Hematopoietic protection against chemotherapeutic compounds using selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors
A kinase-dependent, cell cycle-dependent technology, applied in the field of hematopoietic protection against chemotherapeutic compounds using selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors, which can solve problems such as inability to provide protection and prevent clinical use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0255] Synthetic PD
[0256]
[0257] Route 1: Synthetic PD
[0258] PD was synthesized as shown in Scheme 1 above. The reactions shown in Scheme 1 were carried out essentially as previously reported, except for the conversion of Compound D to Compound E and the reaction of Compound F to Compound G (see VandelWel et al., J. Med Chem., 48, 2371-2387 (2005); and Toogood et al., J. Med. Chem., 48, 2388-2406 (2005)).
[0259] Compound D is converted to Compound E :
[0260]
[0261] Compound D (40 g, 169 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous THF (800 mL) under nitrogen and the solution was cooled in an ice bath, to which MeMgBr (160 mL, 480 mmol, 3M in ether) was added slowly and stirred for 1 h. with saturated NH 4 The reaction was quenched with aqueous Cl and partitioned between water and EtOAc. The organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, followed by MgSO 4 dry. Concentration...
Embodiment 2
[0271] Selective G1 arrest in CDK4 / 6-dependent cell lines
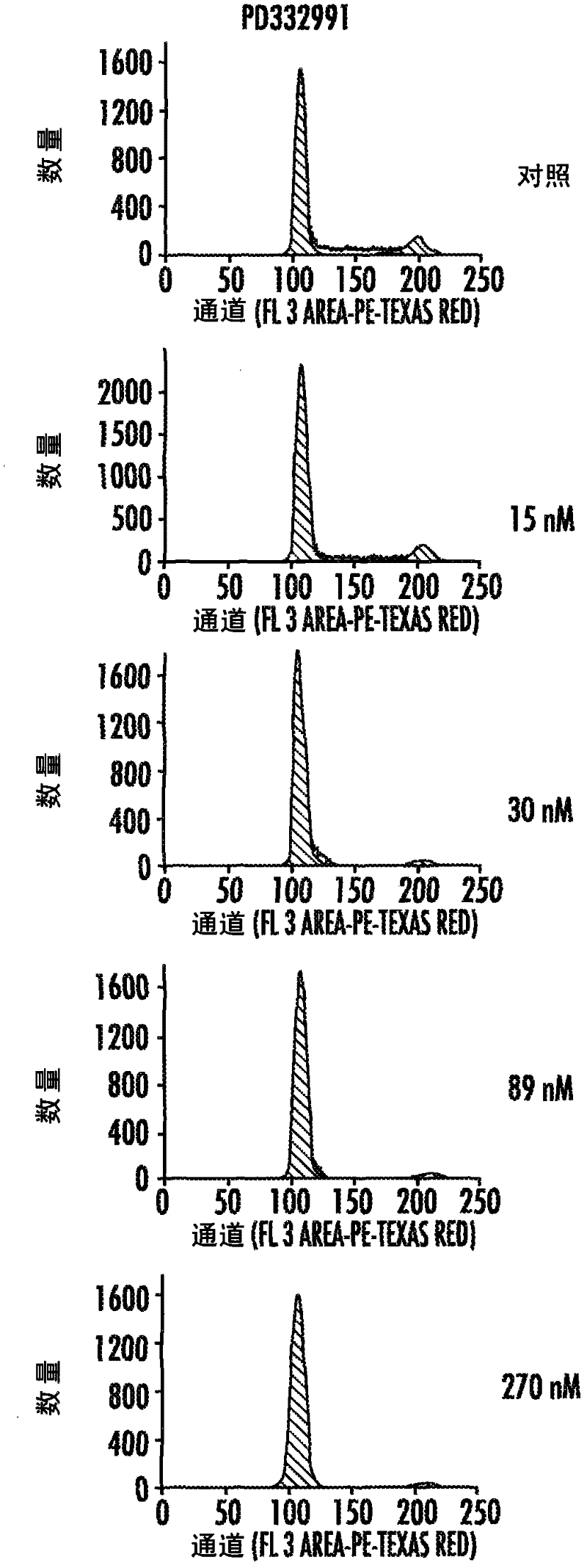
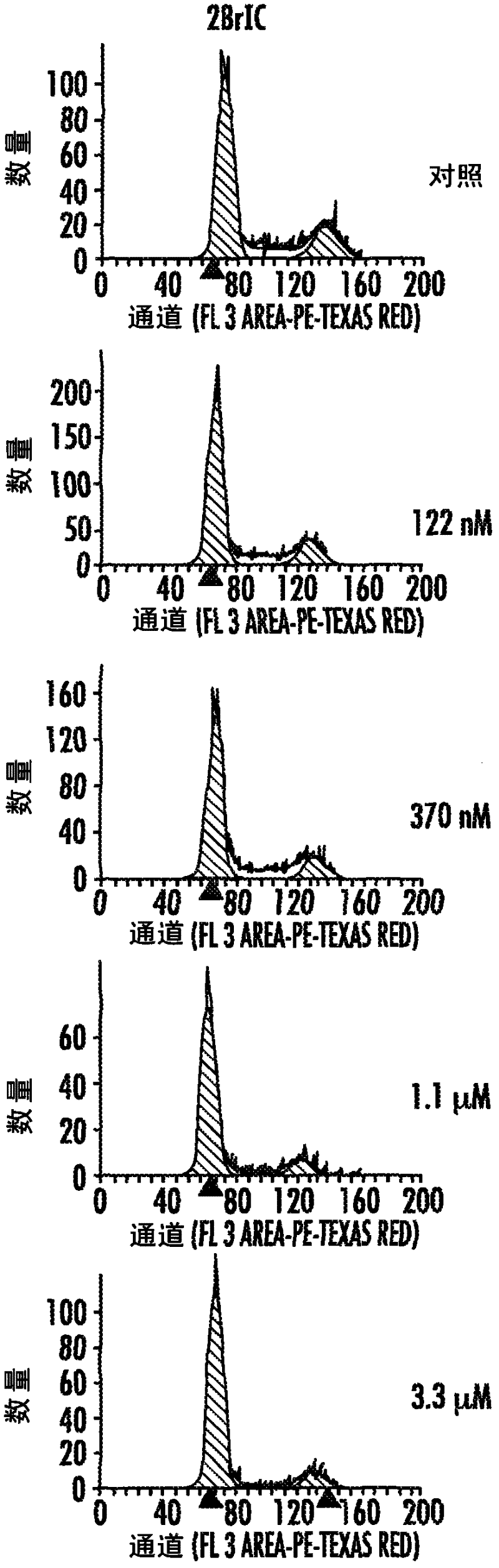
[0272] Several human cell lines were exposed to various small molecule kinase inhibitors. Cell cycle analysis was performed as described in the Methods section above.
[0273] After exposure to the potent and selective Cdk4 / 6 inhibitors PD0332991 or 2BrIC, CDK4 / 6-dependent cell lines, including telomerized human diploid fibroblasts (HS68) and the human melanoma cell line WM2664 Shows a pronounced, pure and reversible G1-arrest. see Figure 2A-2E . In addition, less selective CDK inhibitors targeting CDK1 / 2 (e.g. compounds 1-6, flavapine ( Figure 20A ), compound 7 (ie R547; Figure 21A ), Roscovitine ( Figure 22A ), genistein and compounds 8-14 ( Figures 24A-24C )) G2 / M blockade, intra-S-arrest or cell death (sub-G0) variably occurs in these cell types. In contrast, the RB-null melanoma cell line A2058 was insensitive to CDK4 / 6 inhibition, as expected, but, after exposure to less specific CDK inhibitors, s...
Embodiment 3
[0275] Prevention of DNA damage in cells treated with chemotherapeutic agents
[0276] The ability of selective CDK4 / 6 inhibitors to attenuate DNA damage in cells exposed to DNA damaging compounds such as carboplatin, etoposide, and doxorubicin was determined in a cell-based assay as described in the Methods section above . Carboplatin, etoposide, and doxorubicin caused extensive DNA damage as measured by γH2AX foci formation in CDK4 / 6-dependent and CDK4 / 6-independent cell lines. see Figures 3A-3C , 4 and 5. Use PD0332991 ( Figures 6A-6C , 7 and 8) or 2BrIC ( Figures 3A-3C , 4 and 5) Treatment followed by carboplatin, etoposide or doxorubicin attenuated γH2AX staining, suggesting that G1 arrest induced by PD0332991 and 2BrIC protects cells from chemotherapy-induced DNA damage.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com