System for detecting solder joint reliability of circuit board by using infrared multipoint temperature measuring heat resistance method
A detection system and circuit board technology, which is applied in the field of detection systems, can solve problems such as normal appearance and unrecognizable virtual solder joints, and achieve good development prospects and high reliability of detection results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
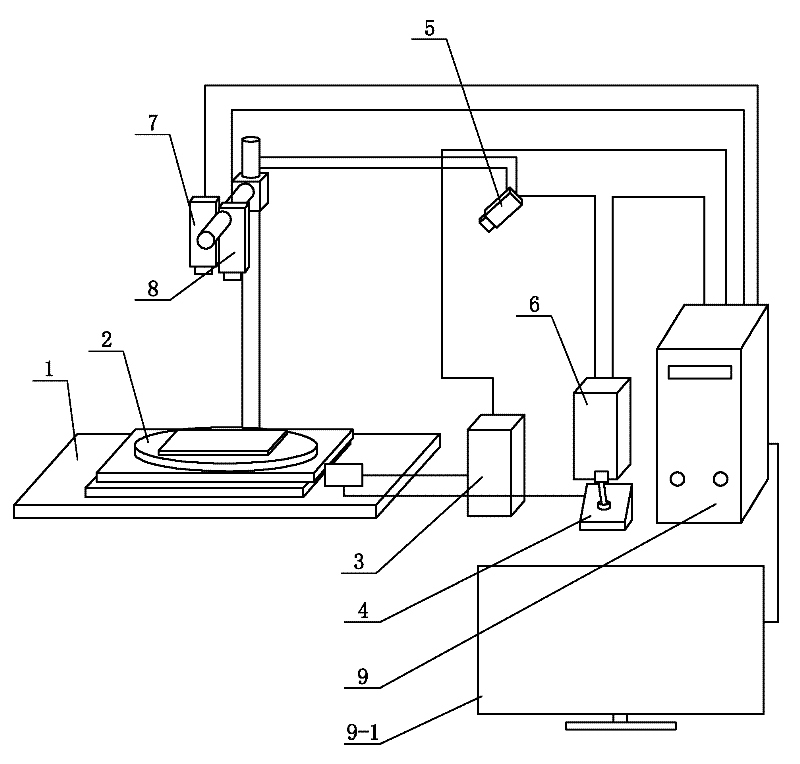
[0025] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 To describe this embodiment,
[0026] This embodiment includes a system platform 1, an XY rotary stage 2, a stage drive controller 3, an infrared laser 5, a laser controller 6, an optical microscope camera 7, an infrared thermal imager 8 and a computer 9,
[0027] The XY rotary stage 2 is set on the system platform 1,
[0028] The optical microscopic camera 7 and the infrared thermal imager 8 are located directly above the XY rotary stage 2, and the infrared laser 5 is positioned above the side of the XY rotary stage 2. The optical microscopic camera 7, the thermal infrared imager 8 and the infrared laser 5 are all fixed on the support of the system platform 1,
[0029] The displacement signal output end of the stage drive controller 3 is connected to the displacement signal input end of the XY rotary stage 2,
[0030] The control signal input end of the infrared laser 5 is connected to the control ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0036] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 1 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that it also includes a stage manual controller 4, and the manual signal output end of the stage manual controller 4 is connected to the manual signal output terminal of the XY rotary stage 2. signal input. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
[0037] In this embodiment, the manual controller 4 is used to control the displacement of the XY rotary stage 2. The manual controller 4 can be used in conjunction with the stage driving controller 3, or can be used separately.
[0038] The manual controller 4 can adopt the driving mode of a manual stepping motor to meet the detection requirements.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0039] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the control signal input end of the stage drive controller 3 is connected to the stage drive signal output end of the computer 9; the control of the laser controller 6 The signal input end is connected to the laser control signal output end of the computer 9, and the signal processing result of the computer 9 is displayed through the display 9-1. Others are the same as the first or second embodiment.
[0040] In this embodiment, the computer 9 is used to comprehensively control the entire system, so that the overall system can be coordinated and coordinated, the positioning is more accurate, the precision is higher, and the automation of the detection system is realized.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com