Real-time quantitative judgment method of hazard of trans-boundary sudden water environmental pollution accident
A real-time quantitative and judgment method technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient risk assessment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
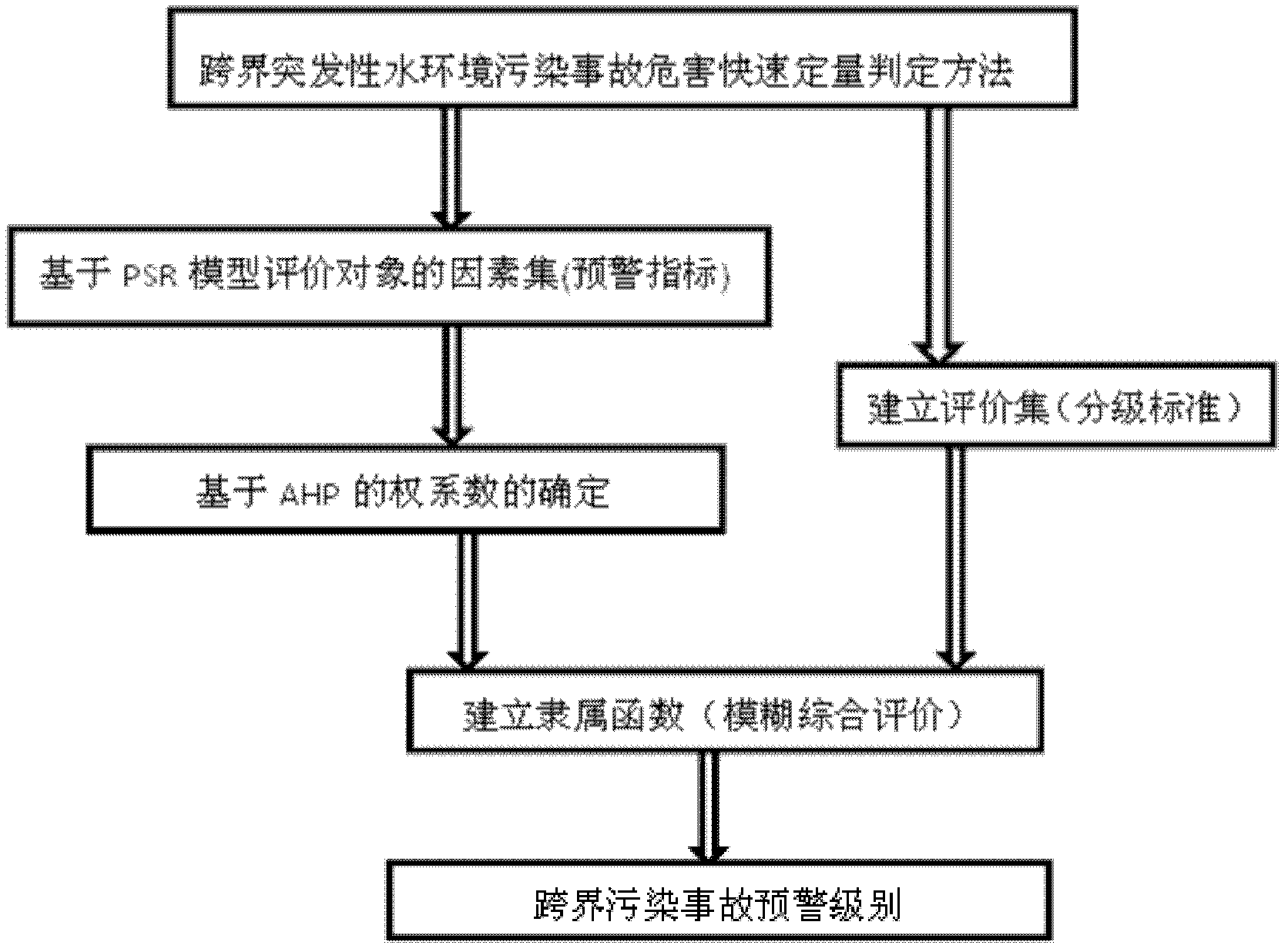
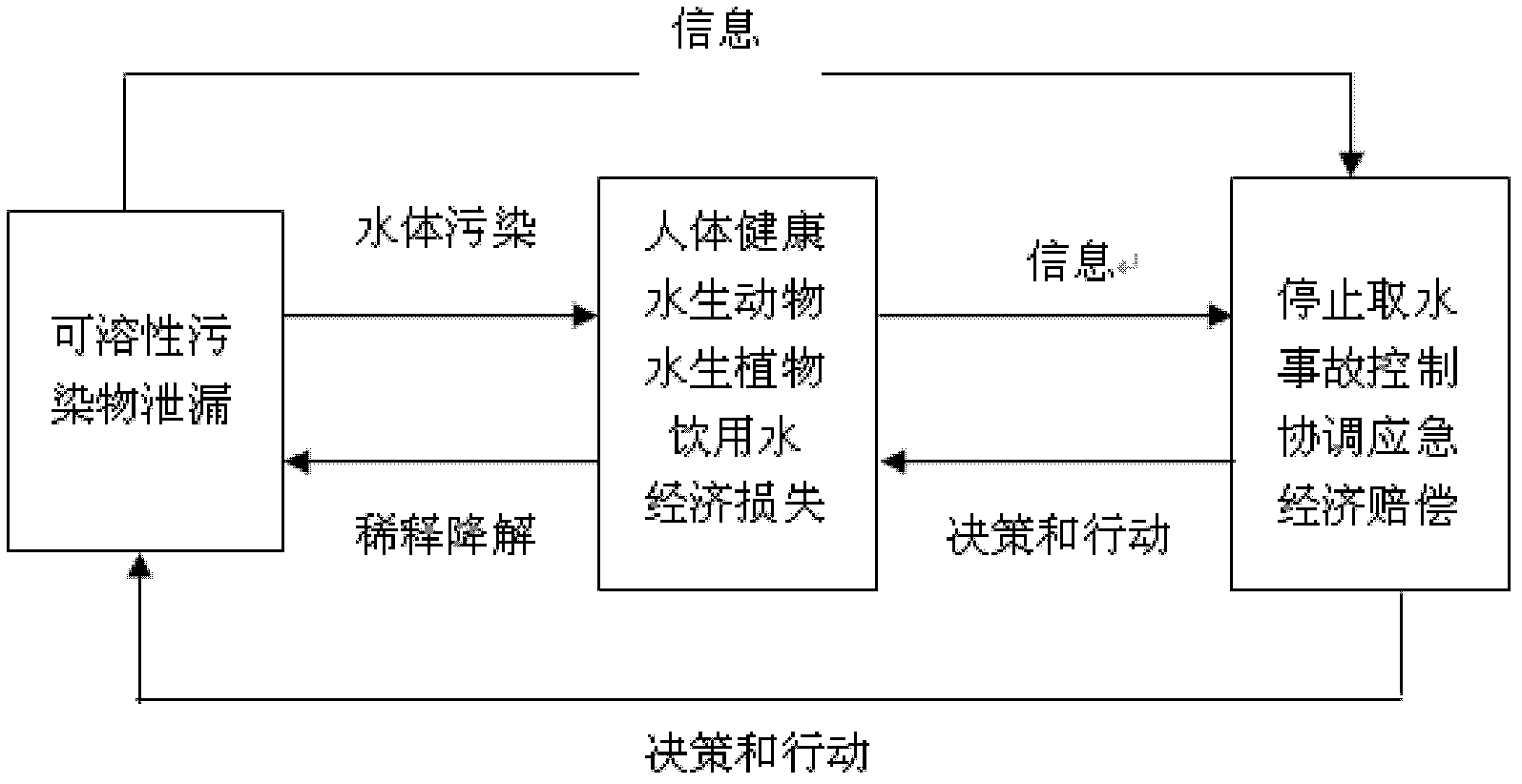
[0040] Embodiment 1: Combining figure 1 Describe the real-time quantitative determination method for the hazard of a transboundary sudden water environment pollution accident in this embodiment, which is realized through the following steps:
[0041] 1. Establish a set of factors for the evaluation object
[0042] Using the pressure-state-response (Pressure-State-Response, abbreviated as PSR) framework model, 5 main factors and 12 early warning indicators were obtained through screening, and an evaluation index system for transboundary sudden water pollution accidents was constructed. The corresponding early warning indicators are as follows:
[0043] The first factor is the source of environmental risk (pressure), which corresponds to the two early warning indicators of the characteristic pollutant concentration exceeding the standard multiple and the pollutant's own toxicity;
[0044] The second factor is security and economic risk (status), corresponding to the two early ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
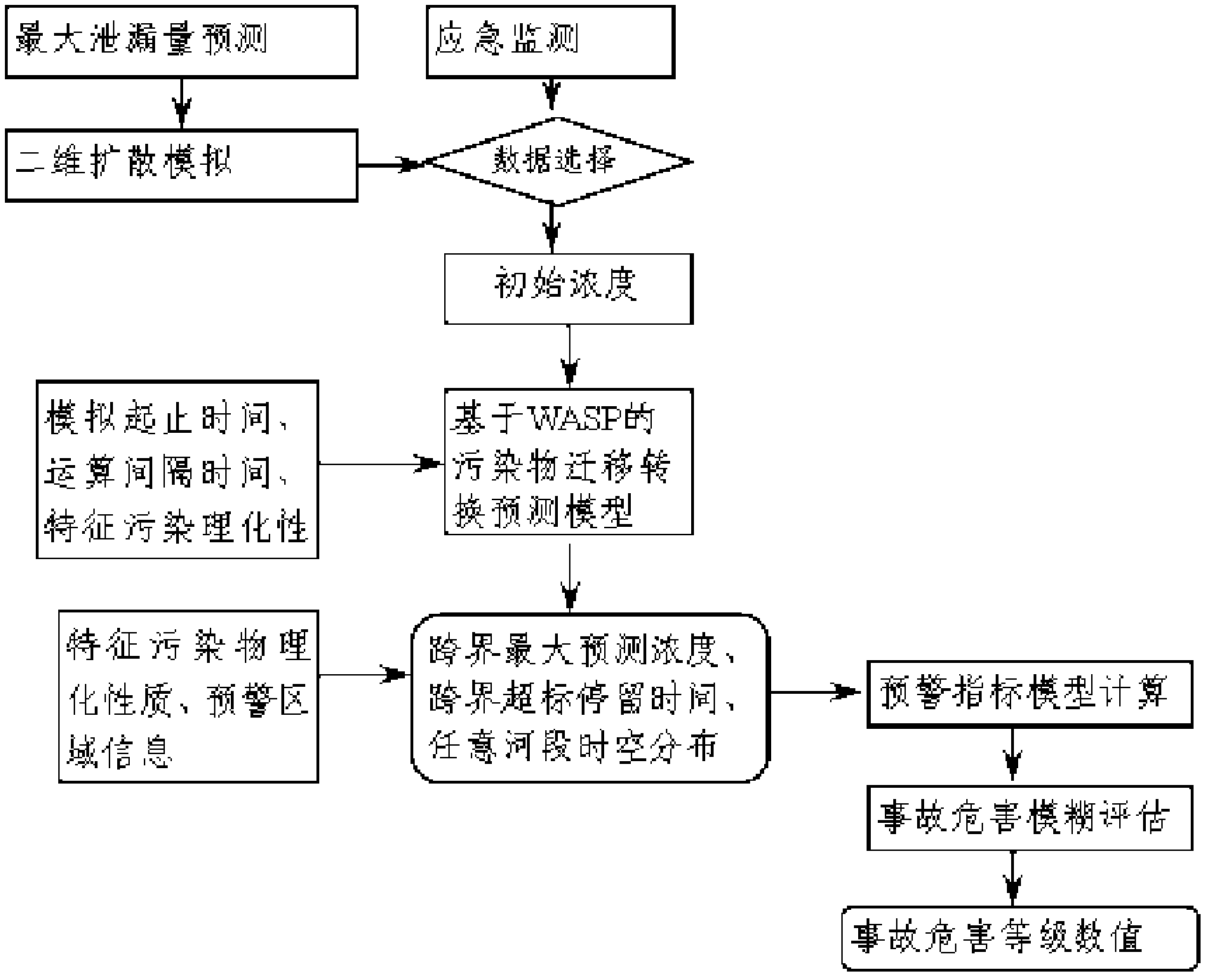
[0070] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is the combination of image 3 , indicating that the early warning process of transboundary sudden water pollution accidents is implemented through the following steps:
[0071] (1) Data selection: collect emergency monitoring data, and estimate the initial pollution concentration according to the prediction and simulation of the maximum leakage when the emergency monitoring data is missing or distorted;
[0072] (2) Real-time simulation of pollutant migration and transformation: Input parameters such as the physical and chemical properties of pollution, accident location, occurrence time, and simulation interval time, and use pollutant migration and transformation model simulation to obtain information on the spatiotemporal distribution of pollutants in transboundary areas.
[0073] (3) Calculation of early warning index model: input various parameters of early warning information and information on ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0076] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 2, the 1-9 scale method in the AHP is used to establish a hierarchical structure model, and the comparison results between the factors are determined as follows:
[0077]
[0078] The random consistency index of the comparison matrix is CR=0.0183<0.1, so the consistency of the comparison matrix is acceptable, and the weight coefficient of each early warning index in the factor set of the evaluation object is obtained. Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com