Method and device for carrying out adsorption quantity improvement and dehydrogenation on radioactive gases
A radioactive gas and adsorption device technology, applied in the field of hydrogen removal in nuclear power plants, can solve problems such as limited effect, hydrogen explosion in nuclear power plants, difficulties for rescuers and equipment to enter nuclear power plants for accident handling and rescue, and achieve the effect of reducing volume and reducing the number of replacements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
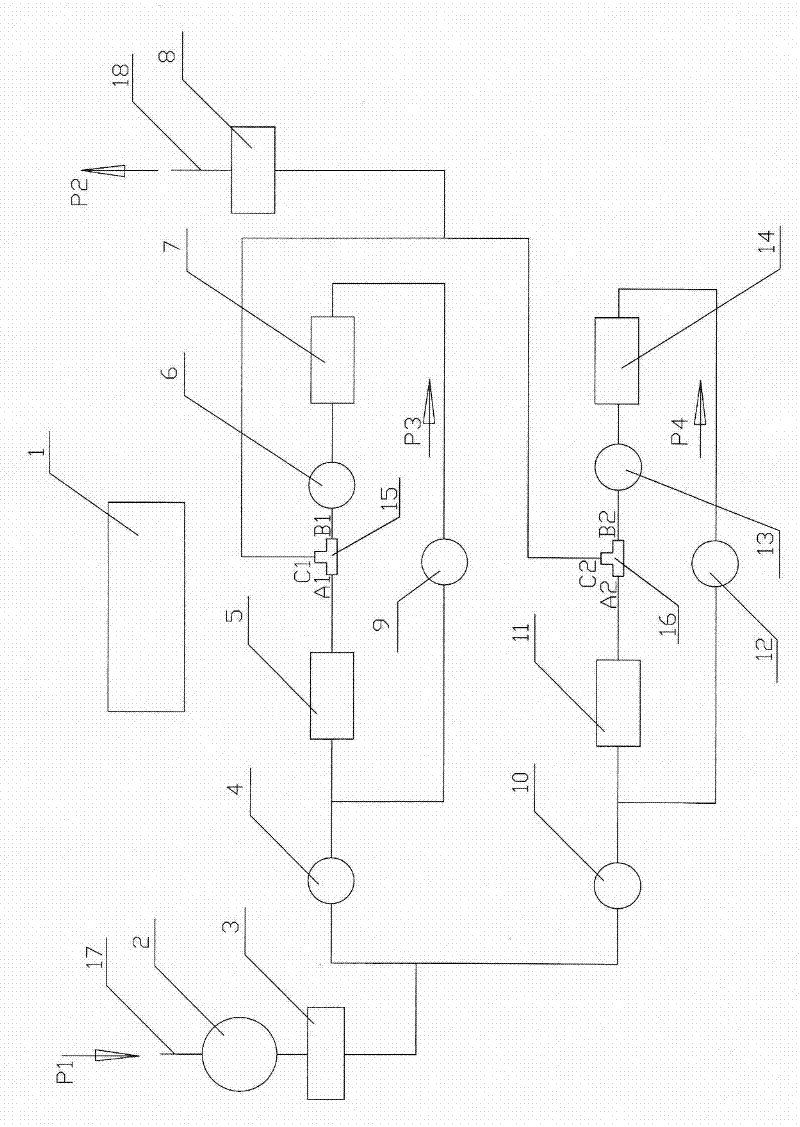
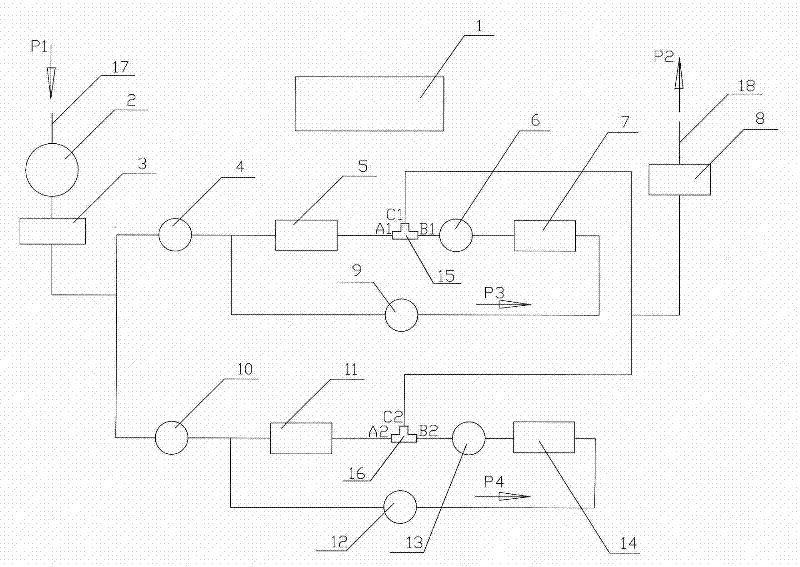
[0021] A method for increasing the adsorption capacity of radioactive gases such as radon. Two or more (including two) adsorption devices form a series loop. And under the action of the throttle valve, the first-stage adsorption device is lower than an atmospheric pressure, and the latter-stage adsorption device is higher than an atmospheric pressure. The ratio of the pressure of the latter-stage adsorption device to the previous-stage adsorption device is n, and the adsorption coefficient is proportional to the pressure. Proportional, so that the latter-stage adsorption device can absorb more than n times the amount of radioactive gas absorbed by the previous-stage adsorption device. Thus, the aerosol in the air can be filtered and the radioactive gas in the air can be absorbed.
[0022] The further technical proposal of this embodiment is to adsorb radioactive gas through parallel connection of more than two (including two) series loops.
[0023] This embodiment also provid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com