Underwater acoustic communication method based on very minimum chirp keying modulation
A linear frequency modulation, keying modulation technology, applied in the field of digital communication, can solve the problem of not using underwater acoustic communication, and achieve the effects of great economic value and social benefits, high frequency band utilization, and fast information transmission rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
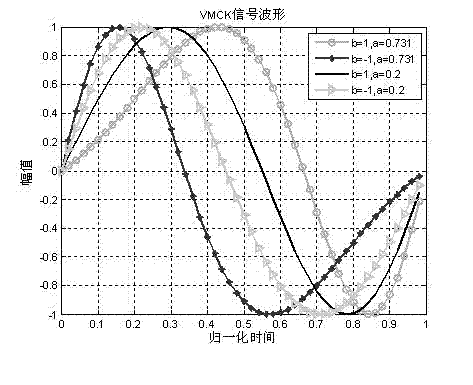
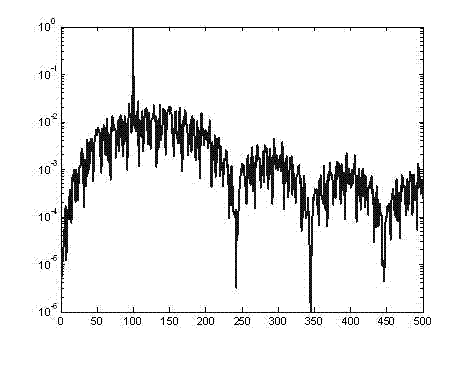
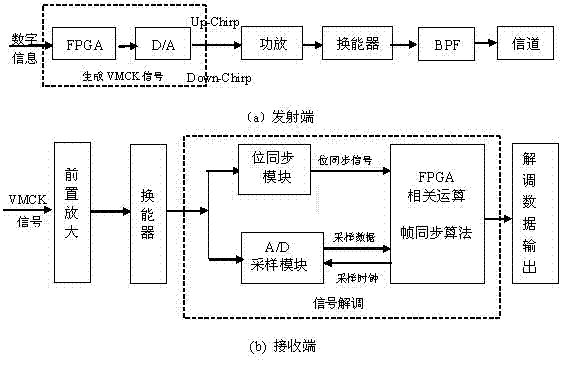
[0043] see image 3 , the underwater acoustic communication method based on very small chirp keying modulation, which is characterized in that the transmitting end uses the ultra-narrowband signal modulated by very small chirp keying as the transmission signal source to drive the underwater acoustic transducer to generate chirp longitudinal waves, Transmission in water; the receiving end converts the acoustic signal into an electrical signal through a transducer and then demodulates it.
Embodiment 2
[0045] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and more detailed descriptions are as follows:
[0046] Sending circuit:
[0047] 1) The data information is input into the FPGA, and the data storage and transmission module is controlled on the FPGA to send the waveform representing "0" or "1", and the D / A module converts the digital information output by the FPGA into an analog waveform to generate Up-Chirp and Down-Chirp Two VMCK signals.
[0048] The ultra-narrowband signal expression of VMCK is:
[0049] (5)
[0050] in, Represents the VMCK signal of one symbol, its expression is:
[0051] (6)
[0052] In the formula, or Indicates the up change or down change of the frequency of the VMCK signal, which is used to represent different transmission signals "1" (Up-chirp) or "0" (Down-chirp), respectively. Indicates the bit transfer rate, Represents the chirp coefficient, which reflects the frequency change degree of very sma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com