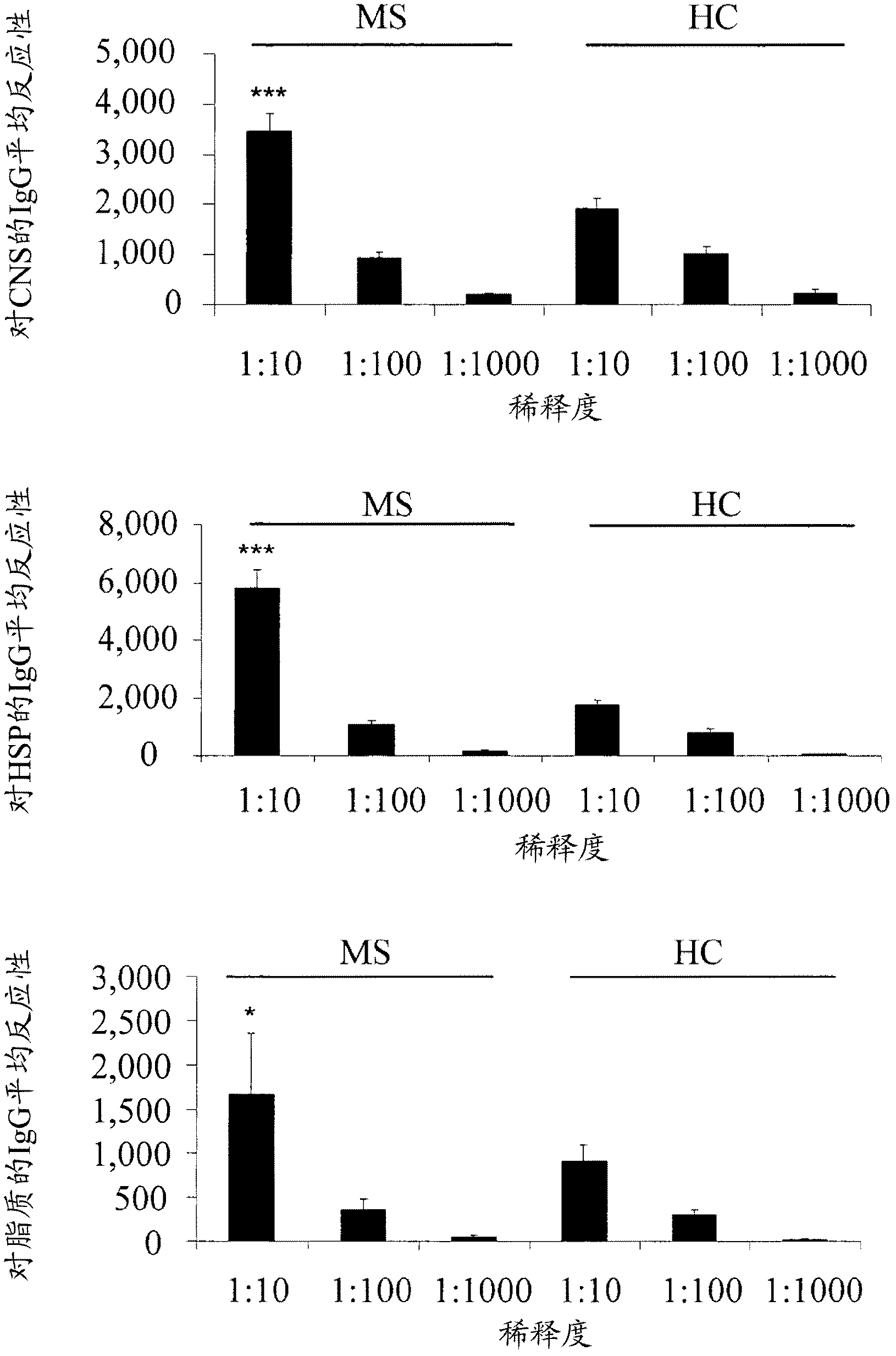Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0220] Conditions for detection of specific microarray autoantibodies in MS
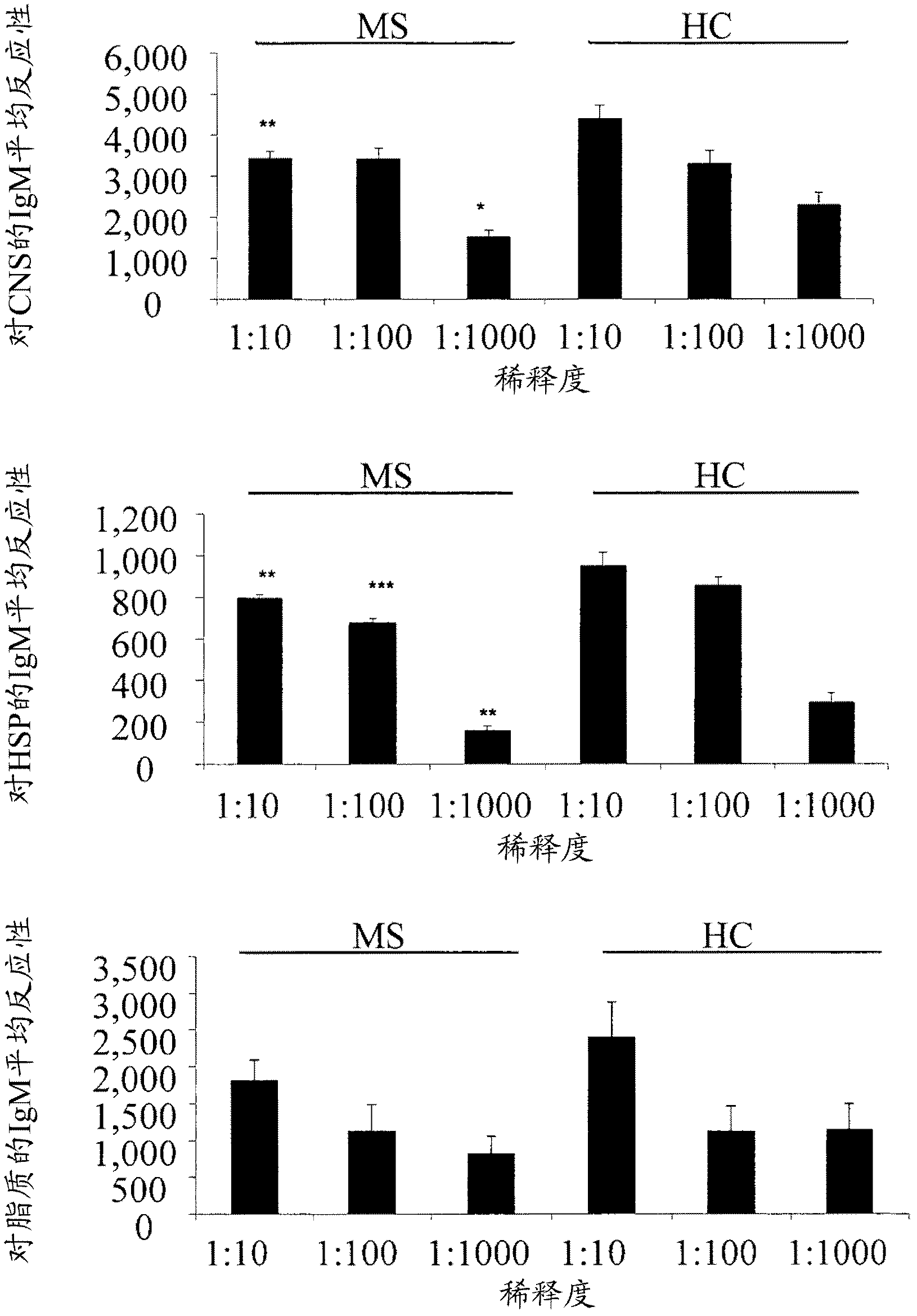
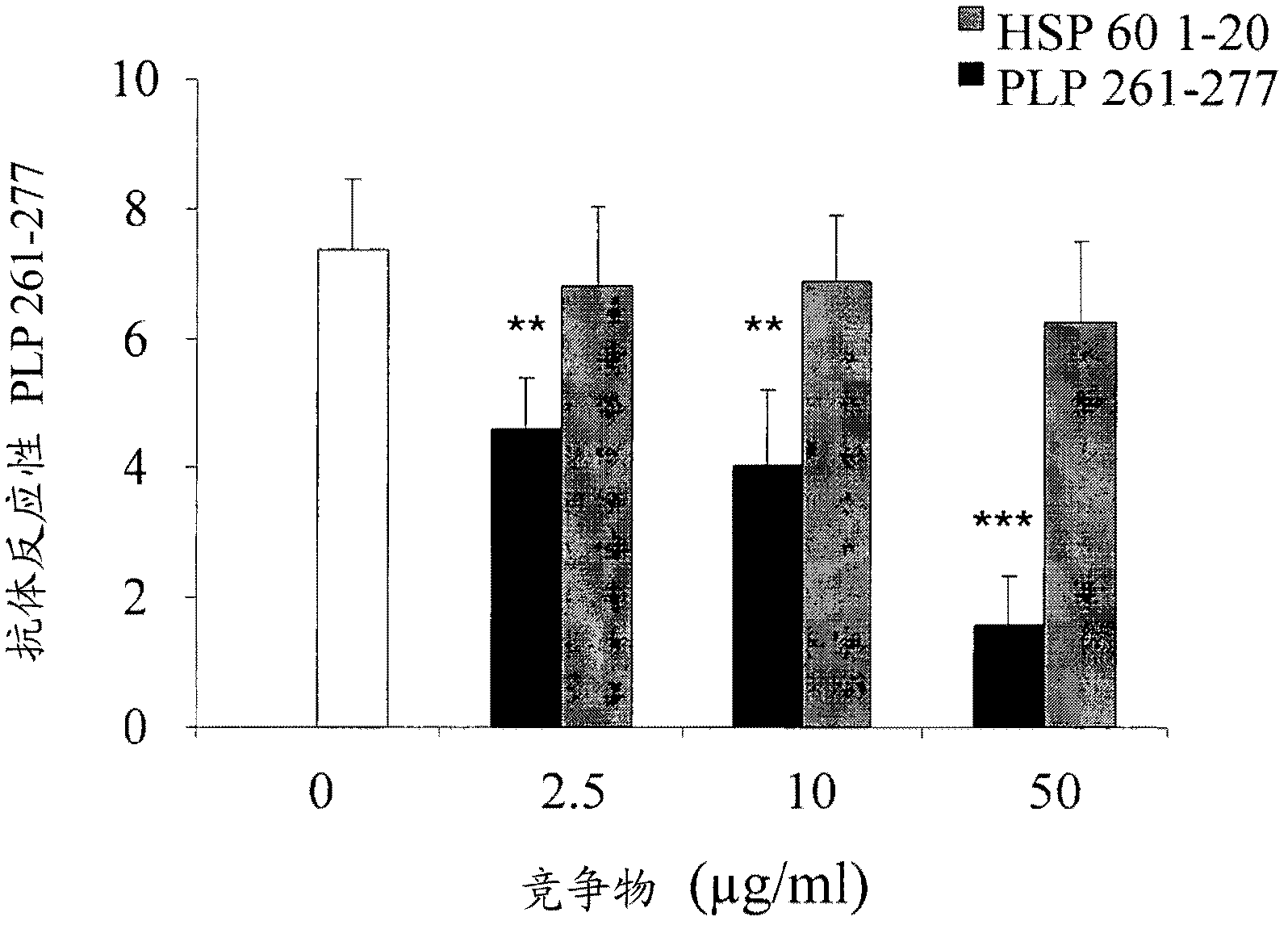
[0221] Antigen microarrays were constructed using 362 myelin and inflammation-related antigens (listed herein above), including CNS antigens suspected to be associated with MS, CNS antigens suspected to be associated with other neurological diseases, and heat shock proteins (HSPs). Antigens were spotted on epoxy glass slides using a robotic arrayer as previously described (Quintana et al., 2004).
[0222] The sensitivity of the antigen microarray technique was compared to that of a standard ELISA technique using commercially available monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against CNS, HSP and lipid antigens. Antigen microarray in log 10 Antigen reactivity was detected by dilution, which was 1-2 log greater than the reactivity detected by using the ELISA method (Table 7). Thus, antigen microarrays appear to be more sensitive than standard ELISA assays.
[0223] Table 7 - Comparison of Antigen Microa...
Embodiment 2
[0229] Autoantibody pattern analysis identifies immune signature markers of RRMS
[0230] To investigate whether unique antibody signatures in RRMS could be identified, the antibody repertoire was studied in 38 patients with RRMS and 30 healthy control (HC) subjects. Samples were assigned to a training set (24 RRMS and 20 controls) and a randomly selected test set (14 RRMS and 10 controls). The training set was used to determine whether patterns of antibody reactivity that could distinguish RRMS from control samples could be identified. If these patterns are found, they are validated against the test set. The training set was analyzed using the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test; the false discovery rate was controlled using the method of Benjamini and Hochberg (Cohen, I.R., 2007, Nat Rev Immunol. 7, 569-74). In Table 6 the clinical characteristics of the patients and HCs are listed.
[0231] Such as Figure 2A As shown in the heatmap in , a reactivity pattern was identified that ...
Embodiment 3
[0237] Autoantibody pattern analysis identifies immune signature markers of PPMS
[0238]PPMS has a different clinical course than RRMS, and it has been suggested that PPMS may involve different disease mechanisms than RRMS (Miller & Leary, 2007, Lancet Neurol. 6, 903-12). 24 PPMS and 25 age- and gender-matched HCs in the training set, and 13 PPMS and 12 controls in the test set samples were studied.
[0239] Figure 2B Antibody reactivity included in the heatmap shown is listed here (in the same order as in the heatmap, i.e. top to bottom): IgM_PLP 215-232; IgG_PLP 215-232; IgM_mMBP; IgG_HSP70 195-214; IgM_smLPS; IgM_HSP70 210-229; IgM_chondroitin sulfate 4; IgG_HSP70166-185; IgG_Bovine MBP; IgM_Bovine MBP; IgG_PLP 137-150; 20; IgG_MOG 16-35; IgG_P2 76-95; IgM_neurofilament 68kDa; IgG_MOG 151-170; IgG_P21-20; IgG_OSP 61-80; IgM_secreted APPα; IgG_PLP 178-191; IgM_gpMBP; IgG_HSP70 16-35; 121-140; IgM_MOBP 61-80; and IgG_OSP 1-20.
[0240] Heatmap ( Figure 2B ) shows tha...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| composition ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com