Magnetic-label sensor and cartridge
A magnetic label and sensor technology, applied in instruments, scientific instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the sensor signal-to-noise ratio and detection limit, and achieve low detection limit, increase capacity, and improve signal-to-noise ratio. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
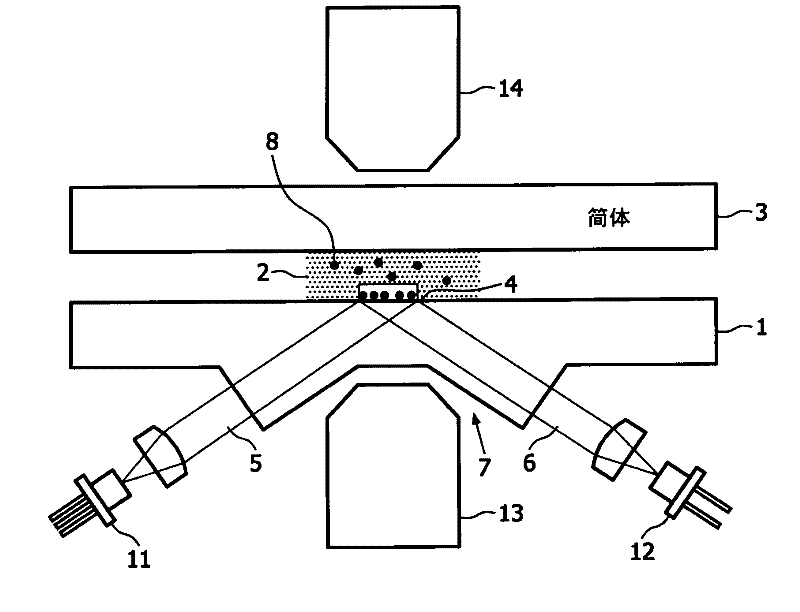
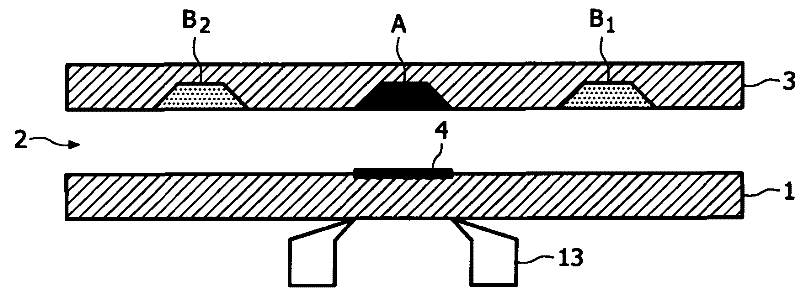
[0025] figure 1 Schematically showing the functional principle of the frustrated total internal reflection (FTIR) optical detection method. The illustrated cartridge comprises a base 1 and a cover part 3 with a fluid passage 2 therebetween. The fluid channel 2 is suitable for filling with a sample and is closed or covered by a cover part 3 . At the bottom, the fluid channel 2 is bounded by a sensor surface or sensor area 4, both terms are used below. Light ray 11 from a laser or LED enters the base 1 along a first optical path 5 , is reflected at said sensor surface 4 and leaves the base 1 along a second optical path 6 . The bottom 1 forms a recess 7 adapted to accommodate means 13 for providing a magnetic field.
[0026]Once the fluid channel 2 is filled or supplied with a fluid sample, the superparamagnetic label particles 8 supplied in dry form diffuse into the solution with the fluid sample. The terms "magnetic particle" and "magnetic label particle" are used equivalen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com