Method and reagent for improving rate of extraction of DNAs of castoff cells in case trace sample
A technology of exfoliating cells and extracting efficiency, which is applied in the field of forensic evidence DNA detection, can solve the problems of large influence of personal experience, high price, incomplete length, etc., to reduce dependence on experience, good stability, and reduce peak loss Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
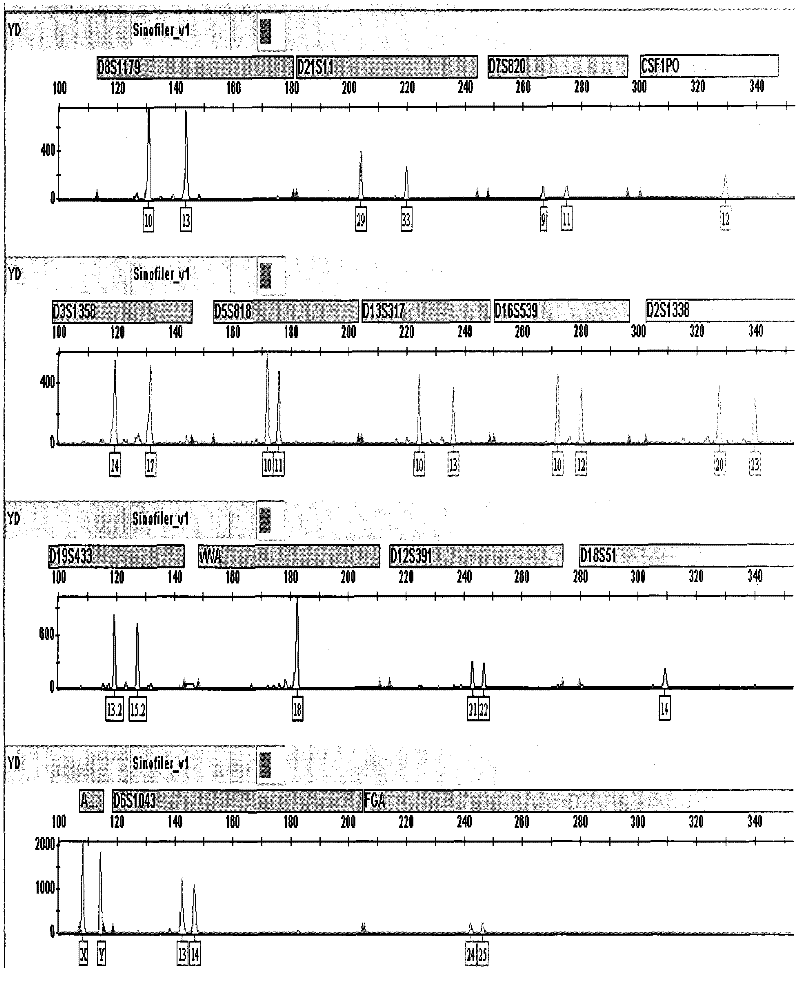
[0035] Example 1 Extraction of trace amounts of DNA from a belt buckle left at the scene of the case.
[0036] (1) Kit preparation
[0037] Prepare a kit for extracting DNA from trace sample materials using magnetic beads, including:
[0038] 1mL silanized magnetic bead solution (0.1mg / μL), a product listed by Wuhan Wawadina Technology Development Co., Ltd. or purchased by Qiagen;
[0039] 100mL lysate, its component is the Tris-HCl buffer solution of pH=8.0;
[0040] 100mL binding solution I, its component volume ratio is 20-50% PEG (molecular weight 8000);
[0041] 20mL combination solution II, its component is ethanol;
[0042] 100mL cleaning solution, its component is ethanol solution with a volume ratio of 80%.
[0043] (2) Use the kit to extract the DNA of the cells shed from the belt buckle left at the scene of the case. The extraction steps are as follows:
[0044] 1) Use the case micro-examination material sticking device to repeatedly stick the belt buckle sever...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment two control experiments
[0061] Using 1 μL of blood diluted 60 times with normal saline as a simulated sample, replacing the exfoliated cell membrane in Example 1, the amplification and electrophoresis were the same as in Example 1, and a series of control experiments for micro sample extraction were designed as follows:
[0062] In control experiment 1, in the extraction step 1), the film was replaced by 1 μL of simulated sample, and the other steps remained unchanged;
[0063] No protease was added in step 2) of control test 2, and the others were the same as control test 1;
[0064] The incubation temperature in step 3) of control test 3 was less than 70 degrees, and the others were the same as test 1;
[0065] In step 4) of control test 4, ethanol was removed from the binding liquid system, and the others were the same as test 1;
[0066] PEG was removed from the binding liquid system in step 4) of control test 5, and the others were the same as test 1...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The ethanol of embodiment three binding solution II is changed into methyl alcohol and propanol, isopropanol
[0072] The ethanol in the binding solution II in Example 1 is replaced with methyl alcohol, propanol, and isopropanol respectively, and the DNA on the slippers, toothbrushes, and porcelain cups for drinking in the on-site case are extracted respectively with the magnetic bead method;
[0073] Except that 80 μL of binding solution II in the extraction step 3 was replaced with 80 μL of methanol, propanol, and isopropanol, the other operations were the same as in Example 1.
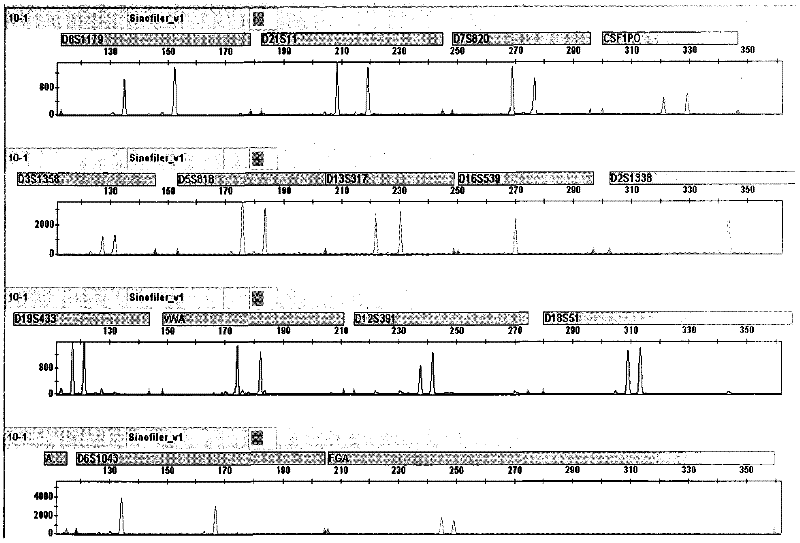
[0074] Figure 10 For the slippers left at the scene of the case, replace the compound STR amplification map of the binding solution II with methanol; Figure 11 For the toothbrush left at the scene of the case, replace the composite STR amplification pattern of the binding solution II with propanol; Figure 12 For the drinking porcelain cup left at the scene of the case, replace the compos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com