Color halftoning image watermarking algorithm based on support vector machine
A technology of support vector machine and image watermarking, which is applied in image data processing, image data processing, computing and other directions, and can solve the problem of watermarking resistance and other problems that have not been studied.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] This embodiment mainly introduces the color halftone image watermark embedding process based on the support vector machine, and its implementation steps are as follows:
[0068] 1) Selection, encryption and dimensionality reduction of binary watermark
[0069] In this paper, the method of Arnold transformation is used to scramble the digital watermark binary image S={S(m,n), 1≤m≤P, 1≤n≤Q}, and record the number of iterations t of the transformation, so as to extract the watermark when used. The selected watermark image and the scrambled image are as follows: image 3 shown. Convert the scrambled P×Q-dimensional watermark image from a two-dimensional image to a one-dimensional watermark sequence M={M(k), 1≤k≤P×Q}.
[0070] 2) Selection of digital watermark embedding position
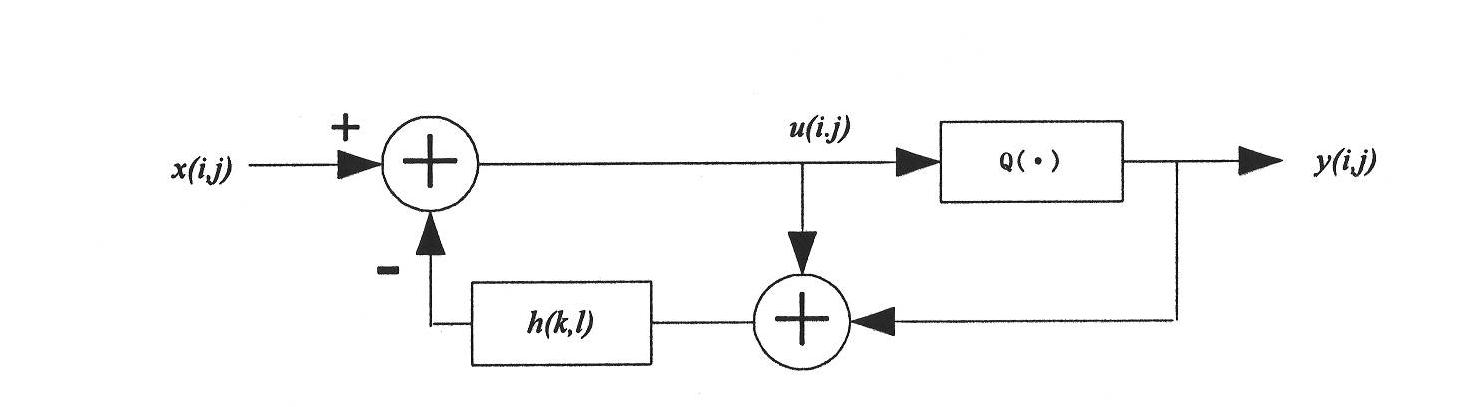
[0071] Adding watermarks to different positions of the image will give different results. Halftone images are only composed of two tones of black or white (0 or 1). If the pixel values are r...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Methods to enhance the robustness of digital watermarking:
[0098] Considering that the color image has three channels, in order to enhance the robustness of the watermark, on the basis of the watermarked color halftone image obtained from step 1) to step 3), select within a 3×3 neighborhood of the watermark embedding position Two positions, used to embed the same watermark bit on the B component (since the human eye is less sensitive to the blue component than other components) to enhance the embedding strength of the watermark. Image 6 (a) shows the location point (x, y) where the watermark is embedded in the G component, Image 6 (b) represents the position points (x-1, y) and (x, y-1) where the same watermark bit is embedded on the B component. When extracting the watermark, if the number of extracted watermark information values of 0 is greater than 1 in a certain watermark embedding neighborhood, then let the extracted watermark information be 0, otherwise it...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Experimental results and analysis:
[0101] In the experiment, a standard color Lena image of 256×256 pixels was selected (such as Figure 7 (a)), the digital watermark uses a 25×25 binary pattern “XD” (such as figure 2 (a)). Figure 7 (b) is the sub-channel color halftone result image, Figure 7 (c) is the result figure of using embodiment 1 to embed the binary watermark, Figure 7 (d) is the result of embedding a binary watermark using Example 2, and the directly extracted watermarks are all on the right side. The quality of the watermarked image and the similarity between the extracted watermark and the original watermark are measured by peak signal-to-noise ratio PSNR and similarity NC.
[0102] right Figure 7 (d) Conduct the following attack experiments. Figure 8 (a) to simulate random alteration, Figure 8 (b) for adding literal attacks, Figure 8 (c) is an image added with "salt and pepper" noise with a noise density of 0.02, Figure 8 (d) is an image...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com