Wireless sensor network compressed sensing measurement matrix based on expander graph and reconfiguring method
A wireless sensor and compressed sensing technology, which is applied in wireless communication, network topology, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of limited compressed sensing, difficult realization of random numbers, and inability to guarantee data collection compression, etc., to achieve reduced number, high recovery accuracy, The effect of saving communication loss between networks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0017] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1 to Figure 7 Describe this embodiment, the implementation steps of this embodiment are:
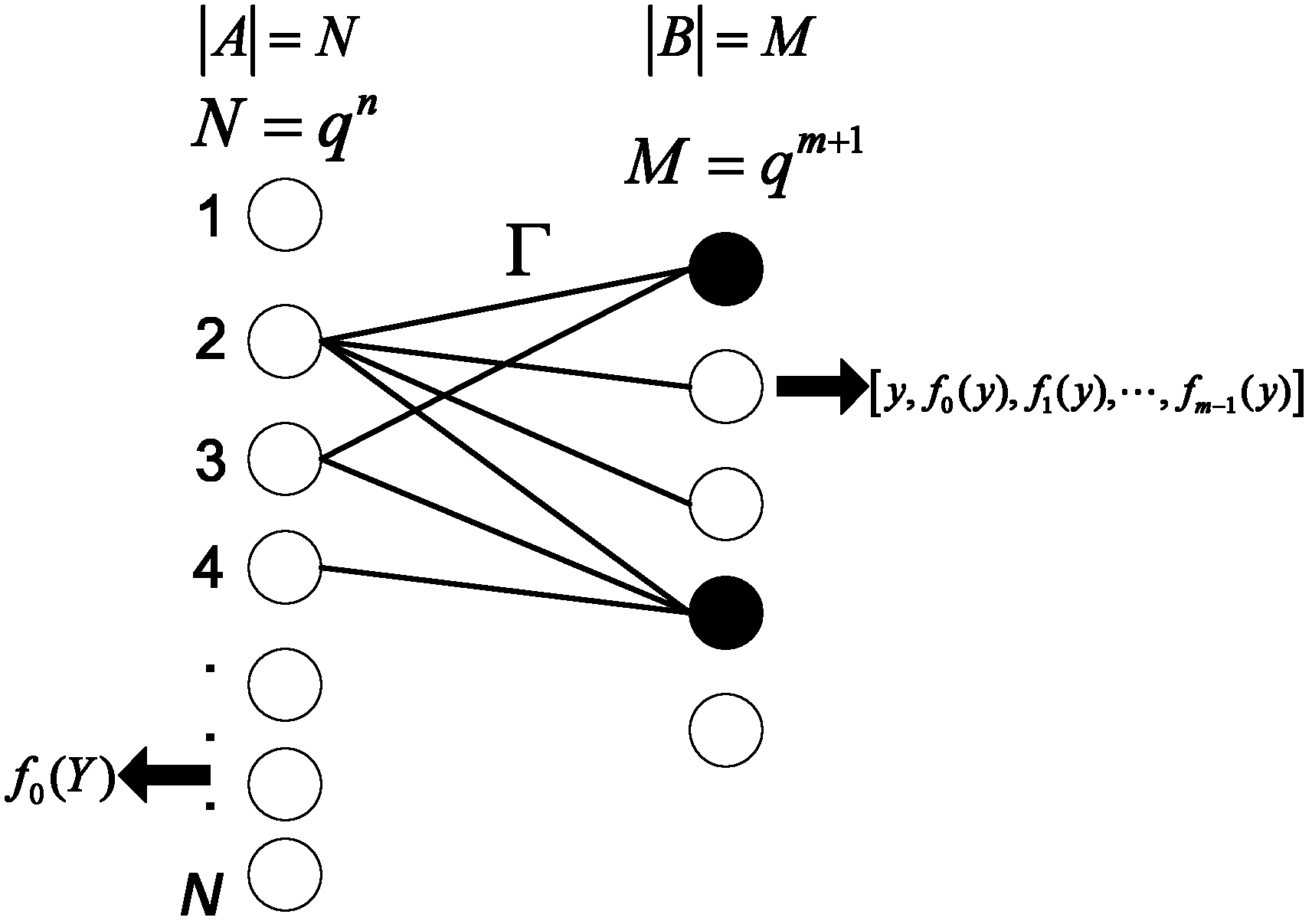
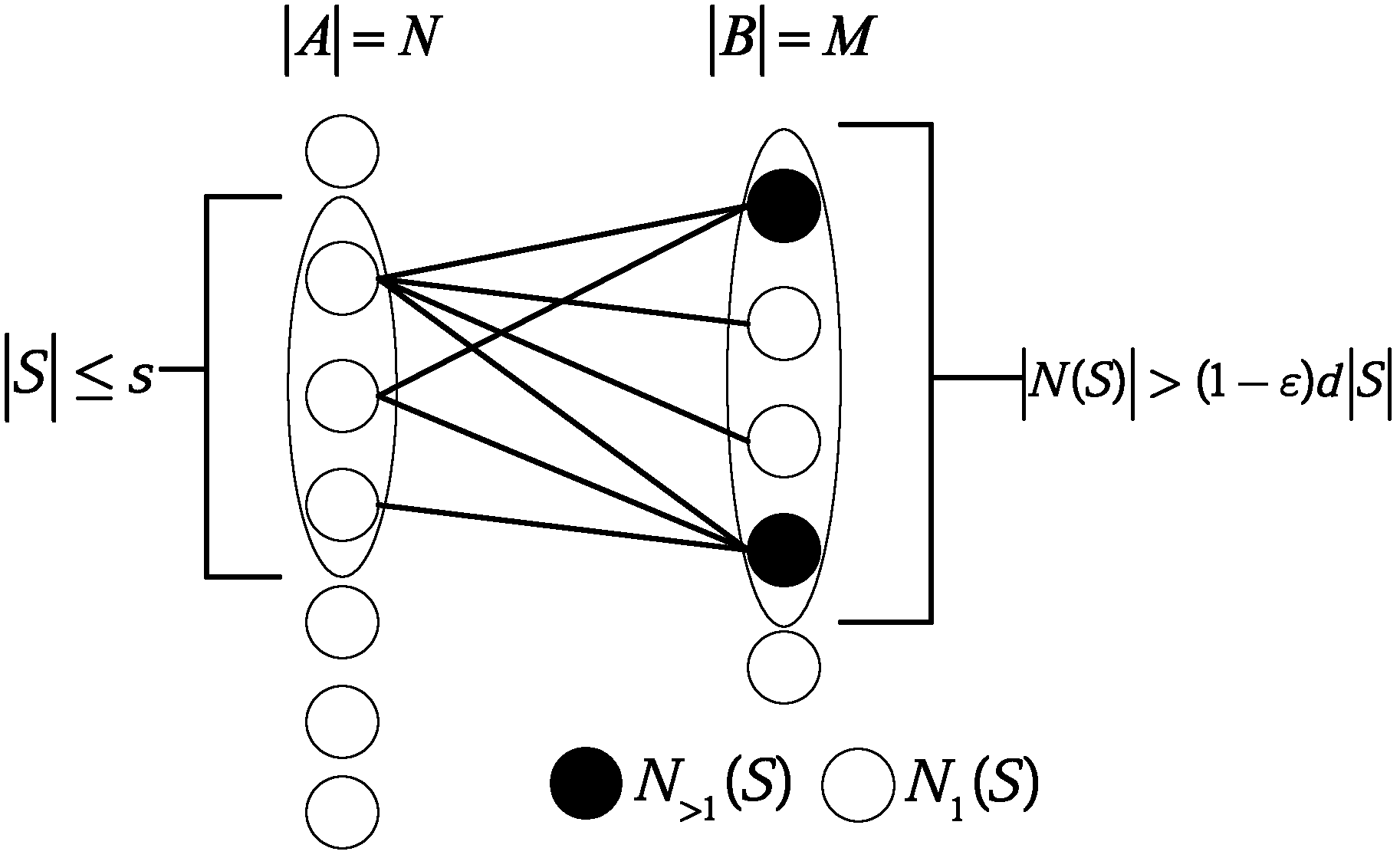
[0018] Step 1: Establish a bipartite graph G=(A, B), |A|=N, |B|=M, the number of left vertices in the left sub-graph corresponds to the number N of wireless sensor nodes, and the number of wireless sensor nodes in the right sub-graph The number of right vertices corresponds to the number of compressed sensing measurements M;
[0019] Step 2: Fix a finite field Then the left subgraph of the bipartite graph is a finite field defined in The set of polynomials whose upper degree does not exceed n-1 Each polynomial corresponds to a vertex of the left subgraph, so the number of vertices on the left is N=q n , the right subgraph is defined in The set of polynomials whose upper degree does not exceed m Each polynomial corresponds to a vertex of the right subgraph, so the number of vertices on the right is M=q m+1 ;in, A finit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com