Method for predicting hydrocarbon process stream stability using near infrared spectra
A near-infrared spectroscopy, process flow technology, applied in the field of predicting the stability of hydrocarbon process flow, can solve problems such as limiting the ability to optimize cracking treatment, achieve the effect of less skills and training, optimize cracking process, and reduce the amount of time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0041] For a series of 24 vistar samples, "stability" and NIR spectra were determined using accepted standard methods. Using partial least squares statistical methods, correlation models were derived between standard stability measurements and absorbance measurements in selected regions of the NIR spectrum. The model was validated using a cross-validation technique in which one sample at a time was excluded from the correlation model and predicted from the correlation.
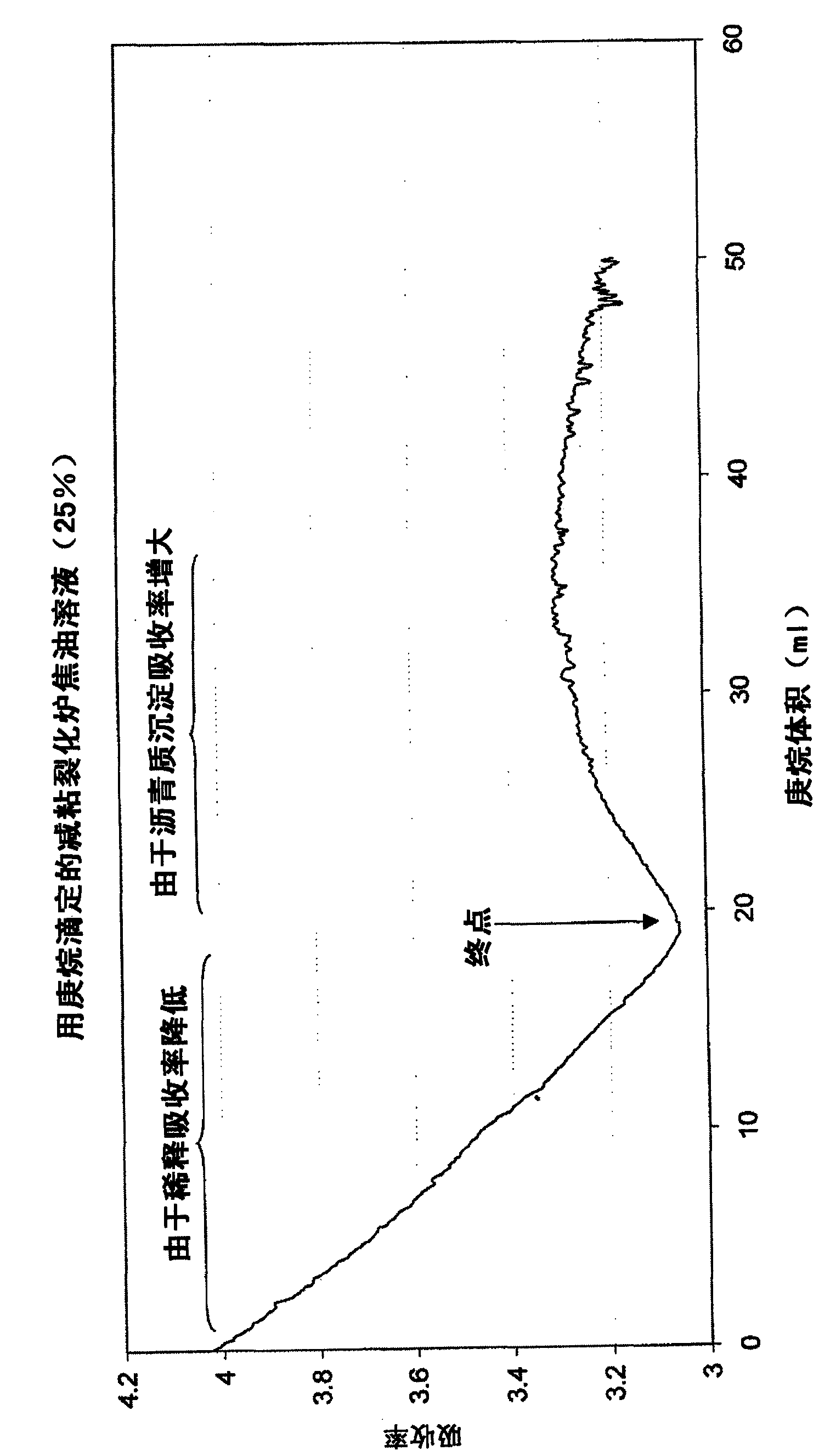
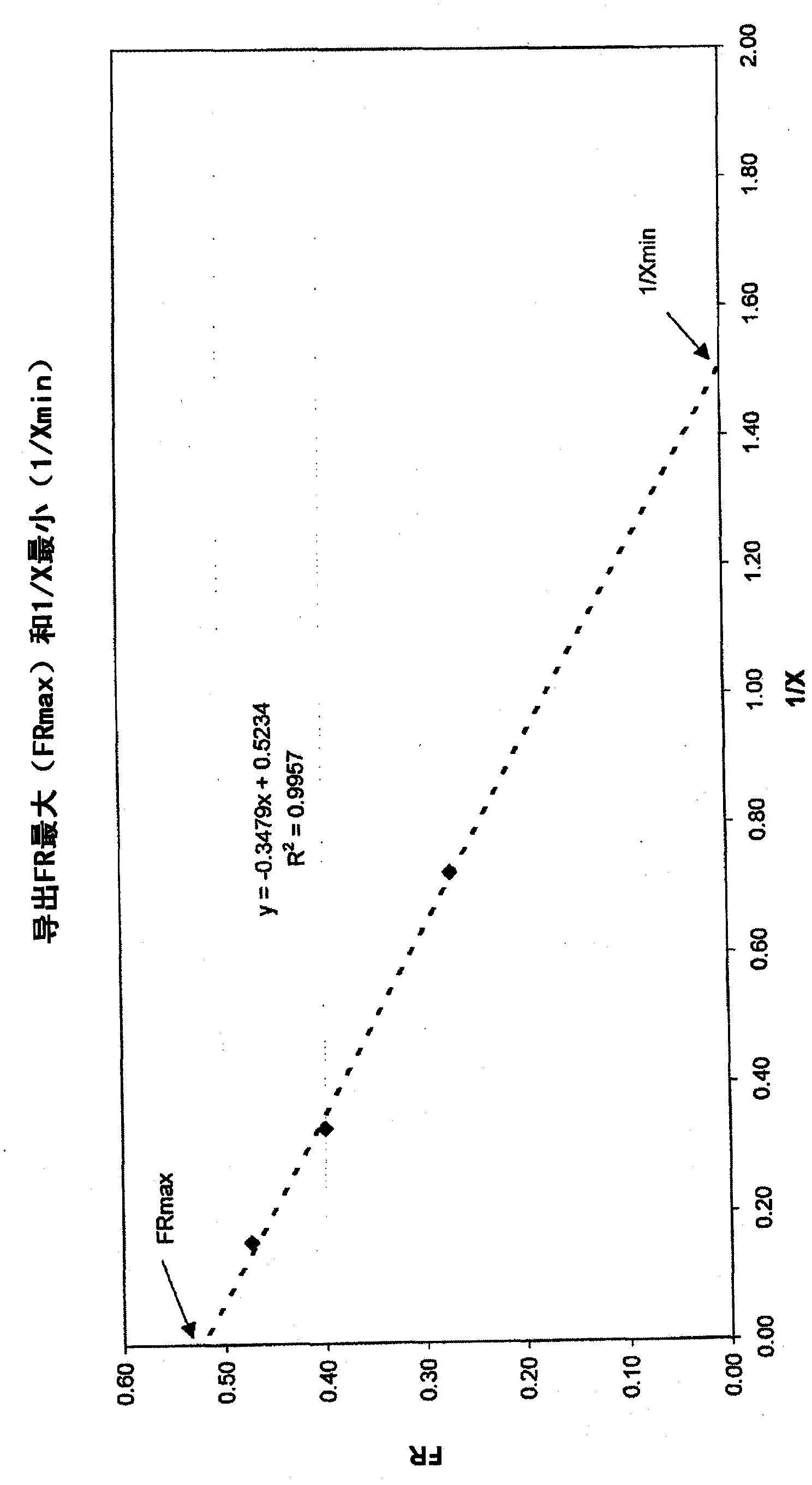
[0042] For the purposes of this illustration, the publication titled "Standard Test Method for Determining the Intrinsic Stability of Asphaltene-Containing Residues, Heavy Fuel Oils, and Crude Oils (N-Heptane Phase Separation; Optical Detection) ( Standard Test Method for Determination of Intrinsic Stability of Asphaltene-Containing Residues, Heavy Fuel Oils, and Crude Oils (n-Heptane Phase Separation; Optical Detection))" to determine the stability of a series of vistar samples. The method assumes a model of...
example 2
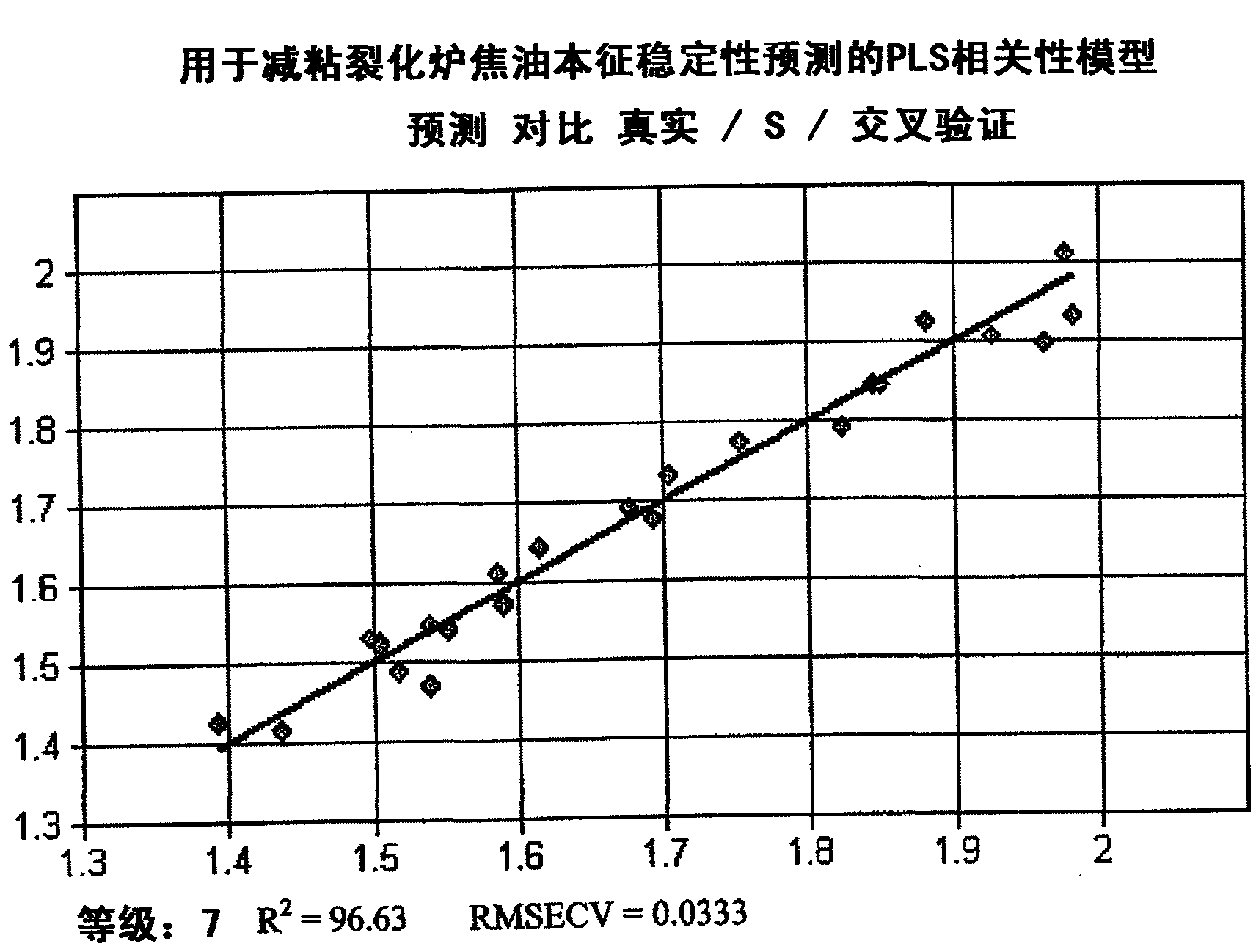
[0047] This example is a model for predicting stability based on a partial least squares analysis of 24 "vistar" samples using the technique described in Example 1. The region of the NIR spectrum covered by this model includes 6102 to 5446 cm -1 and 4601 to 4247cm -1 , and use 7 main components. This component is a statistically orthogonal variable derived from the PLS analysis. The statistical parameters of the model are R 2 = 0.948 and RMSEV = 0.0423. Representative results for three samples are shown in Table 1.
[0048] Table 1
[0049] Actual "S" Stability
example 3
[0051] In principle, the described system can be adapted for on-line monitoring. A side stream from the cleaved vistar bottoms can be fed to a monitoring unit where NIR spectroscopy can be measured. The computer system will compare vistar spectra to correlation models and calculate predicted stability results. This result can be transmitted to the control system and manipulated manually, or integrated into a control mechanism whereby, based on this result, the severity of the pyrolysis process will be increased or decreased. A similar on-line system can be used to monitor the feed to the device to automatically determine the specific calibration model for this mode of operation. Alternatively, pyrolysis can also be determined by taking a grab sample of the feedstock to be analyzed and manually selecting the correlation model for the vistar analysis, since the feedstock only needs to be tested each time the feedstock is changed A drastic desired increase or decrease.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com