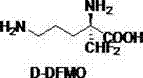
Chemical-enzyme method for preparing D-basic amino acid hydrochloride
A technology of amino acid hydrochloride and amino acid, which is applied in the chemical-enzymatic field of preparing D-basic amino acid hydrochloride, can solve the problems of low resolution yield, low optical purity of D-lysine, and resolution conditions Difficult to control and other issues to achieve high optical activity and reduce process costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
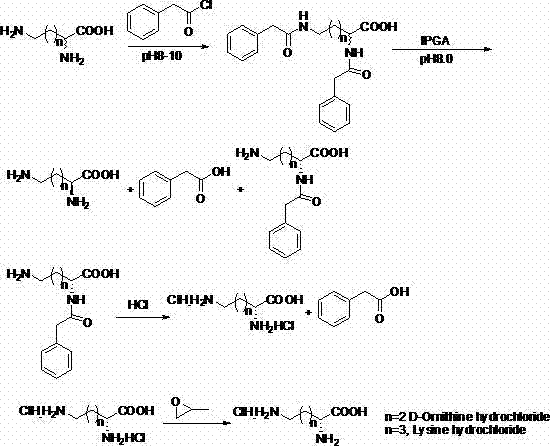
[0023] Example 1 : Preparation of DL-2, 5-N-diphenylacetylornithine
[0024] Add 52.9g (0.4mol) DL-ornithine and 40g NaOH (1.0mol) into 1000ml water, stir to dissolve. 128ml (0.97mol) of phenylacetyl chloride was added dropwise under ice bath conditions. After the dropwise addition was completed, the reaction was carried out overnight. Cool in an ice bath to 5°C, filter with suction, wash the solid with a small amount of deionized water, and dry to obtain 135.6 g of DL-2, 5-N-diphenylacetylornithine with a yield of 92%.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: DL-2, 5-N-diphenylacetylornithinase-catalyzed hydrolysis
[0026] Add 110.5g (0.3mol) of DL-2, 5-N-diphenylacetylornithine into 1000ml of water, and adjust the pH to 8.0 with ammonia water. 44 g of immobilized penicillin acylase was added, and the reaction was stirred at 30° C. for 24 h. Suction filtration to remove immobilized penicillin acylase. The filtrate was adjusted to pH 1-2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid, filtered with suction, the solid was washed with cold water, and dried to obtain 31.5 g of D-α-N-phenylacetylornithine with a yield of 42%.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: Preparation of D-ornithine hydrochloride
[0028] Dissolve 31.5g D-α-N-phenylacetylornithine in 200mL 6 mol / L concentrated hydrochloric acid, hydrolyze at 90°C for 12h, extract three times with ethyl acetate (200ml×3), evaporate the water layer to dryness under reduced pressure, add Dissolve the solid in 100ml of absolute ethanol, then add 100ml of propylene oxide, filter with suction, wash the solid with a small amount of ethanol, and dry to obtain 19.1g of D-ornithine hydrochloride, with a yield of 90%. The ee measured by HPLC is 99.6%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com