Scene-based filtering method and self-adapting filter
A scene and filter coefficient technology, applied in the communication field, can solve problems affecting system performance and achieve good filtering effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
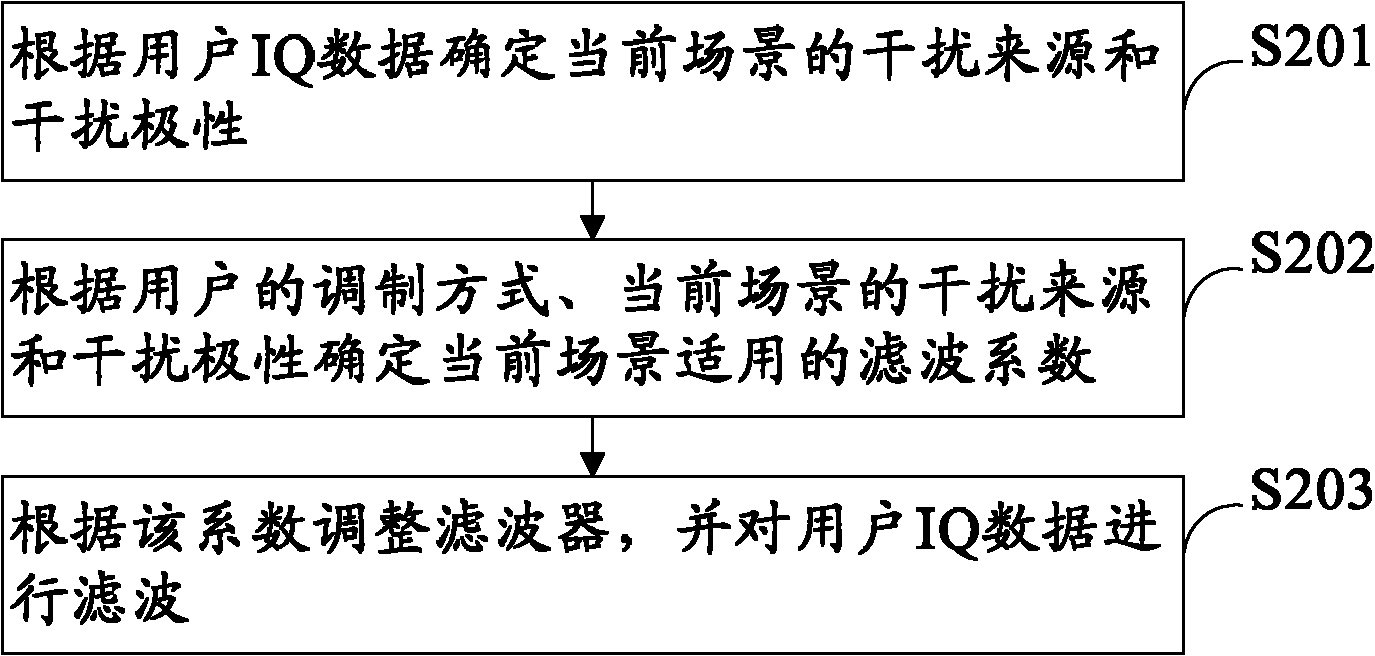
[0028] The scene-based filtering method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the method steps include:
[0029] S201. Determine the interference source and interference polarity of the current scene according to the user IQ data.
[0030] S202. Determine a filter coefficient applicable to the current scene according to the modulation mode of the user, the interference source and the interference polarity of the current scene.
[0031] S203. Adjust the filter according to the coefficient, and filter the user IQ data.
[0032] The scene-based filtering method provided by the embodiment of the present invention determines the interference source and interference polarity of the current scene according to the user IQ data; then determines the applicable filter coefficient for the current scene according to the user's modulation mode, the interference source and interference polarity of the current scene ; Then adjust the filter accordi...
Embodiment 2
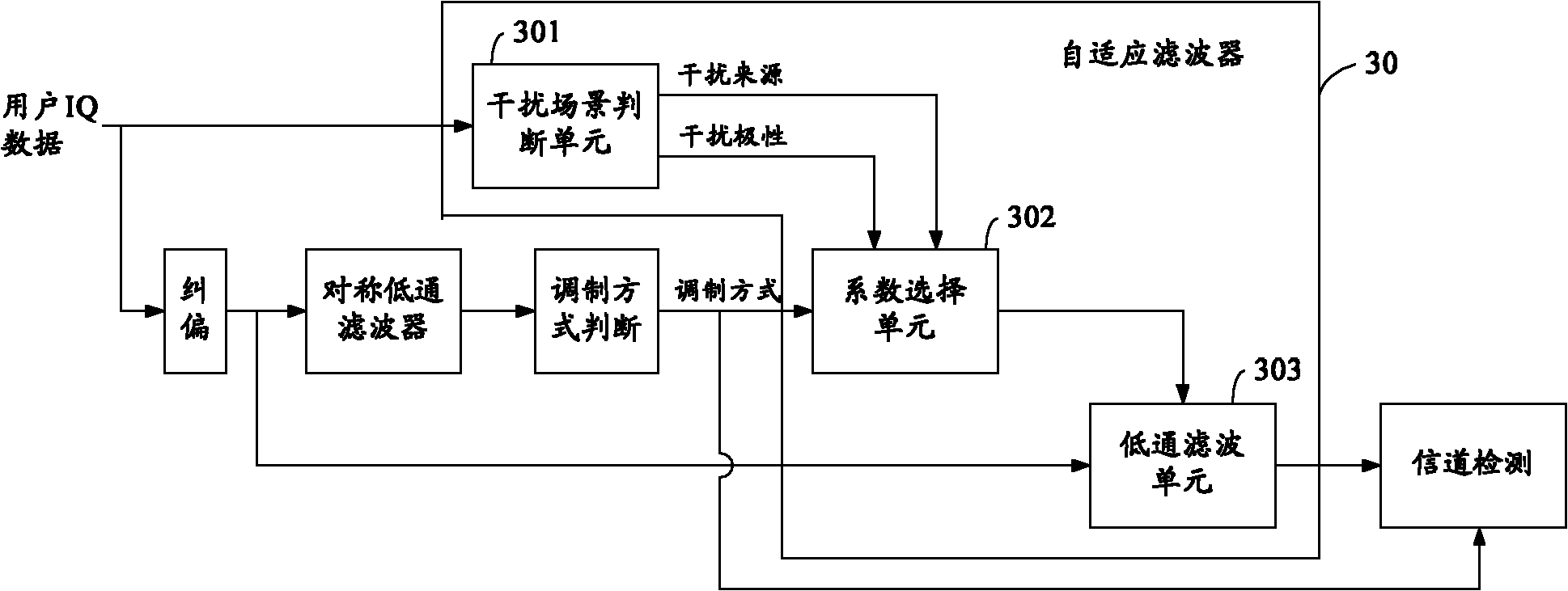
[0034] The adaptive filter 30 provided by the embodiment of the present invention, such as image 3 shown, including:
[0035] The interference scene judging unit 301 is configured to determine the interference source and interference polarity of the current scene according to the user IQ data.
[0036] The coefficient selection unit 302 is configured to determine the filter coefficient applicable to the current scene according to the user's modulation mode, the interference source and the interference polarity of the current scene determined by the interference scene judgment unit 301 .
[0037] A low-pass filtering unit 303, configured to adjust the filter according to the coefficient determined by the coefficient selecting unit 302, and filter the user IQ data.
[0038] The adaptive filter provided by the embodiment of the present invention determines the interference source and interference polarity of the current scene according to the user IQ data; then determines the f...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Utilize above-mentioned embodiment two and appendix below image 3 , 4 The scene-based filtering method provided by the embodiment of the present invention is described.
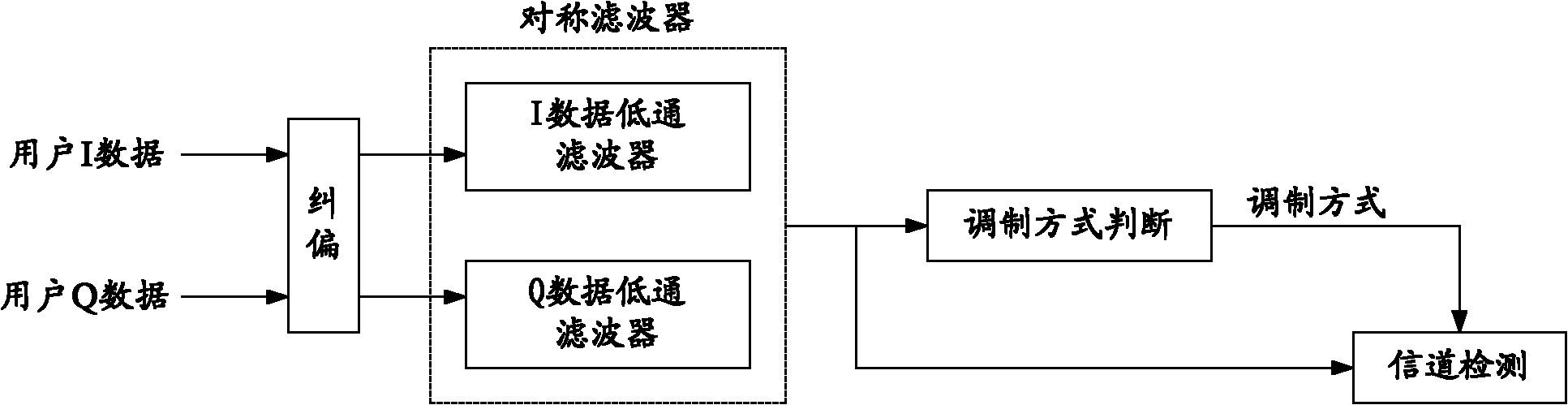
[0049] Such as image 3 As shown, the user IQ data is divided into two parallel paths, one path is as in the prior art, and performs symmetrical low-pass filtering after deviation correction; the other path is input into the adaptive filter 30 provided by the embodiment of the present invention. In the adaptive filter 30, the interference scene judging unit 301 determines the interference source and interference polarity of the current scene according to the input user IQ data. Wherein, the interference source includes unilateral interference, bilateral interference and no interference; the interference polarity is used to indicate left adjacent channel interference or right adjacent channel interference in a unilateral interference scenario.
[0050] Specifically, such as Figure 4 , Figure 5 A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com