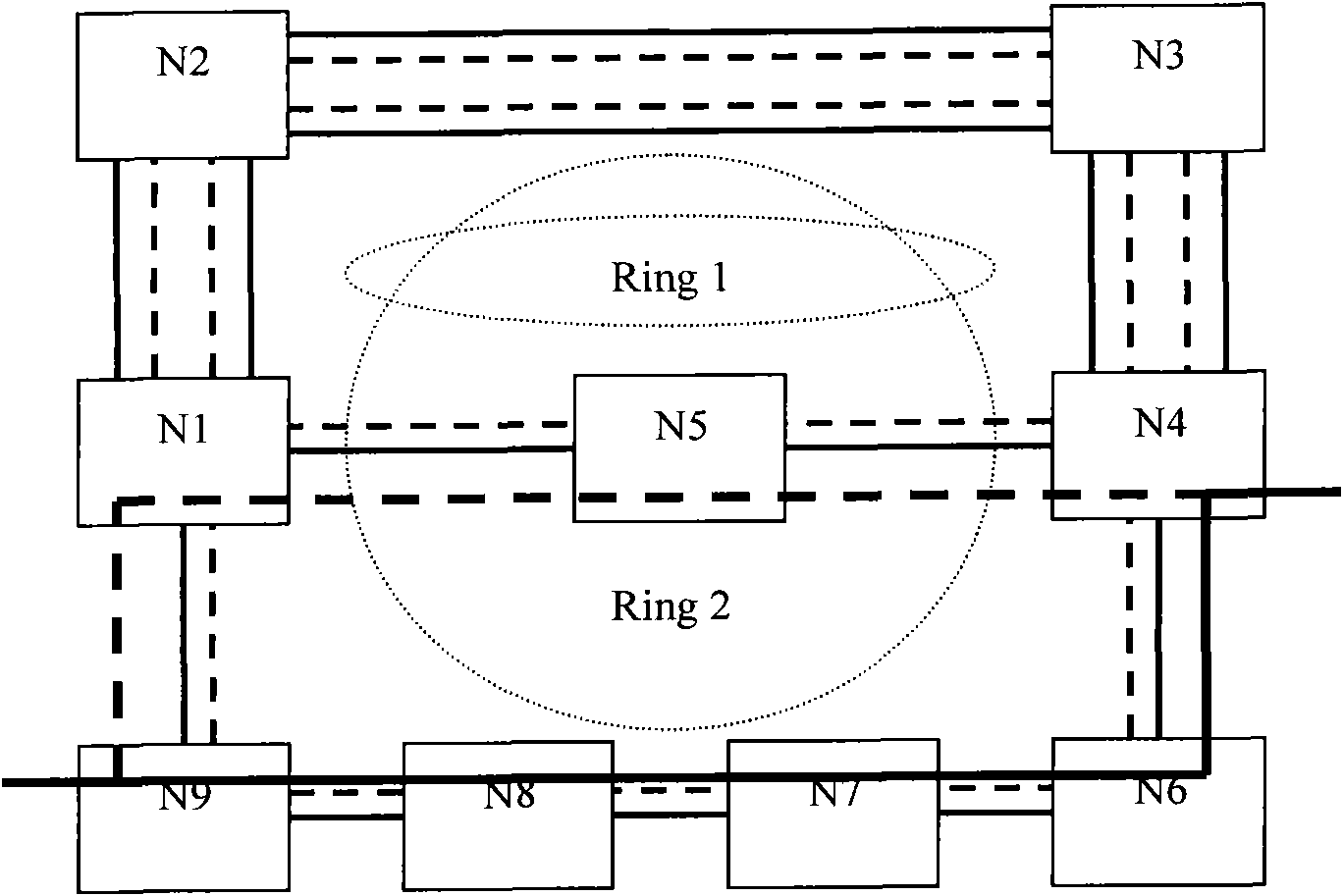
[0139] When two rings share a pair of optical fibers and different rings use different time slots of the optical fibers, it is necessary to specify which time slots belong to which ring when the routing protocol publishes link information.
[0140] Such as Figure 9 As shown, it is assumed that there are two 2-fiber multiplex section rings in the network, and the optical fiber between A-B is STM-16, and the time slots 1-8 of each fiber are used by ring Ring1 (time slots 1-4 are working path, time slots 5-8 are protection paths), and time slots 9-16 are used by Ring2 (time slots 9-12 are working paths, and time slots 13-16 are protection paths).
[0141] There are also multiple routing publishing schemes:
[0142] Solution 1: You can bind W1+W2 of Ring1, P1+P2 of Ring1, W1+W2 of Ring2, and P1+P2 of Ring2 into four TE links respectively, and assign a link ID to each TE link distinguish. In this case, the protection type of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com