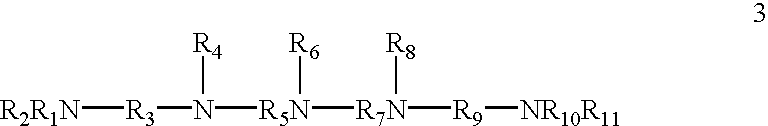
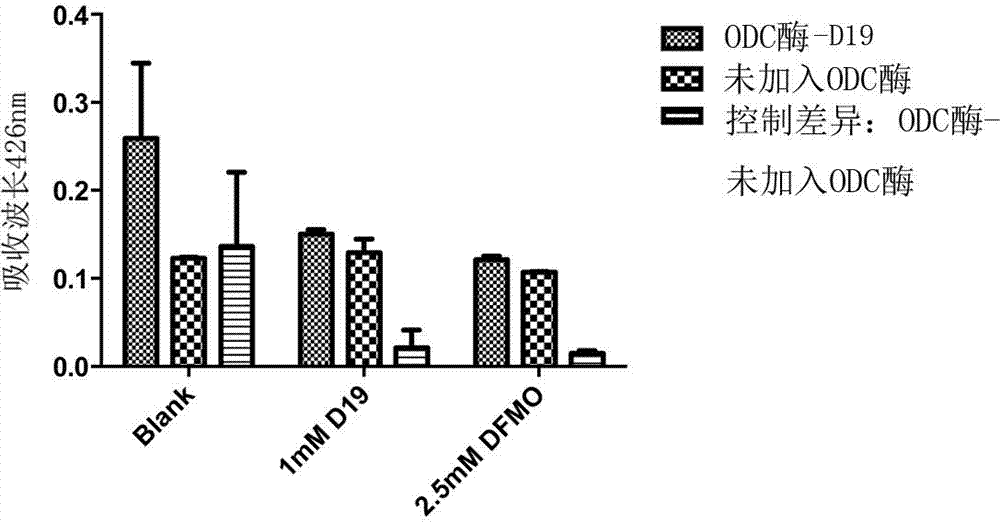
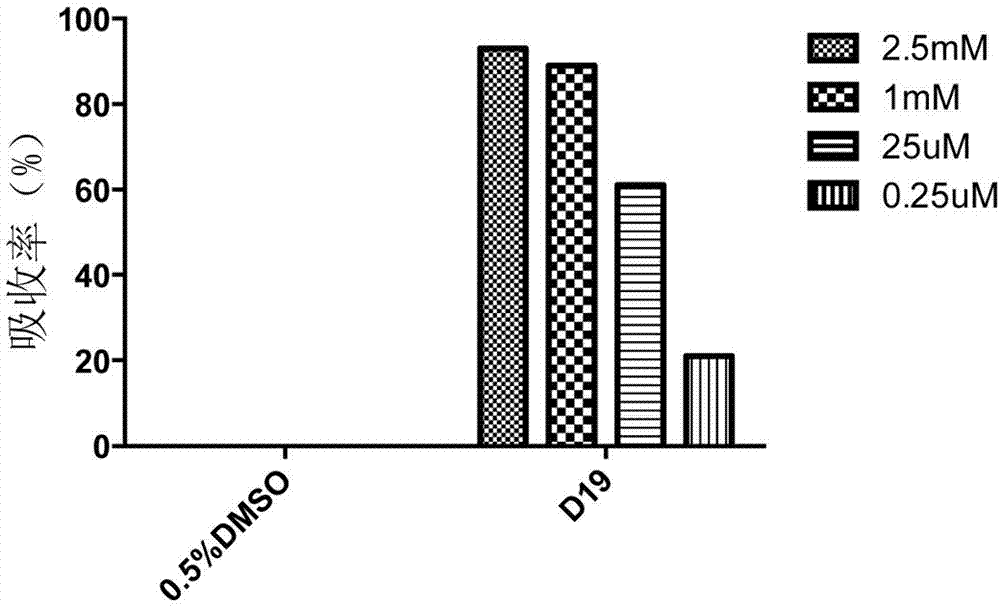
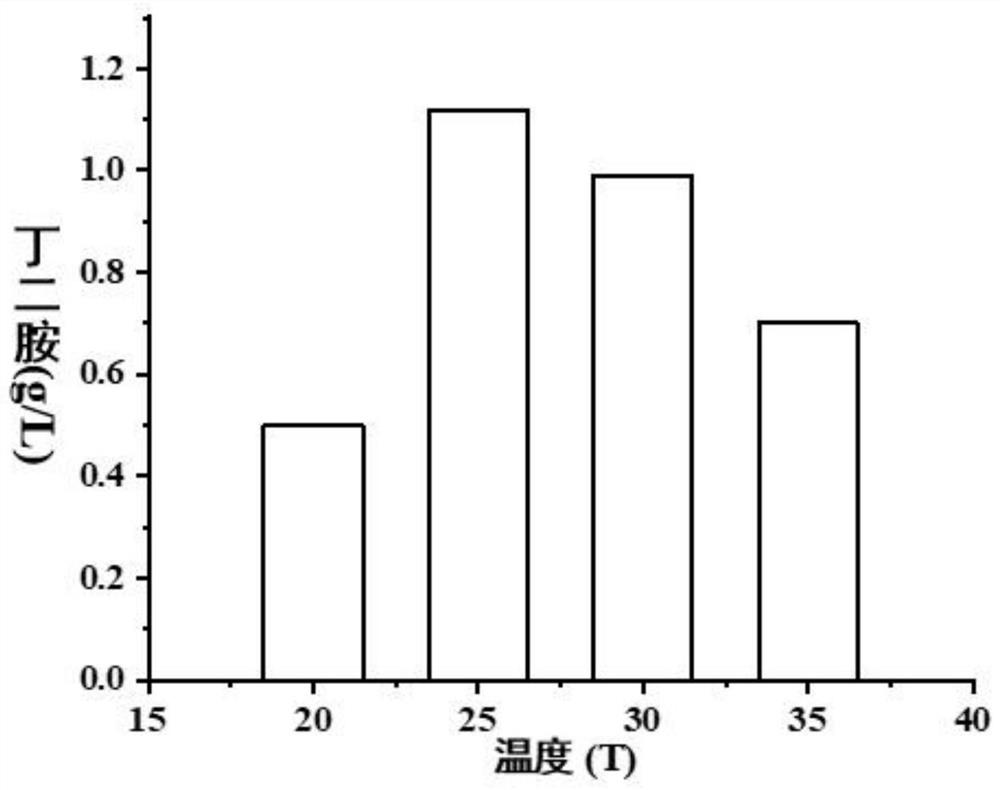
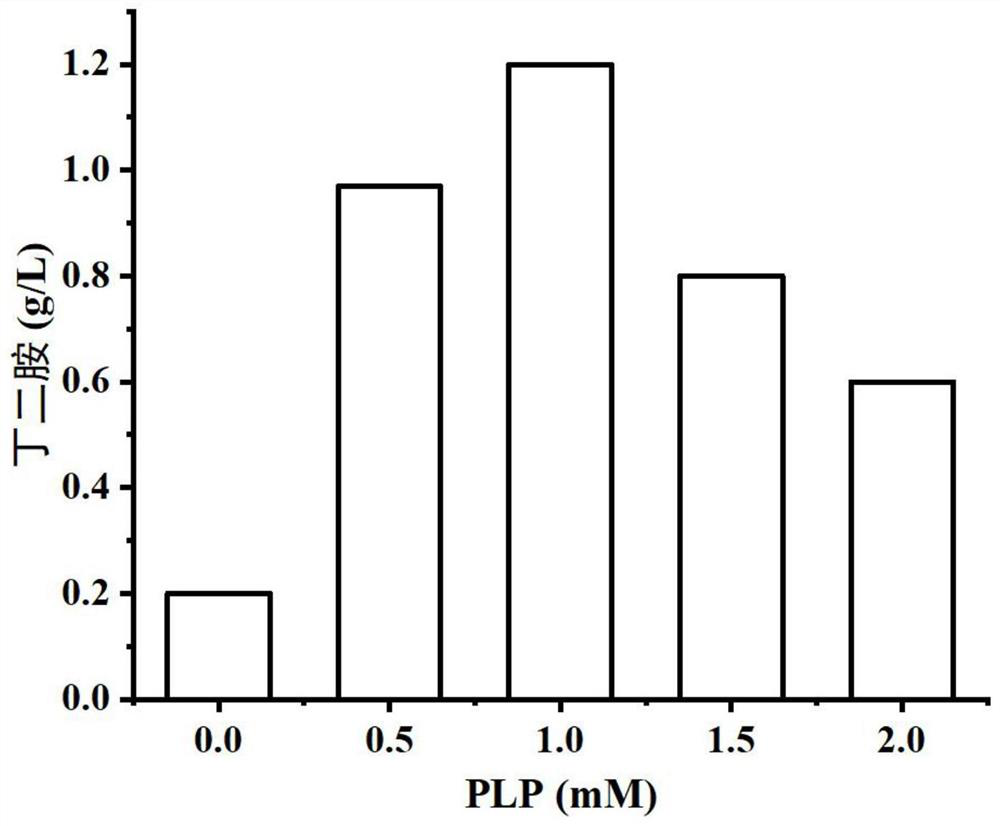
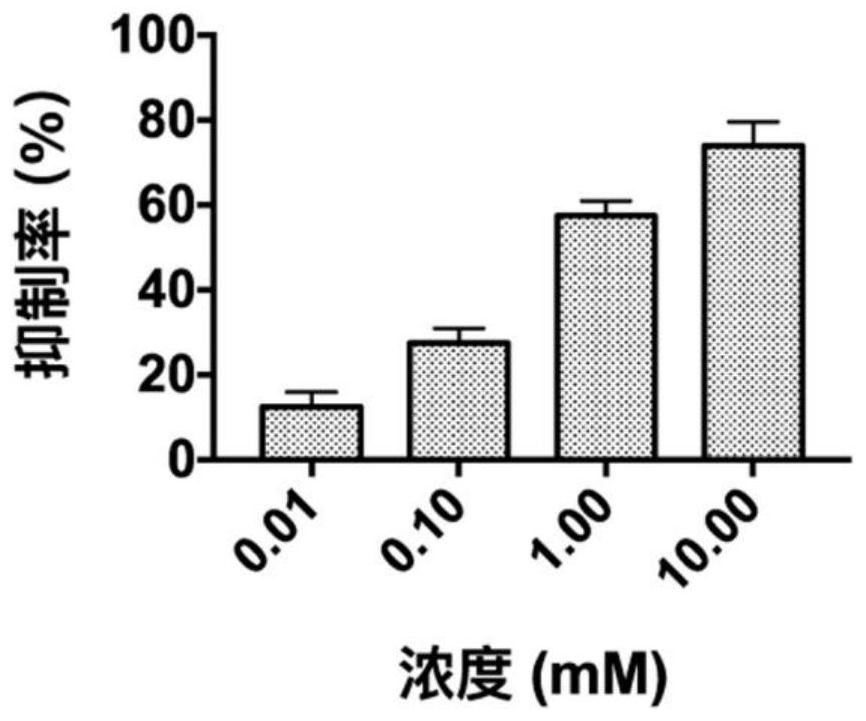
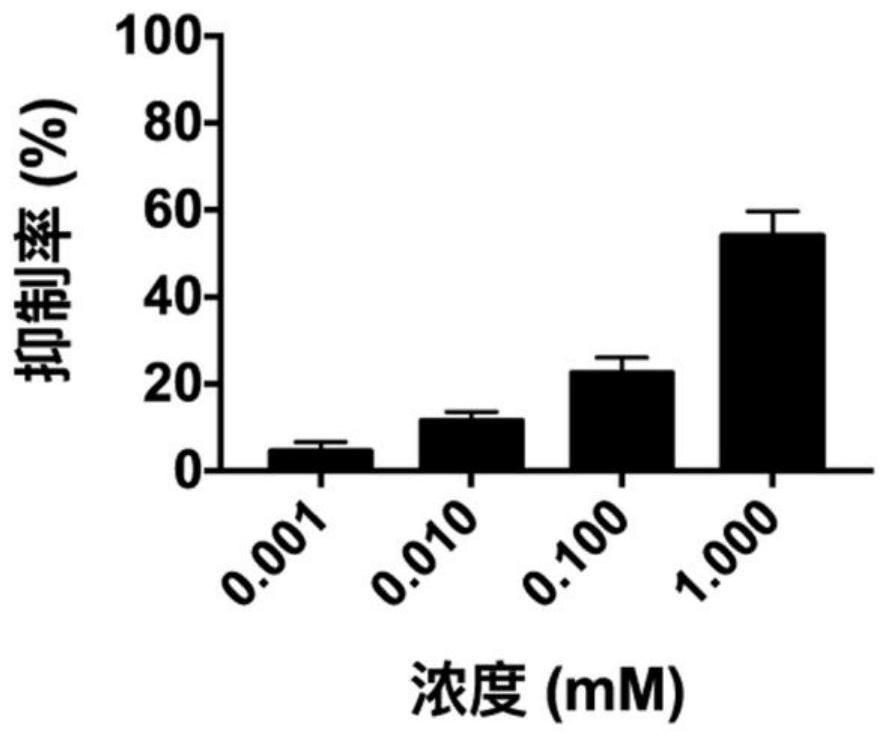
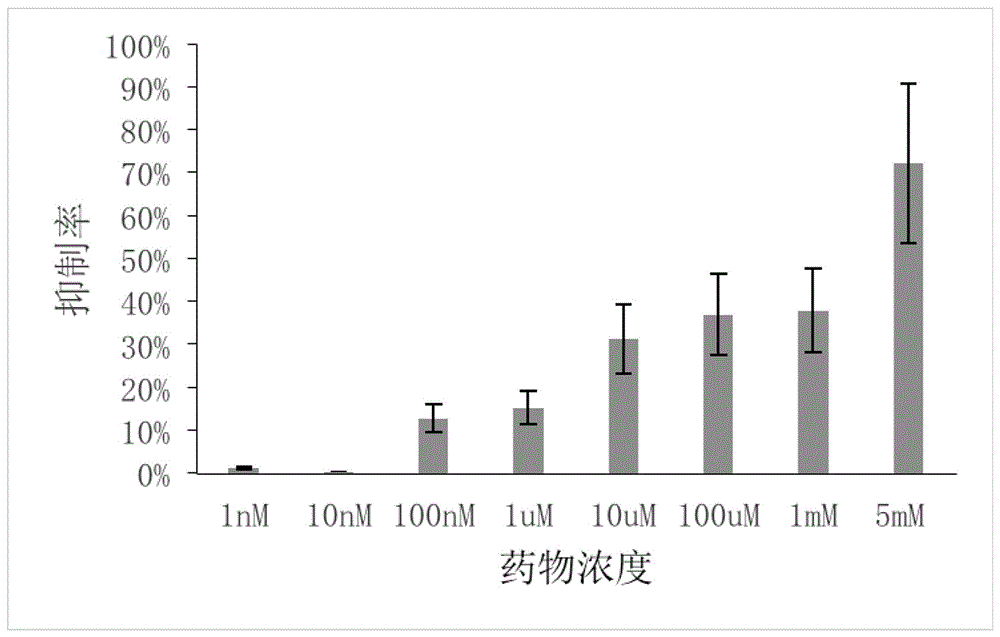
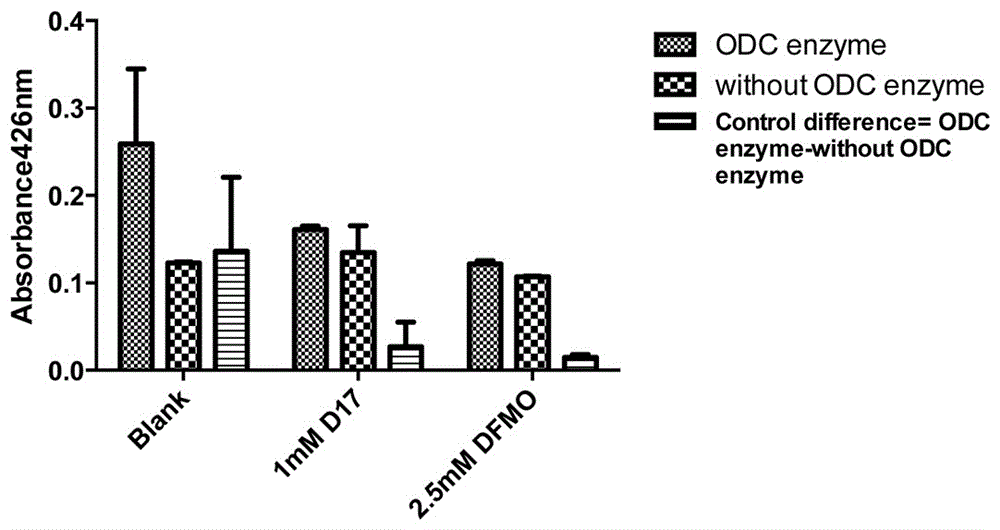
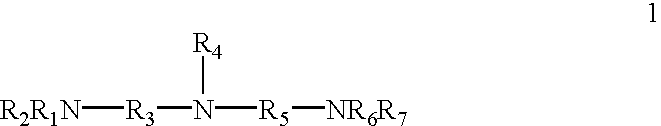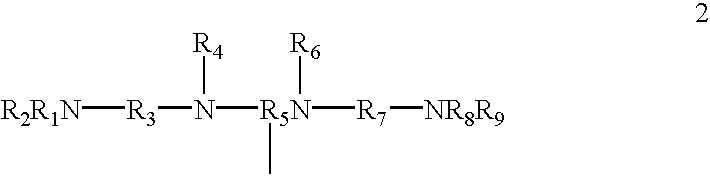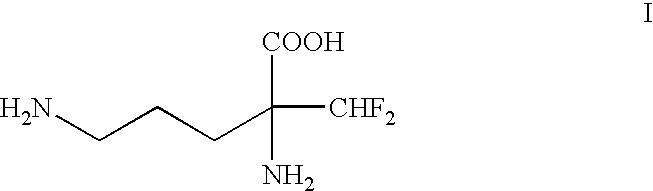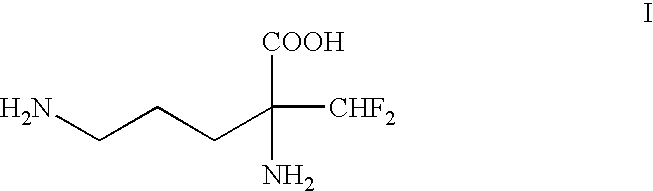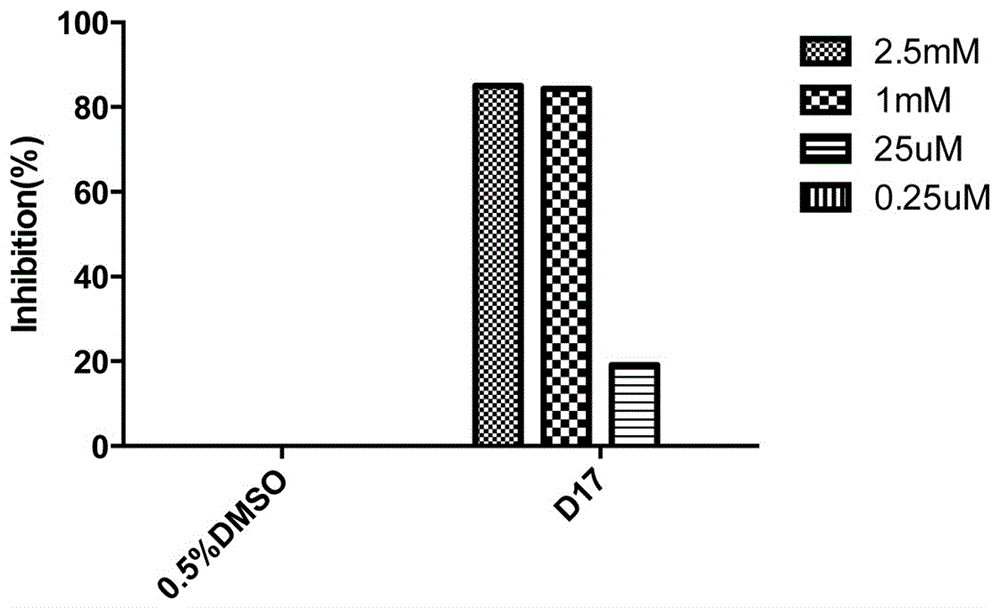Patents
Literature
43 results about "Ornithine decarboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
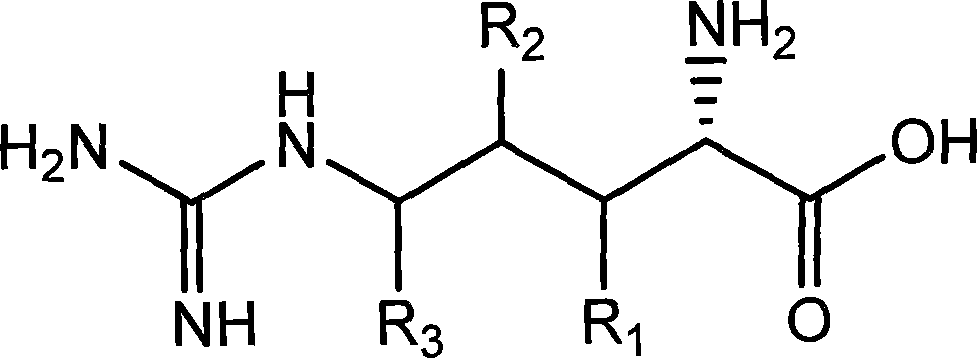
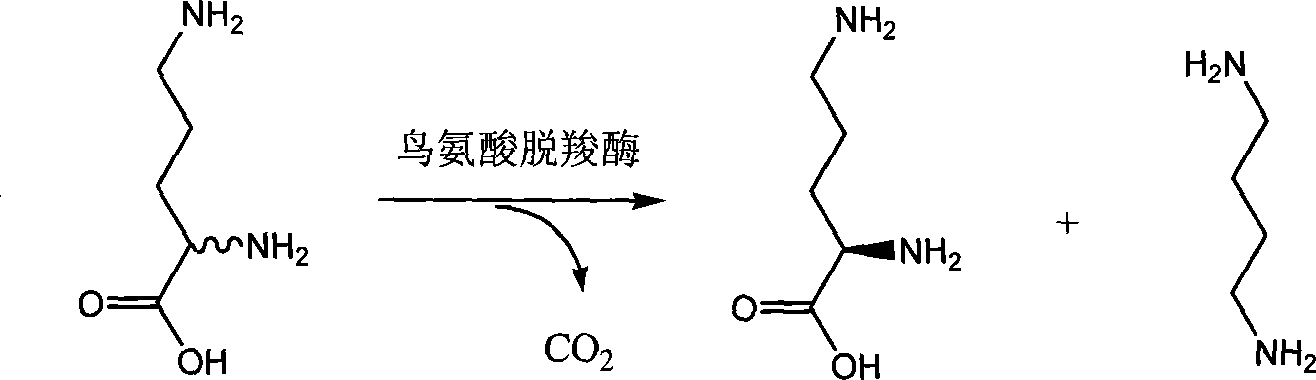
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer.
Treatment of neurodegenerative disorders through the modulation of the polyamine pathway
InactiveUS20030158262A1Extend your lifeSlow and arrest progressCompound screeningBiocidePharmacometricsNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention provides methods and compositions for modulating polyamine pathway activity as a means for ameliorating neurodegenarative disorders. In particular, for ameliorating the symptoms or onset of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) by modulating the gene and protein products involved the polyamine pathway, such as by inhibiting the enzyme, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), involved in the synthesis of the polyamine, putrescine. Compositions and methods are disclosed for inhibiting the polyamine pathway producing lower polyamine levels resulting in a beneficial effect on ALS. This can be accomplished by using modulating agents such as analogs, or polyamine analogs, and antiproliferative drugs. Screening assays for pharmacological agents that are capable of decreasing polyamine levels and / or reducing cell proliferation are also disclosed.
Owner:ALS THERAPY DEV FOUND INC
Nucleotide sequences coding for cis-aconitic decarboxylase and use thereof
InactiveUS20110099670A1Maximizing numberMinimize the numberFungiSugar derivativesNucleotidePlant cell
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences encoding polypeptides with cis-aconitic decarboxylase activity, the cells transformed with such nucleotide sequences, preferably fungal or plant cells, and to methods wherein such transformed cells are use for the production of itaconic acid.
Owner:KOOPS ANDRIES JURRIAAN +3
Microorganisms for producing putrescine and method for producing putrescine using same
ActiveUS20140004577A1Efficient productionMore effectiveBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismExtracellular
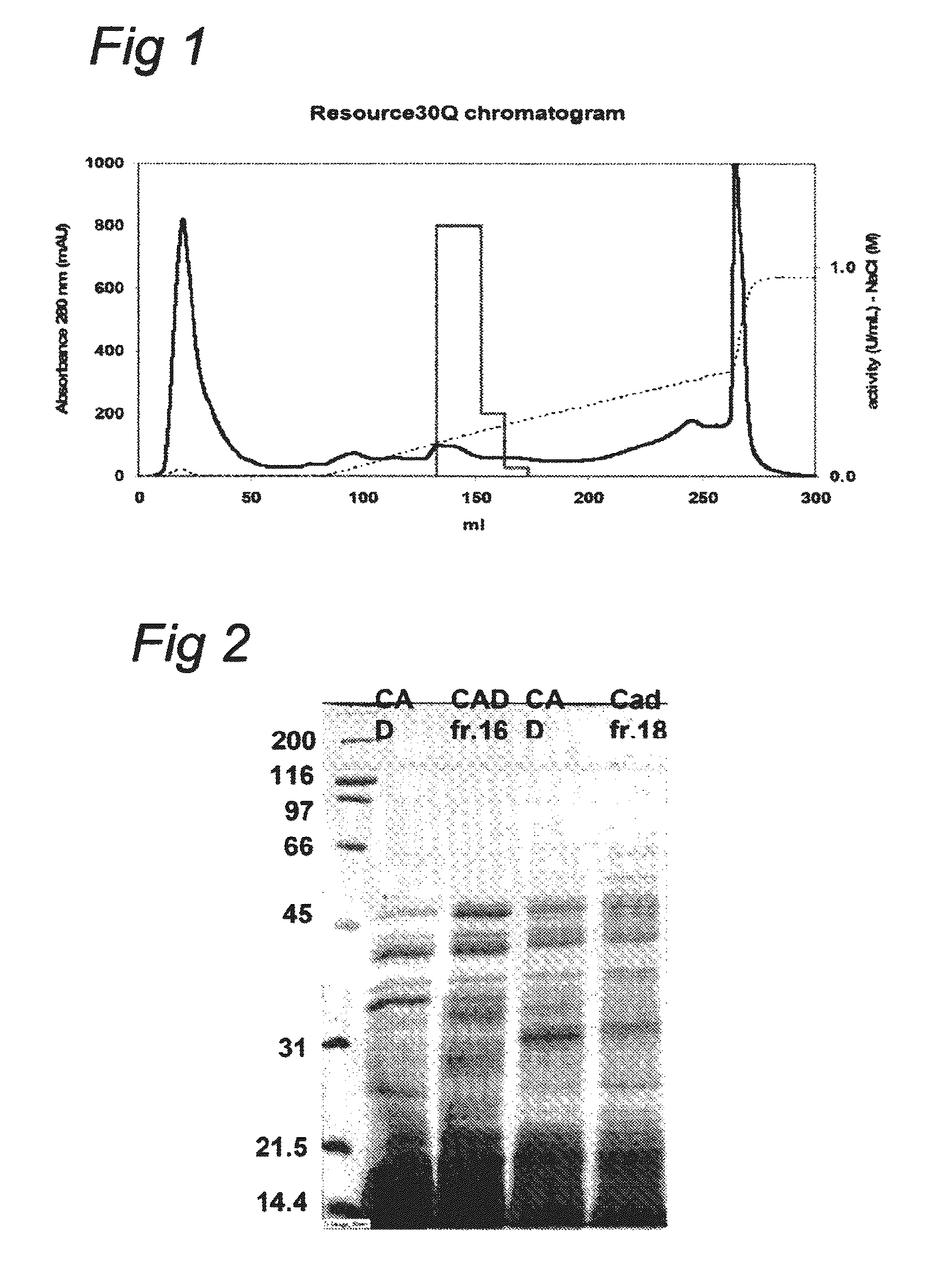
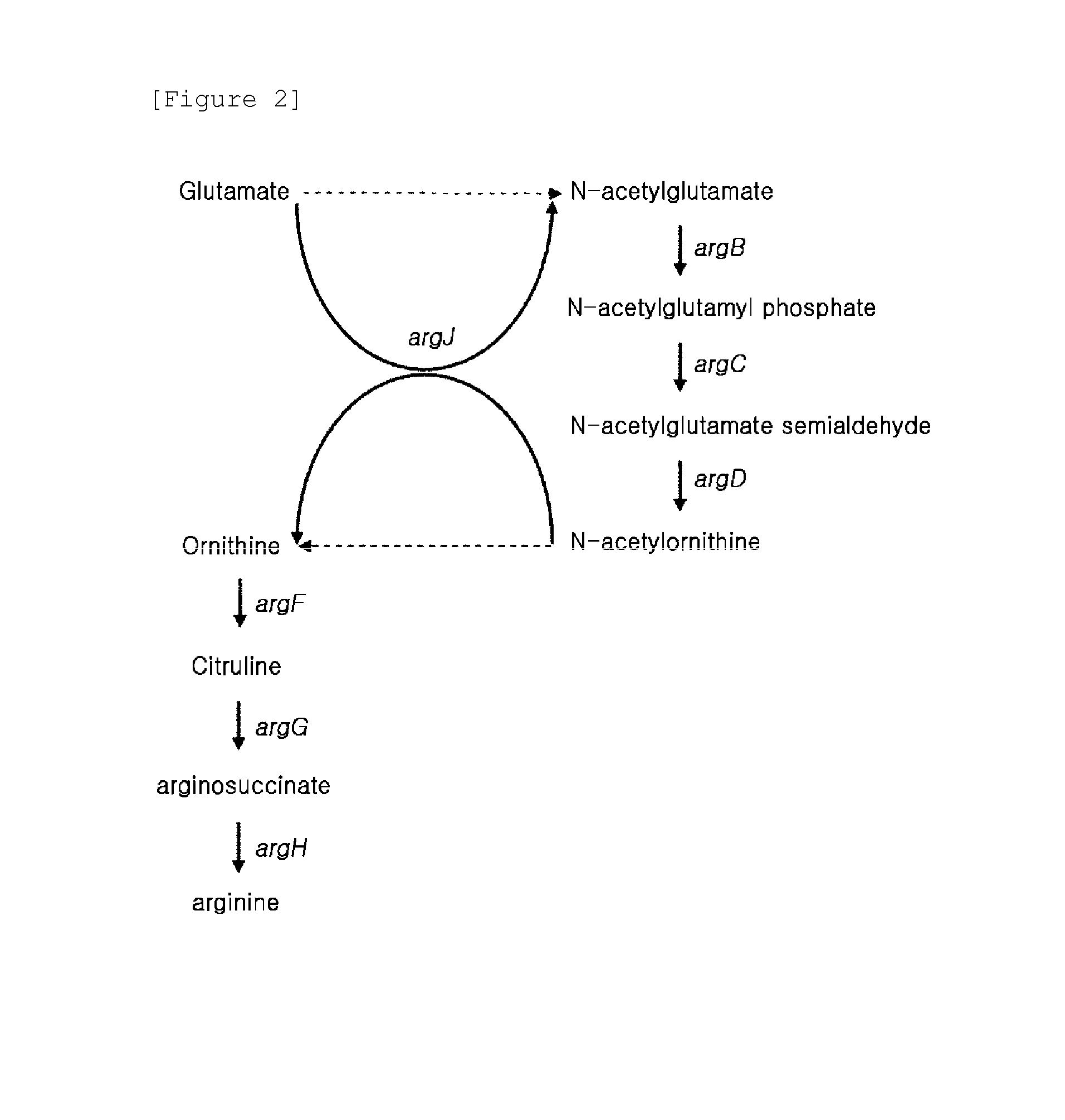
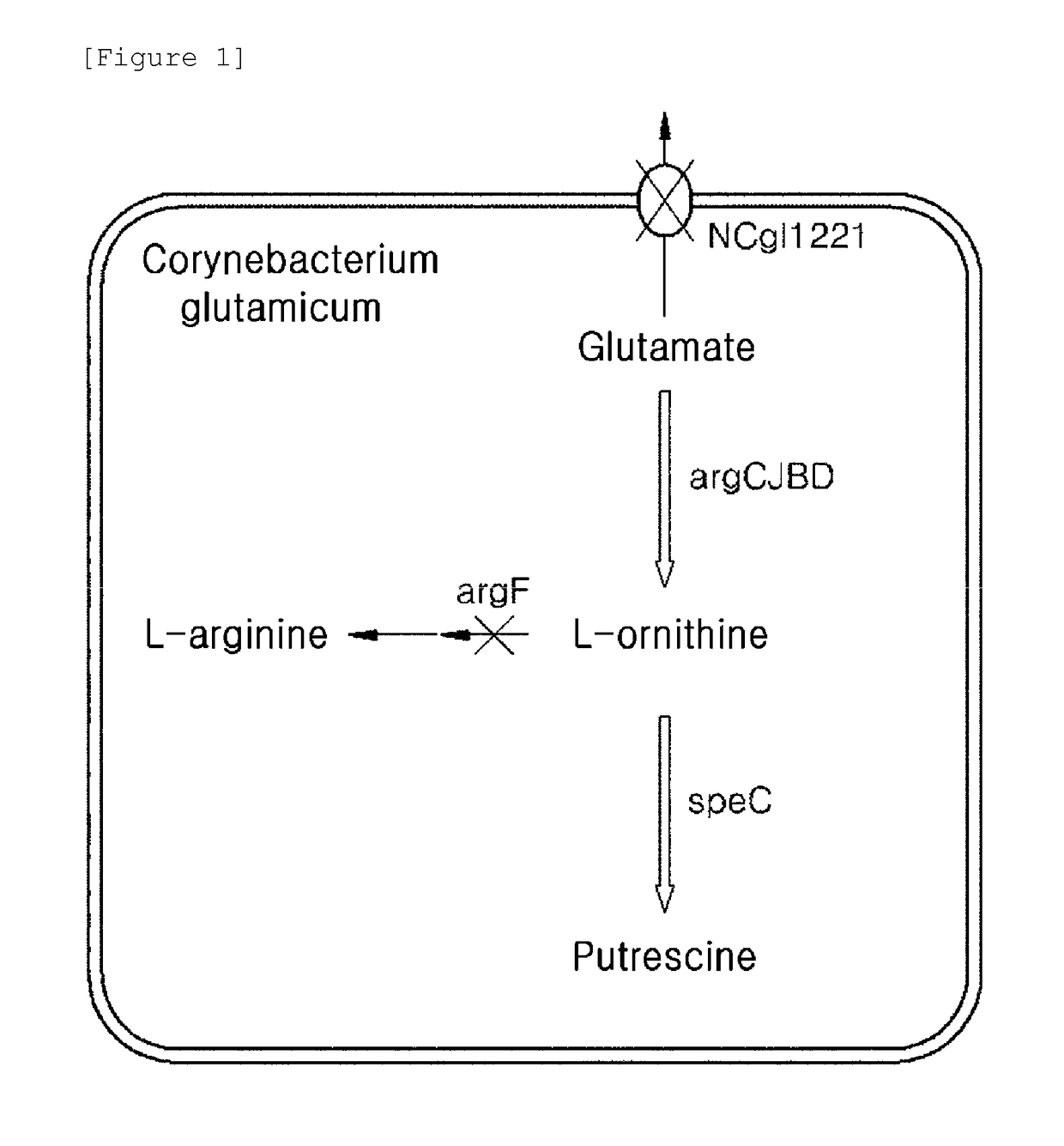
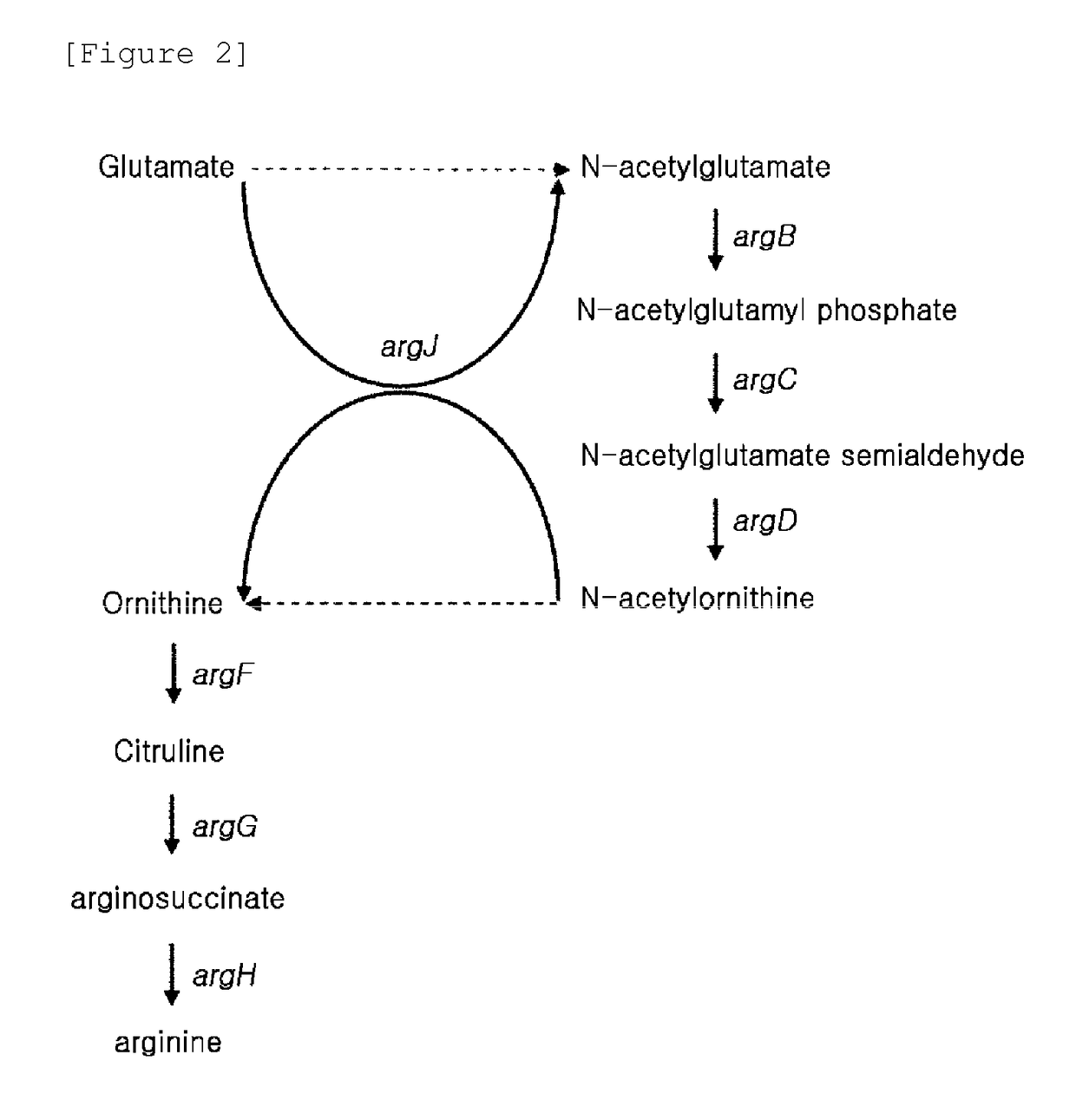
The present invention relates to a putrescine-producing microorganism and a method for producing putrescine using the same. To be more specific, the present invention is directed to a microorganism given the ability to produce putrescine which is generated by blocking a biosynthetic pathway from ornithine to arginine, increasing the intracellular level of glutamate, enhancing the biosynthetic pathway of ornithine from glutamate, and introducing extracellular ornithine decarboxylase; and a method for producing putrescine by using the microorganism.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
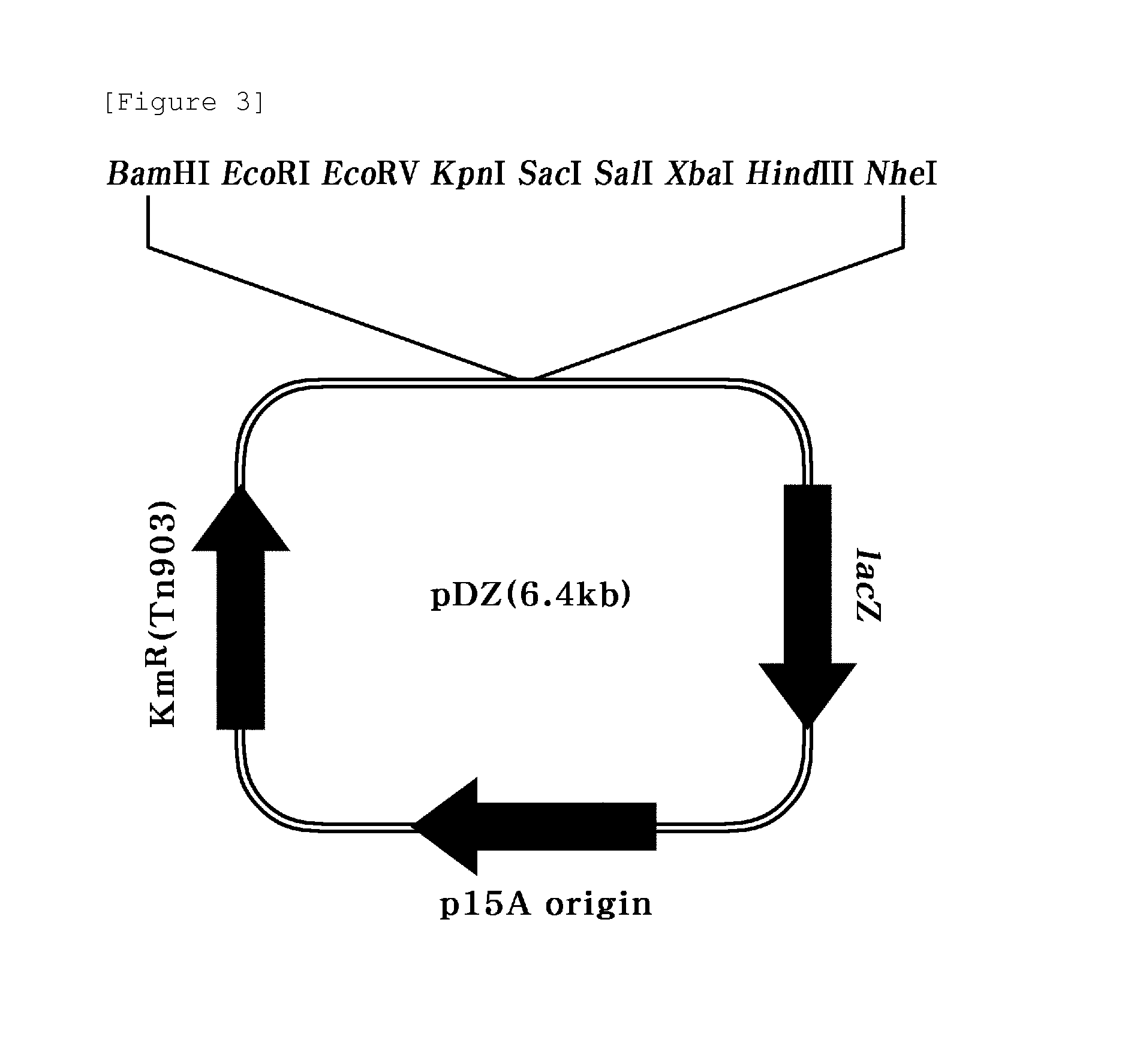
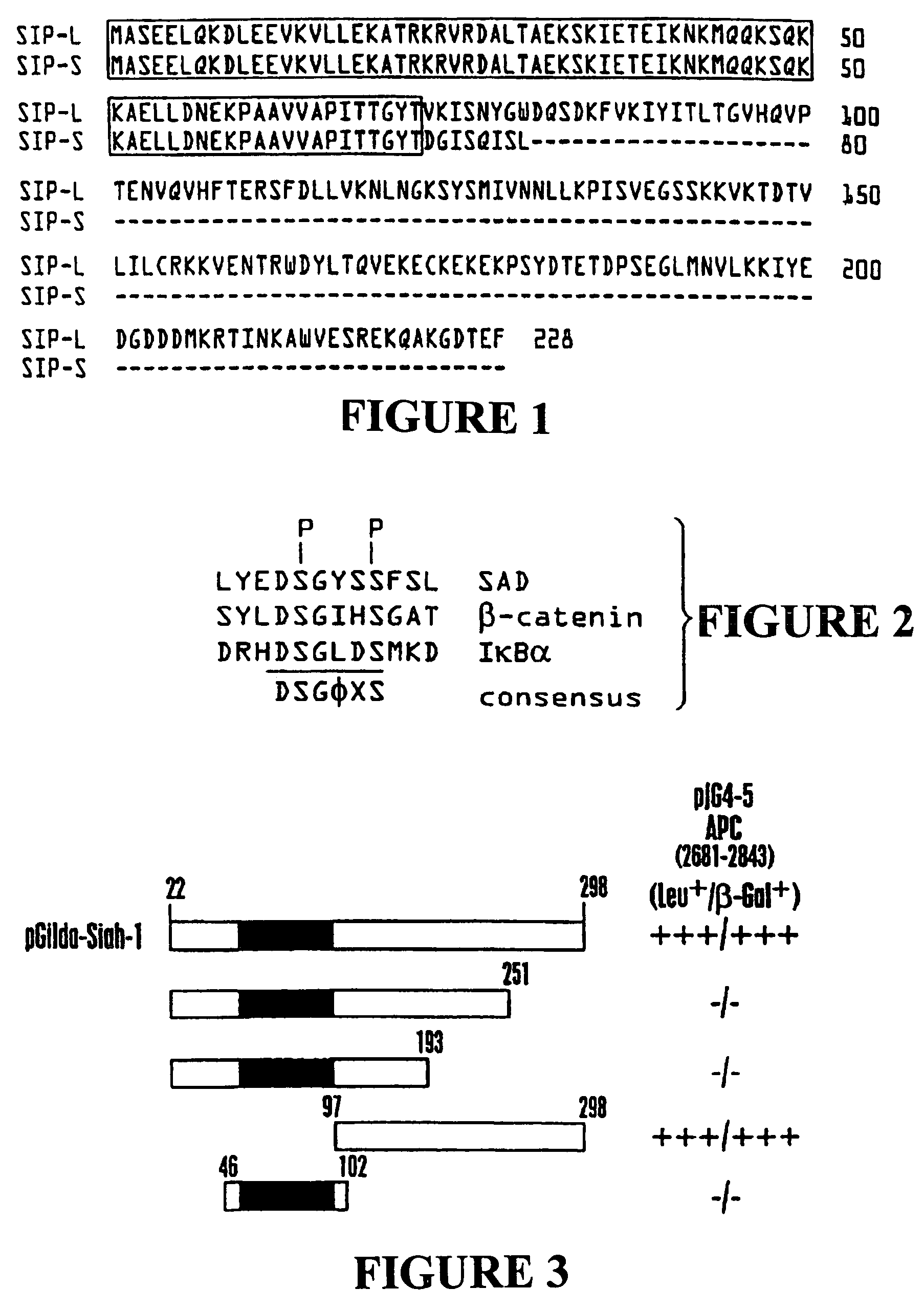
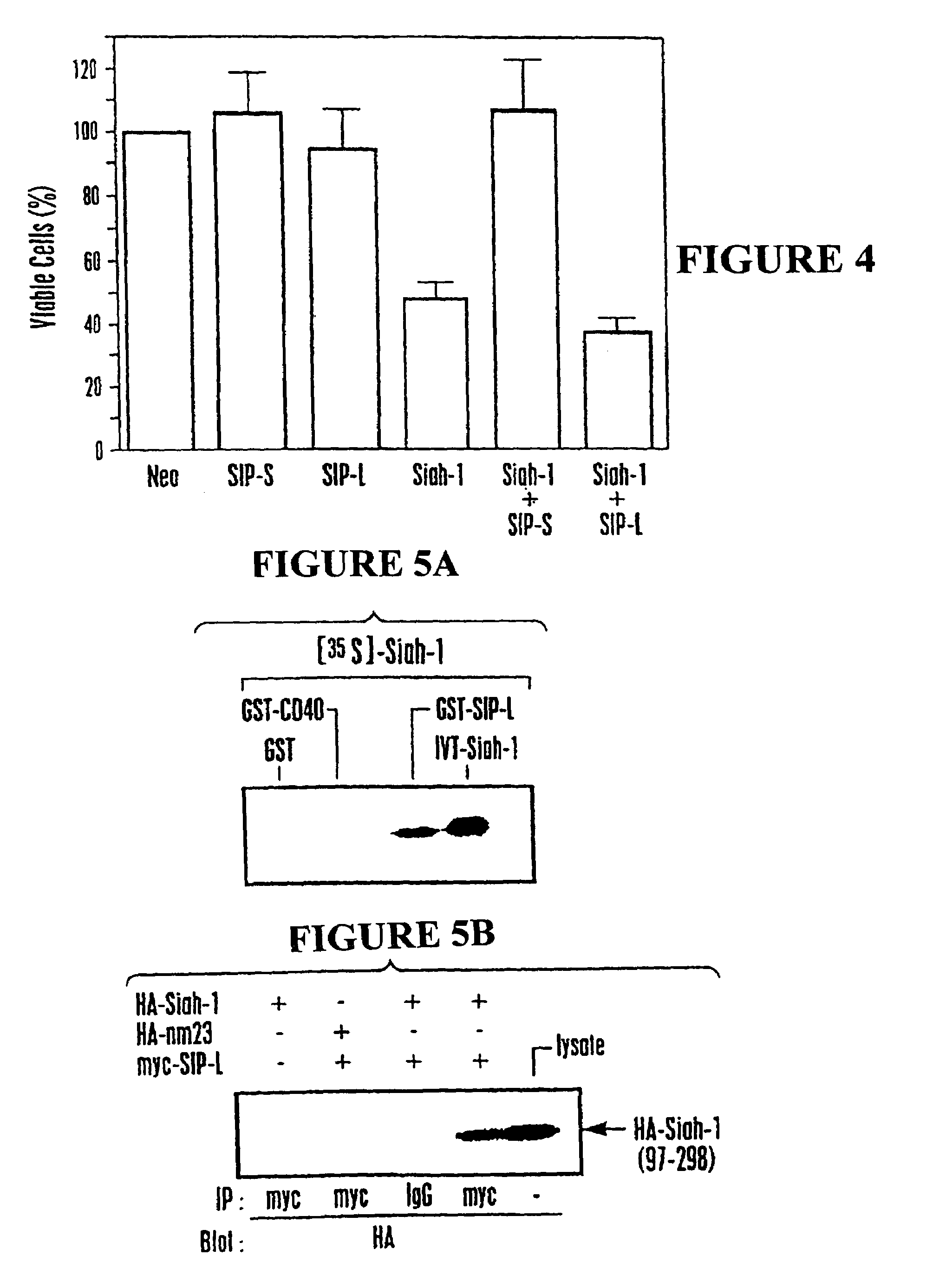
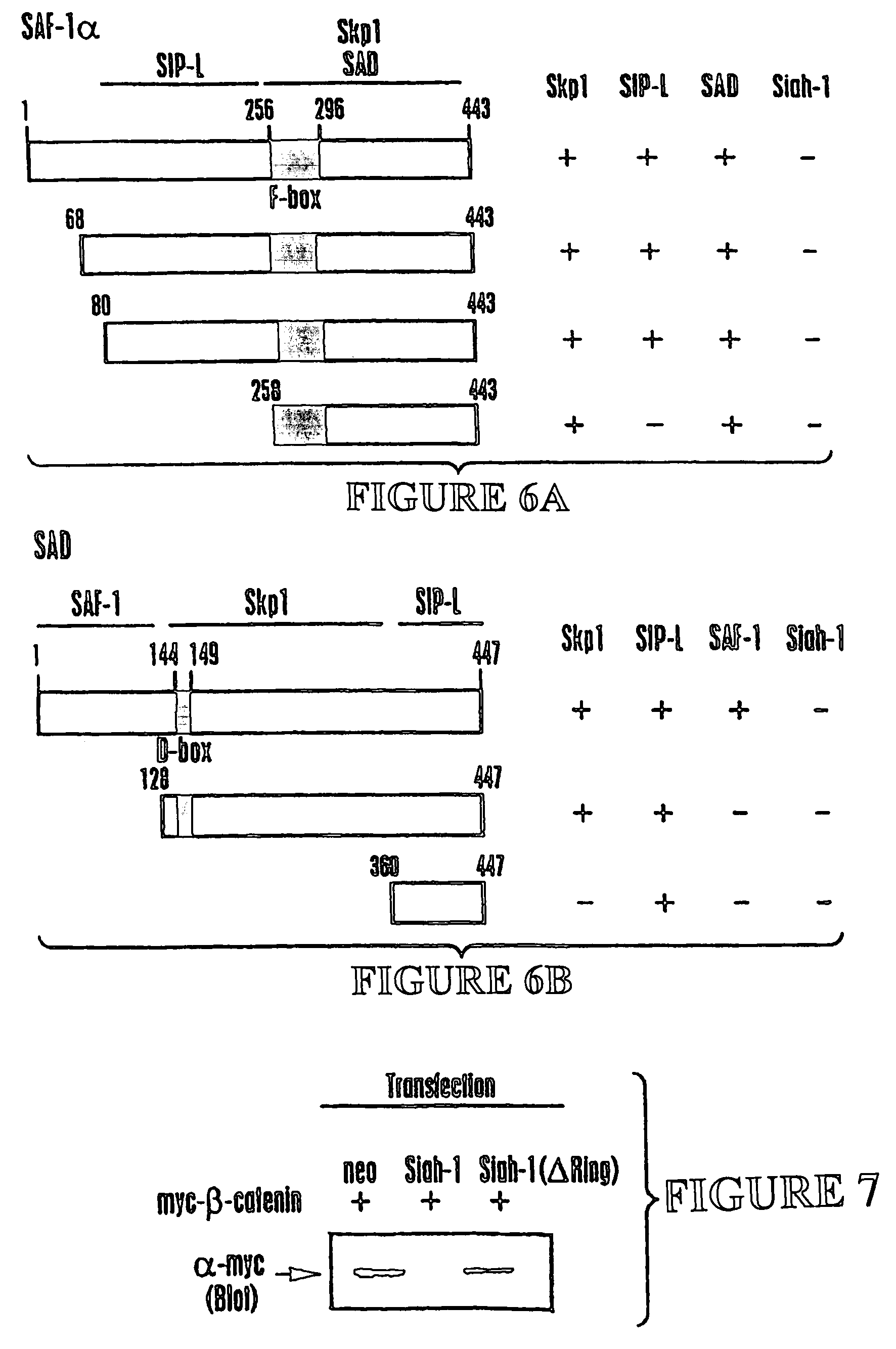
Nucleic acid encoding proteins involved in protein degradation, products and methods related thereof
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES THE
Small molecule inhibitor and application thereof to inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (ODC)
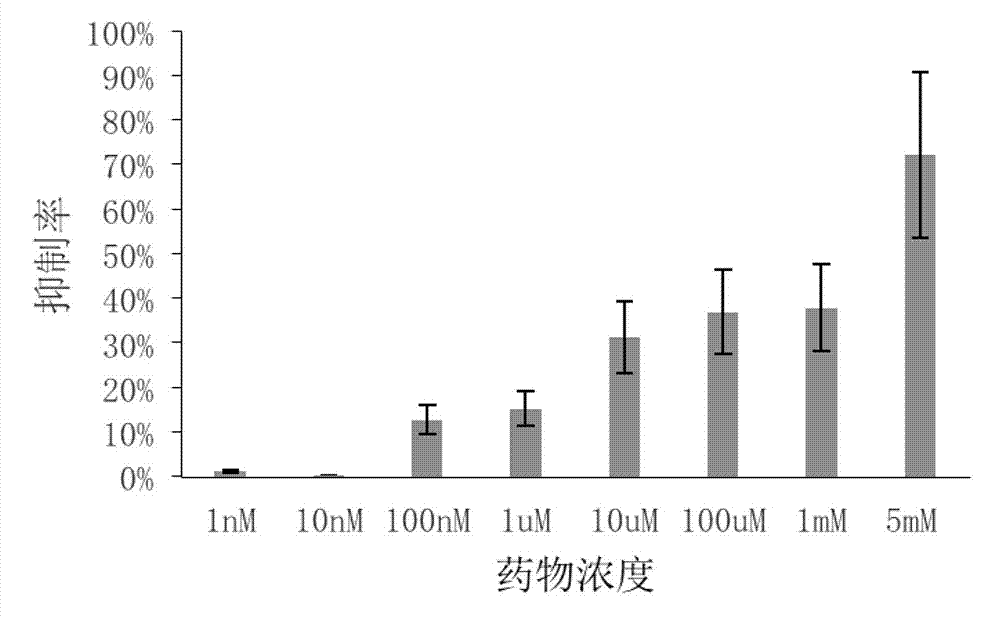
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and relates to a small molecule inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and an application thereof. A novel small molecule inhibitor aiming at ODC is found through computer-aided high-throughput medicine screening. Verification of the effects of the novel small molecule inhibitor finds that the novel small molecule inhibitor has good inhibiting effects on ODC and can be especially used for inhibiting human-derived ODC, preventing, treating and diagnosing tumor diseases and pathogenic microorganism infection and developing and preparing tumor medicines or medicines against pathogenic microorganism infection.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
High-level soluble expression method and application of recombined tyrosine decarboxylase
ActiveCN103421734AImprove expression levelEasy to purifyNervous disorderBacteriaEscherichia coliEngineered genetic
The invention relates to a high-level soluble expression method and application of recombined tyrosine decarboxylase, belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering, and relates genetically engineered strain E. coliBL21(DE3) / pET24-TDC for recombined expressed lactobacillus brevis tyrosine decarboxylase, a construction method of the genetically engineered strain, a high-level soluble expression method for the TDC and application of the TDC. A TDC encoding gene is connected to an expression vector and passed to an escherichia coli expression host; glucose is added to fermentation medium; accordingly, soluble expression of the recombined TDC (rTDC) can be increased significantly, protein yield is up to 224mg / L from fermentation broth. The rTDC with His-Tag at the Ni column purified C-end is used, so that the recovery rate is 90%. The rTDC has 133.5U / mg specific enzyme activity against substrate L-tyrosine. The soluble expression method of the rTDC has the advantages of high expression level, purification simplicity, high recovery rate, low cost and the like and can be applied to the preparation of tyramine and dopamine and the treatment study on Parkinson's disease.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
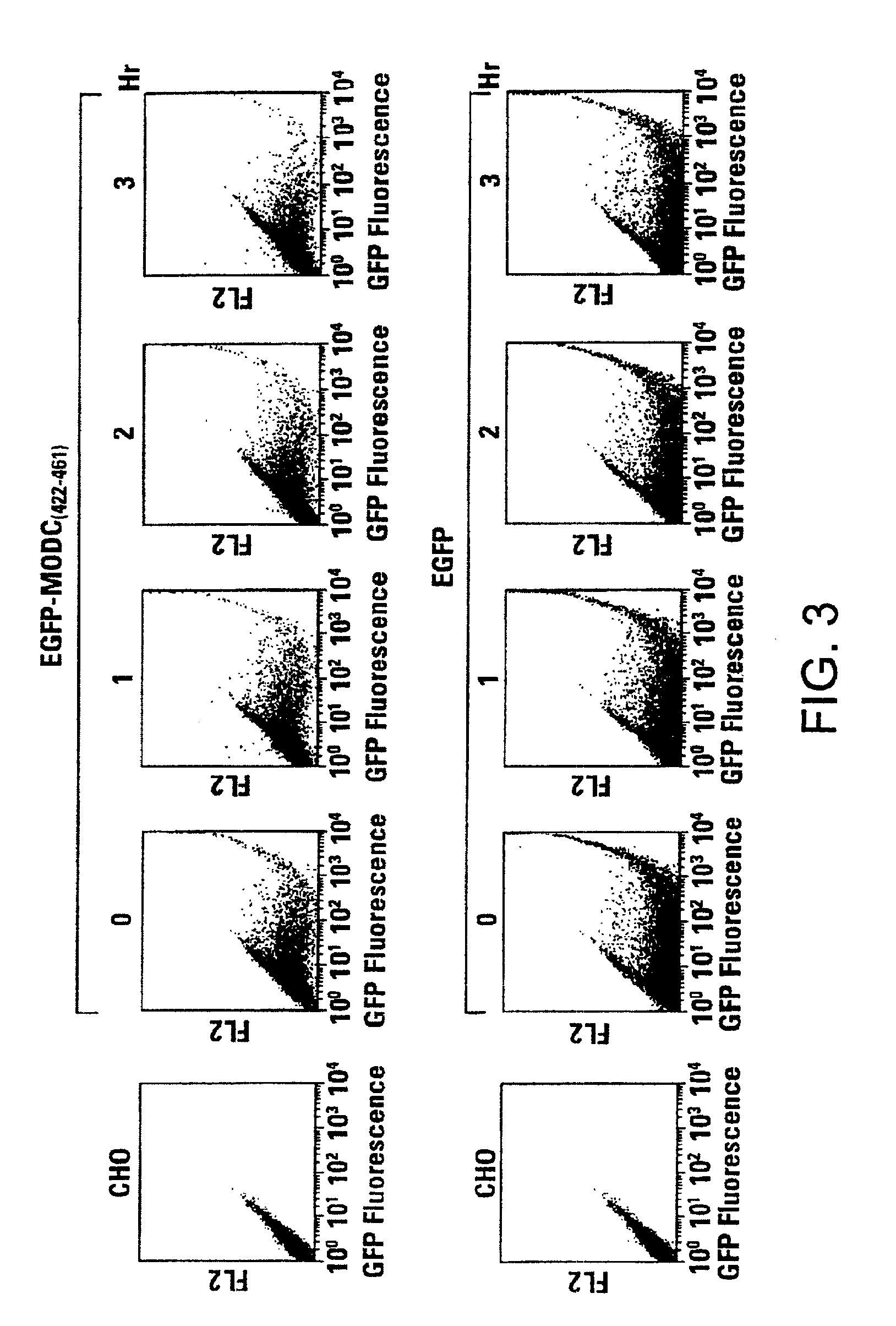
Rapidly degrading GFP-fusion proteins and methods of use
InactiveUS6956112B2Faster turnaroundRapid destabilizedFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeADAMTS Proteins
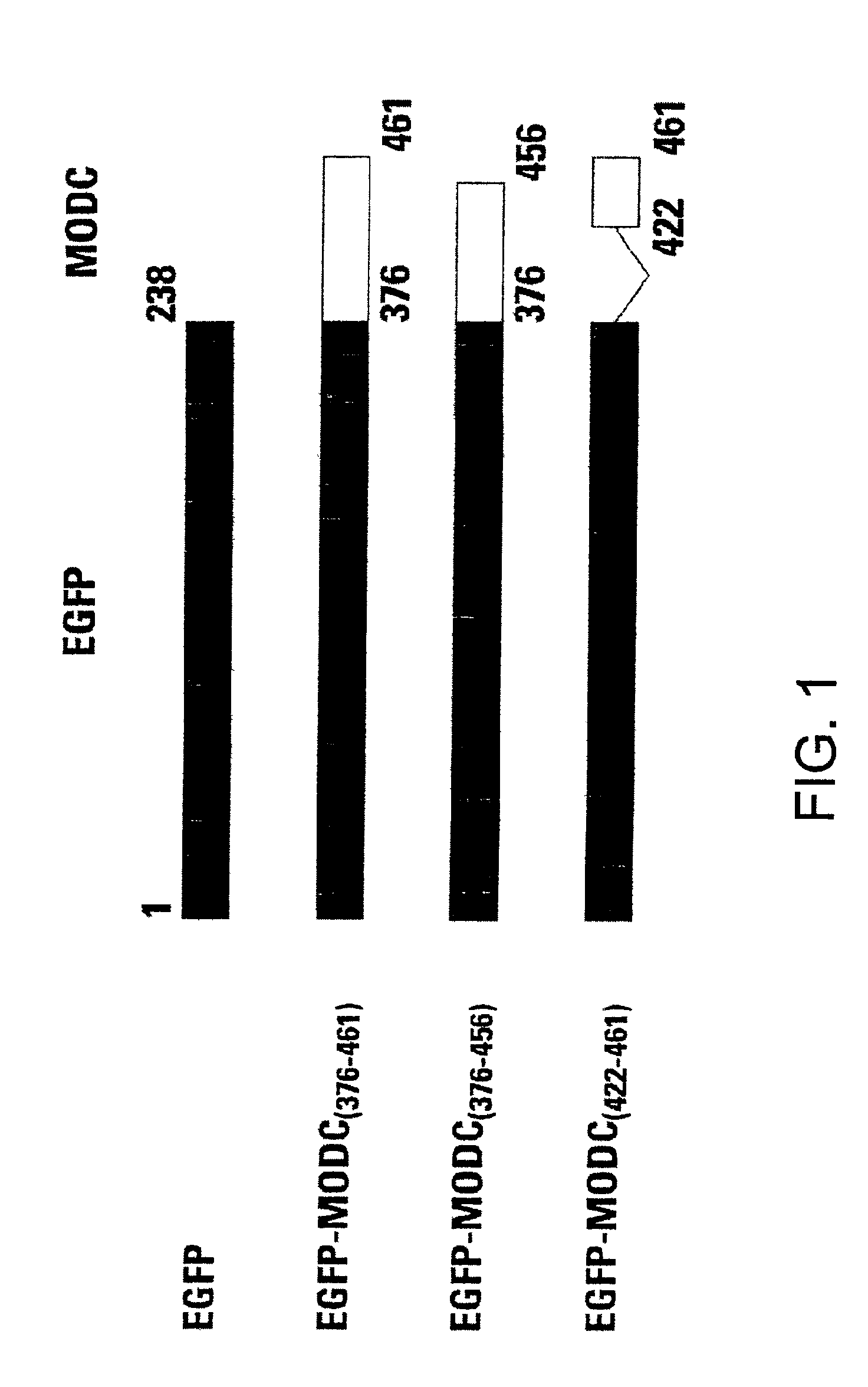
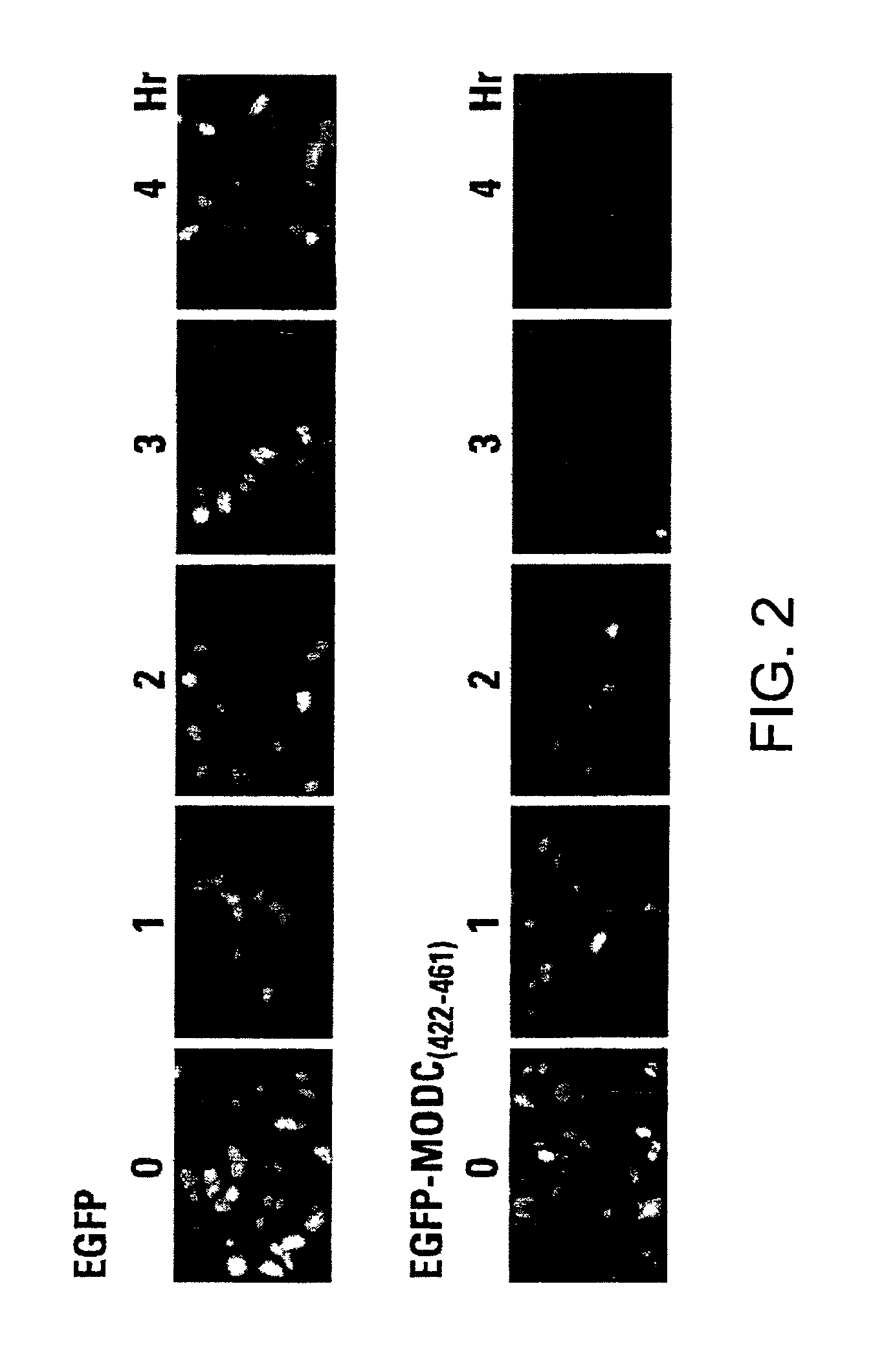
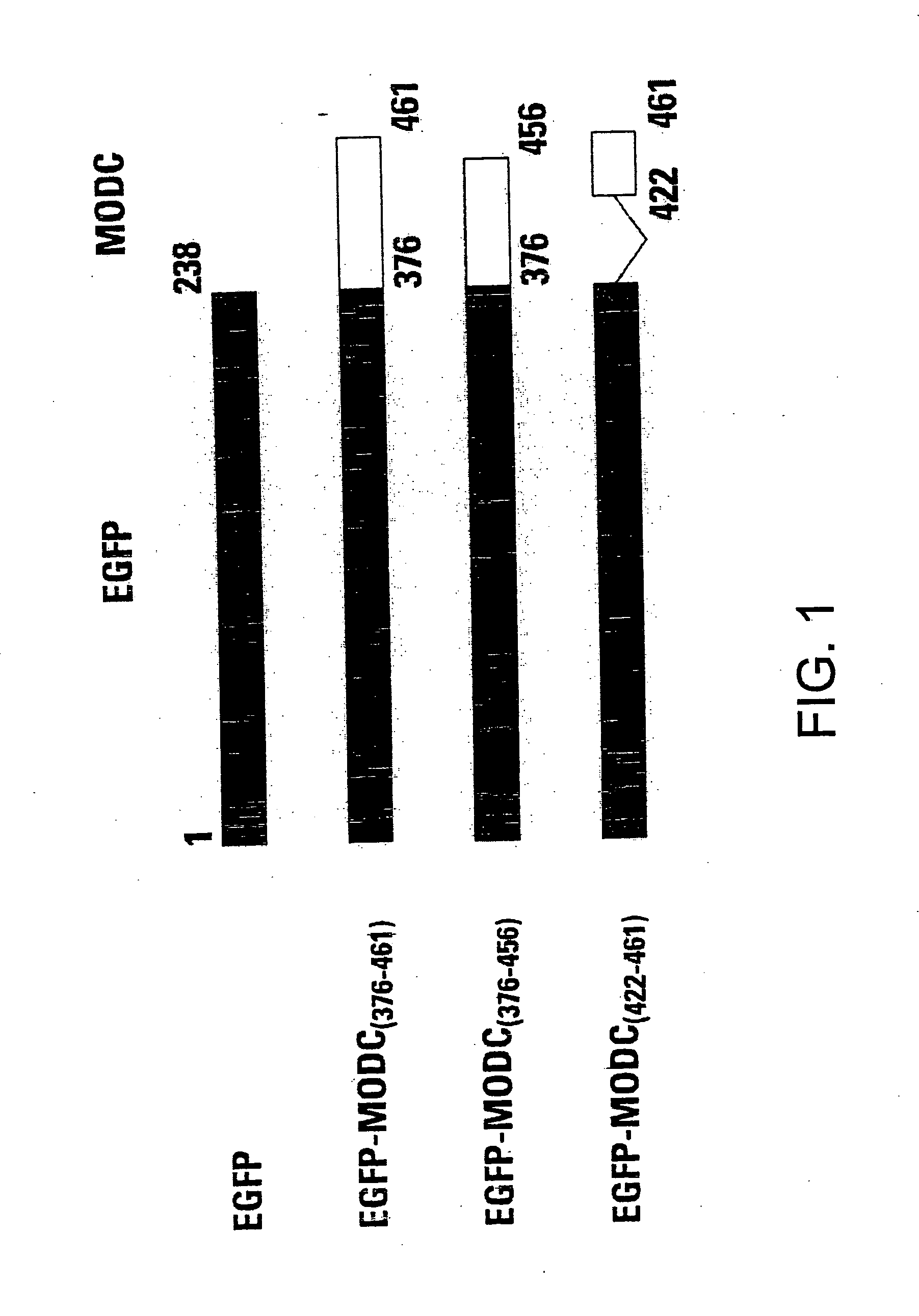
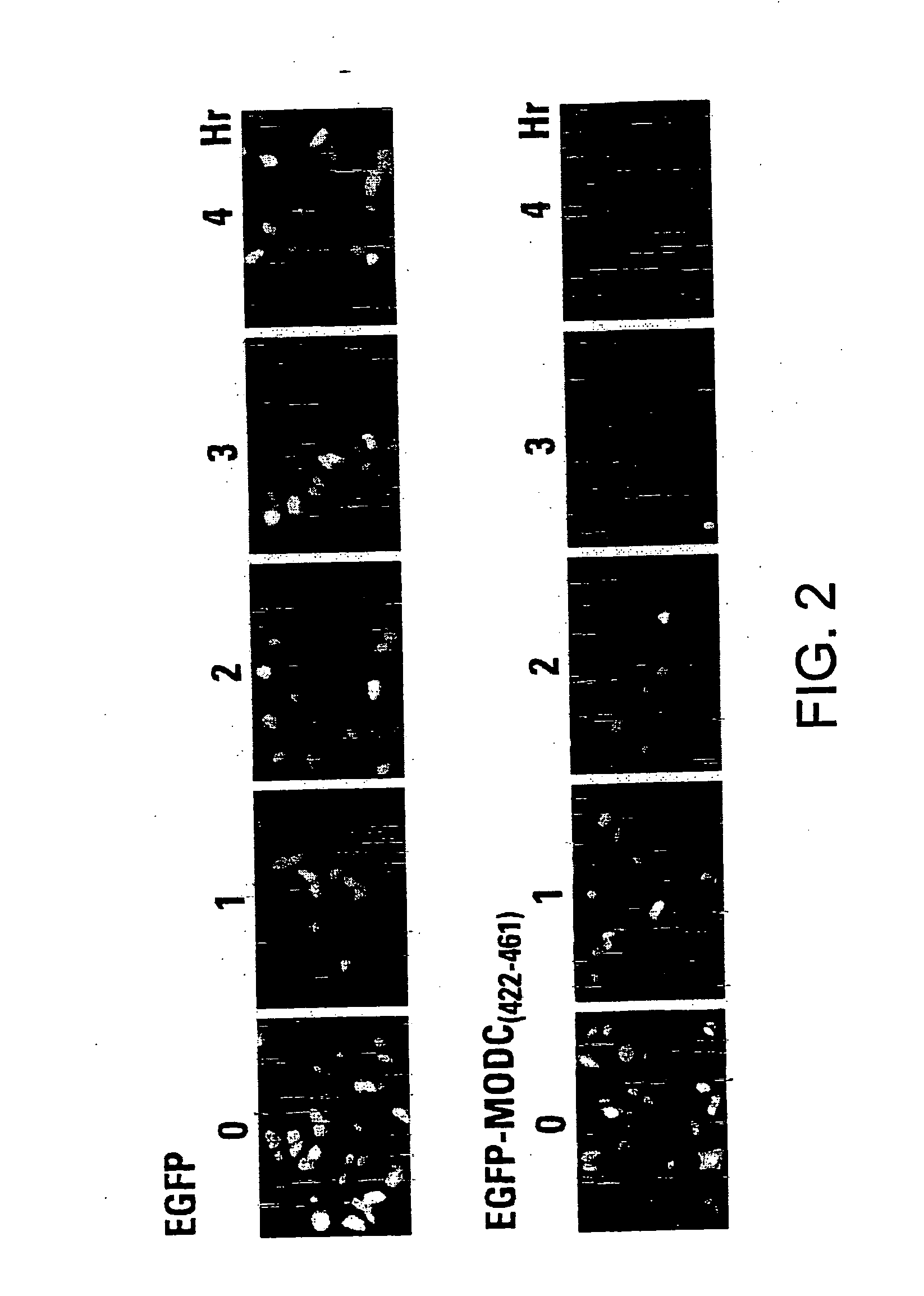
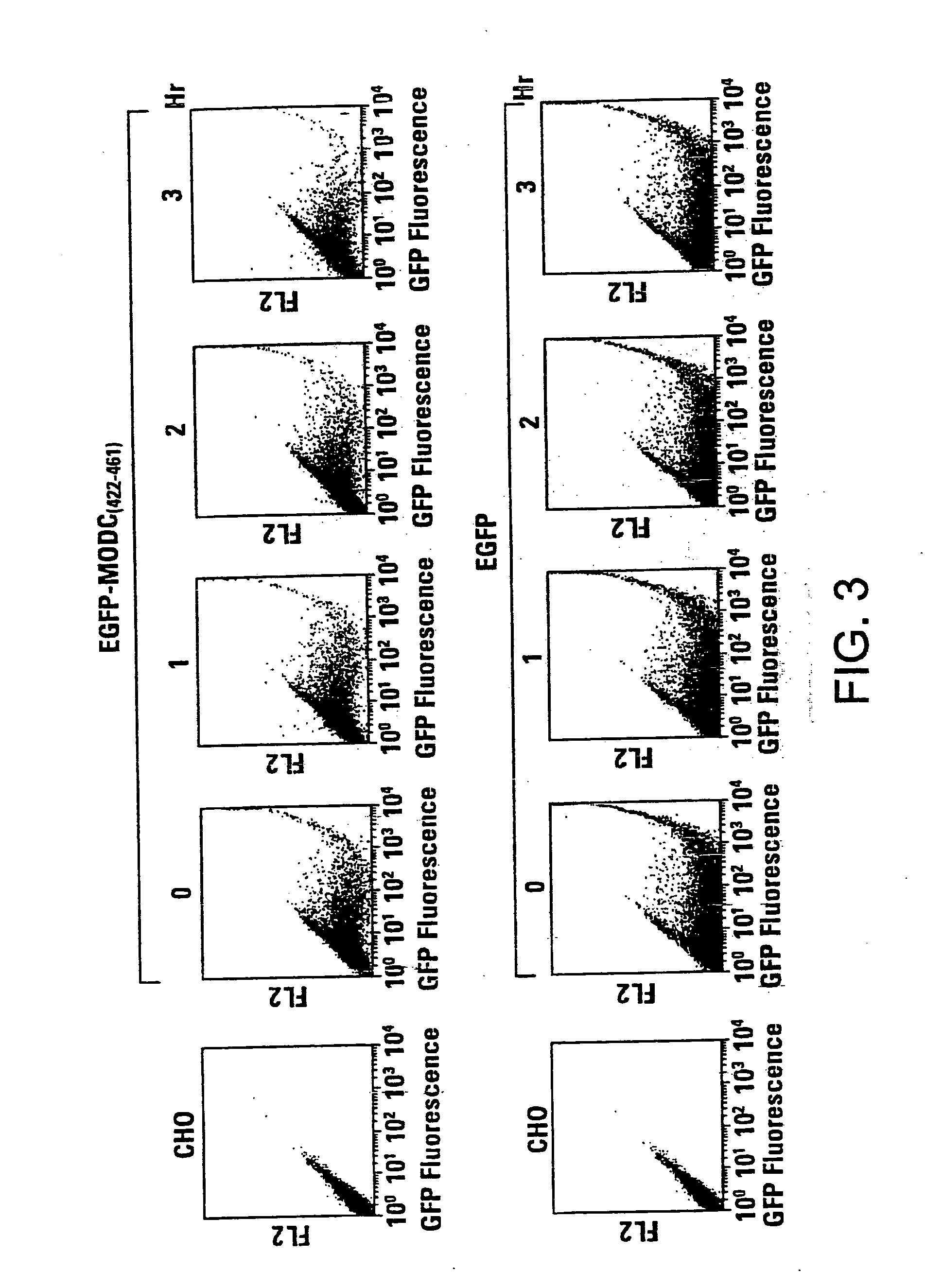
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is widely used as a reporter in determining gene expression and protein localization. The present invention provides fusion proteins with a half life of ten hours or less with several embodiments having half lives of 4 hours or less. Such proteins may be constructed by fusing C-terminal amino acids of the degradation domain of mouse ornithine decarboxylase (MODC), which contains a PEST sequence, to the C-terminal end of an enhanced variant of GFP (EGFP). Fluorescence intensity of the fusion protein in transfected cells is similar to that of EGFP, but the fusion protein, unlike EGFP, is unstable in the presence of cycloheximide. Specific mutations in the MODC region have resulted in mutants with varying half lives, useful for a variety of purposes.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Producing microorganism for trans-glycosylation beta-galactosidase
The invention discloses a glycosyl-transferbeta-galactosidase production bacterium, which is characterized by the following: the name of this bacterium is Enterobacter cloacae B5, which is Gram-negative bacterium; the conservation code is CGMCC No.1401; the bacterium shape changes along culture time extension on the LB culture medium from long rod to short rod, ellipsoid shape and ball; the colouring size is 0.5-1.5*0.7-9.0 mm with single, couple or short-chain arrangement; the bacterium can move by peripheral flagellar without gemma and can apply citrate or acetate as only one carbon source, which products acid and gas by fermenting glucose at 37 deg.c and glycerin without gas, hydrolyzing aesculin and indole; V.P. detects positive and methyl red detects negative; the nitrate is reduced and Lys is not decarboxylation with ornithine decarboxylase, arginine dihydrolase and urease; the nucleotide sequence of this bacterium 16S rDNA is described as SEQ ID No.1; the beta-galactosidase can take lactin as substrate, which catalyzes to produce oligomer galactose.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
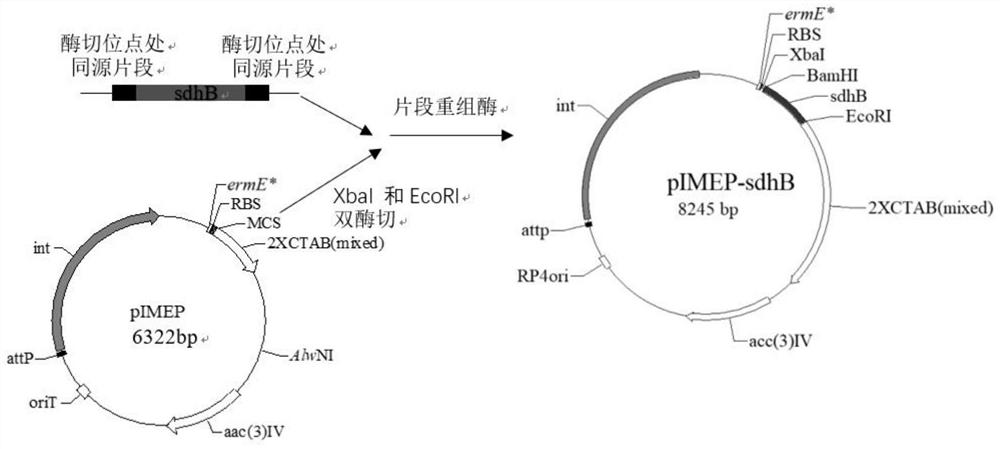
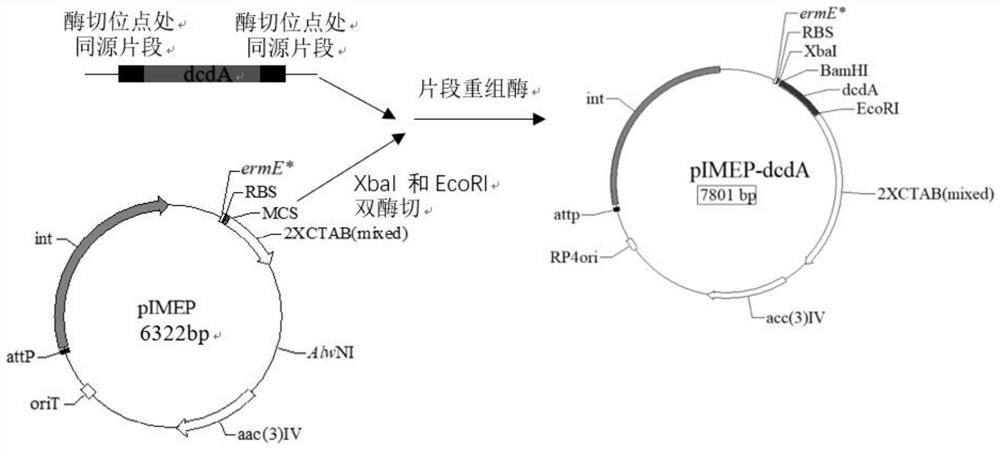
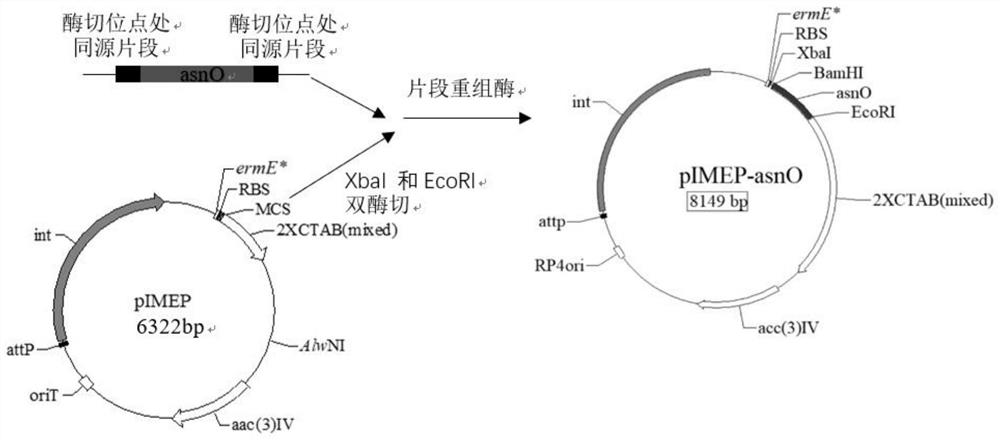
Genetically-engineered high-producing strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes, production method of epsilon-polylysine and application
ActiveCN111621454AIncreased ability to produce ε-polylysineRaise the level of fermentationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAmylaseSuccinic acid
The invention relates to a genetically-engineered strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes with high production of epsilon-polylysine. The streptomyces diastatochromogenes is obtained by over-expressing three key genes, in different metabolic pathways, of a succinate dehydrogenase gene sdhB, a lysine / ornithine decarboxylase gene dcdA and an asparagine synthetase gene asnO in streptomyces diastatochromogenes TUST separately. According to the genetically-engineered strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes with high production of the epsilon-polylysine, by over-expressing the key genes in the different metabolic pathways, the genetically-engineered recombinant strain is obtained, and an experiment proves that the epsilon-polylysine-producing capability of the streptomyces genetically-engineeredstrain is improved compared with that of the original strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes TUST in the same situation, so that the excellent strain is provided for production of epsilon-polylysine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Microorganisms for producing putrescine and method for producing putrescine using same
The present invention relates to a putrescine-producing microorganism and a method for producing putrescine using the same. To be more specific, the present invention is directed to a microorganism given the ability to produce putrescine which is generated by blocking a biosynthetic pathway from ornithine to arginine, increasing the intracellular level of glutamate, enhancing the biosynthetic pathway of ornithine from glutamate, and introducing extracellular ornithine decarboxylase; and a method for producing putrescine by using the microorganism.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Chlorine resisting strain No.1 and screening process thereof
InactiveCN1793326AImprove growth performanceEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationArginine
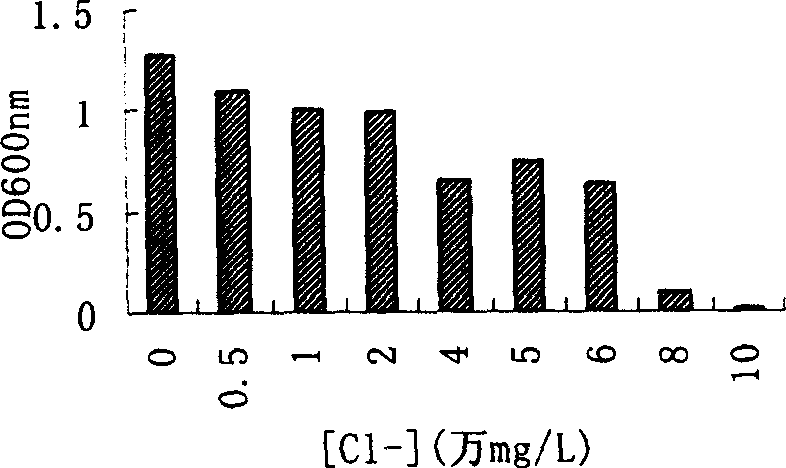
The invention relates to chlorine proof microorganism. It is chlorine proof strain No.1. Its features are as follows: it is brevibacterium linens B723-1 CCTCC NO.M205122; its colonial morphologies are creamy white, rule circular, un-transparent, smooth, stiff, and pink after 5M KOH processing; physiological characteristics that young bacterial is irregular baculiform, 0.6-1.2um*1.5-6.0um, single or pairs arrangement, common V shape; old is irregular globular, and gram positive; its main biological and chemical features are concurrently character anaerobic, chemoheterotrophic bacteria, contacting enzyme positive, oxidase negative, producing arginine double hydrolase, lysine decarboxylase, ornithine decarboxylase, and urease, and producing acid from glucose, no moving, no spore; its optimum temperature is 25-37 centigrade degree. It can live in high concentration chloride ion condition, and high effectively degrade high concentration organic pollutant.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
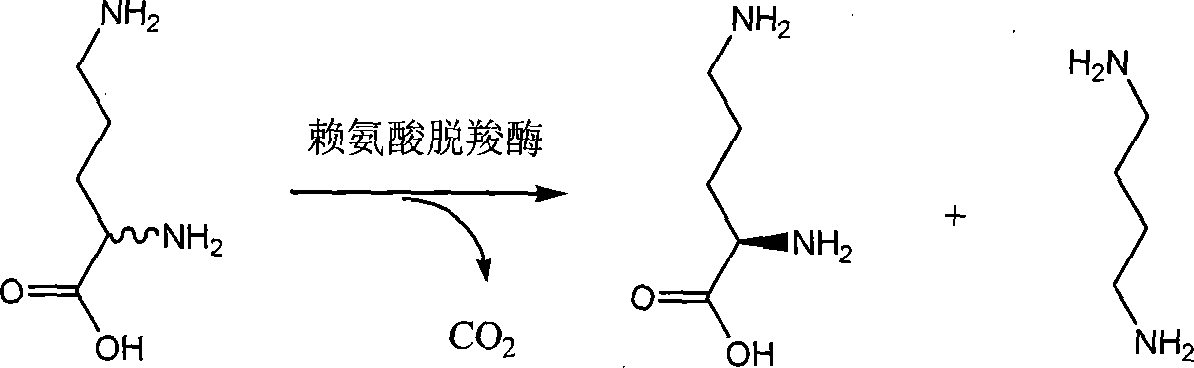
Process for the preparation of (-)-alpha-(difluoromethyl)ornithine-monohydrochloride monohydrate
InactiveUS6462229B1High yieldHigh optical purityOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationOrnithine aspartateMedicinal chemistry
(±)-alpha-(Difluoromethyl)-ornithine is separate into its isomers using (-)-O,O'-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid. (-)-alpha-(Difluoromethyl)-ornithine monohydrochloride monohydrate and in particular the (-)-isomer are inhibitors of ornithine decarboxylase and thereby have numerous pharmacological actions.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Method to treat cancer using arginine delpetor and ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) inhibitor
InactiveUS20180271960A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineCompound (substance)
One example embodiment is a method of treating lung carcinoma in a subject in need thereof. The method includes administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of an arginine reducing compound and a therapeutically effective amount of an ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) inhibitor to provide a combination therapy that has a synergistic therapeutic effect compared to an effect of the arginine reducing compound and an effect of the ODC inhibitor, in which each of the arginine reducing compound and the ODC inhibitor is administered alone.
Owner:BIO CANCER TREATMENT INT
Nucleic acid encoding proteins involved in protein degradation, products and methods related thereof
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided novel Siah-Mediated-Degradation-Proteins (SMDPs) and / or SCF-Complex Proteins (SCPs). Nucleic acid sequences encoding such proteins and assays employing same are also disclosed. The invention SMDPs and / or SCPs can be employed in a variety of ways, for example, for the production of anti-SMDP and / or SCP antibodies thereto, in therapeutic compositions, and methods employing such proteins and / or antibodies for drug screening, functional genomics and other applications. Also provided are transgenic non-human mammals that express the invention protein. Also provided are compositions and methods for targeting the destruction of selected polypeptides in eukaryotic cells based on the ubiquitin-independent mechanism by which ornithine decarboxylase is degraded by the 26S proteasome.
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES THE
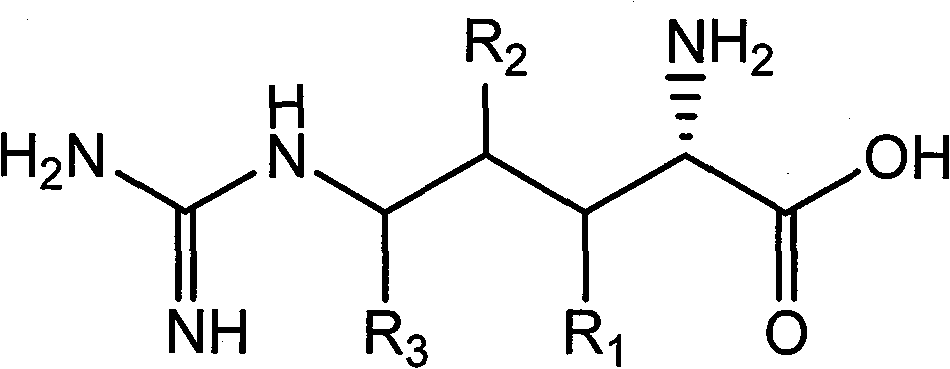
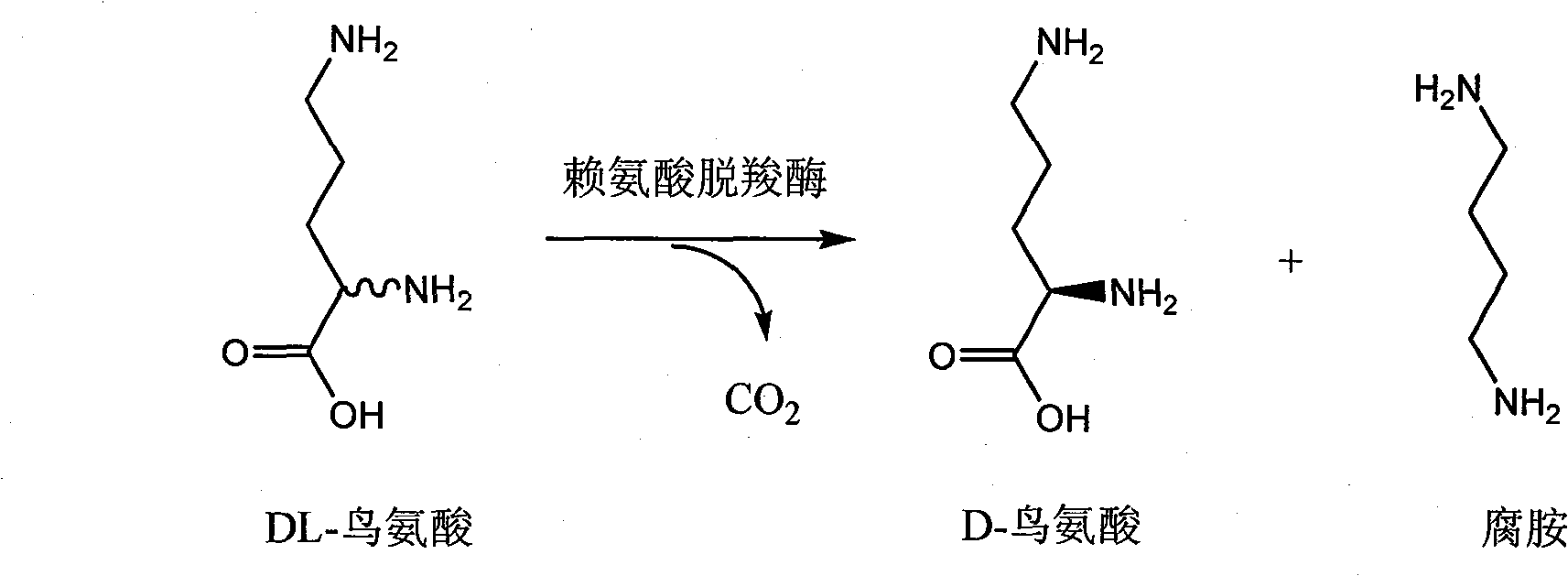
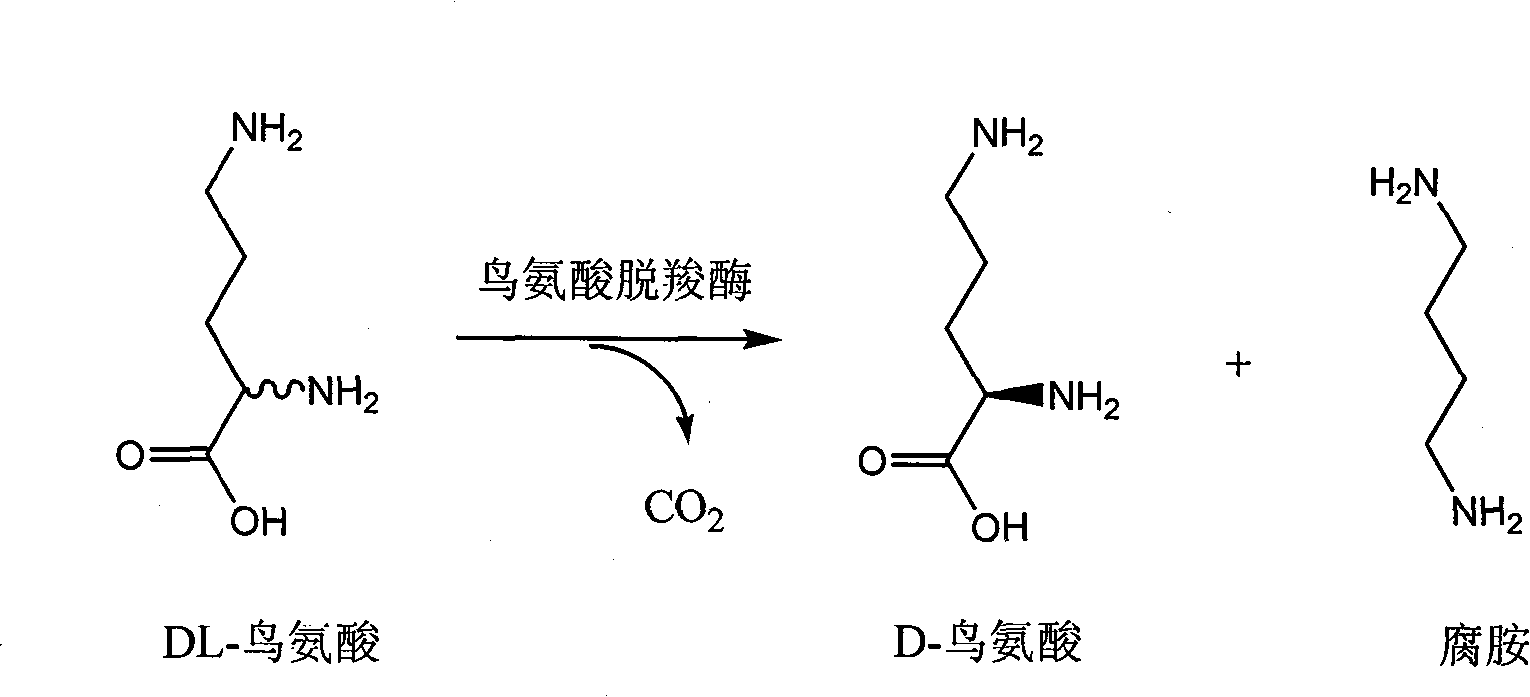
Chiral method for preparing D-ornithine and putrescine or derivatives thereof
InactiveCN101235403AEfficient Splitting EfficiencySuitable for industrial productionFermentationSalicylaldehydeSolvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of chiral compounds biological transformation separation, in particular relates to a method for preparing chiral organic coumounds and a method for preparing D-ornithine and putrescine, and is also suitable for preparing other D-ornithine compounds and aliphatic amine. The method for preparation comprises: mixing L-arginine or salt of the L-arginine with salicylal or derivant of the salicylal according to proportion, dissolving in alkaline or acidic dissolvant, obtaining DL-ornithine after racemization reaction, taking the DL-ornithine, biotransforming with microorganism or enzyme which contains lysine decarboxylase or ornithine decarboxylase under the temperature from 25DEG C to 45DEG C, obtaining the D-ornithine and the putrescine, then, using an isoelectric point crystallization method or a cation exchange resin separation method to separate the D-ornithine and the putrescine, and obtaining optically pure D-ornithine and putrescine. A chemical racemization method of the invention main takes water as the dissolvant, the catalyst consumption is little, the dissolvant which is used does not have poison and has low cost, the microorganism is easily cultured, and the invention is suitable for large scale industrial production.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Small molecule inhibitor and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and relates to a small molecule inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and an application thereof. A novel small molecule inhibitor aiming at ODC is found through computer-aided high-throughput medicine screening. Verification of the effects of the novel small molecule inhibitor finds that the novel small molecule inhibitor has good inhibiting effects on ODC and can be especially used for inhibiting human-derived ODC, preventing, treating and diagnosing tumor diseases and pathogenic microorganism infection and developing and preparing tumor medicines or medicines against pathogenic microorganism infection.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
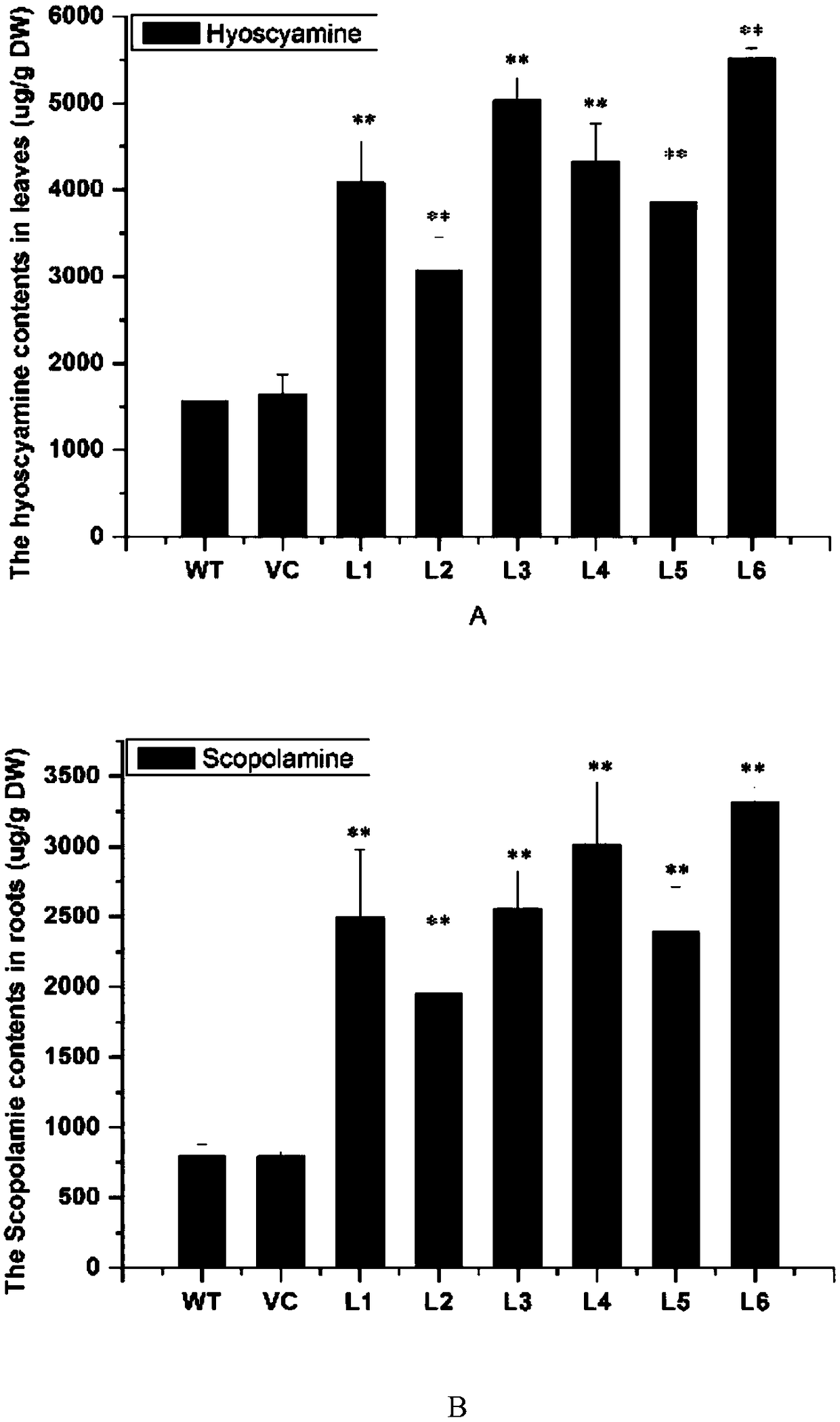
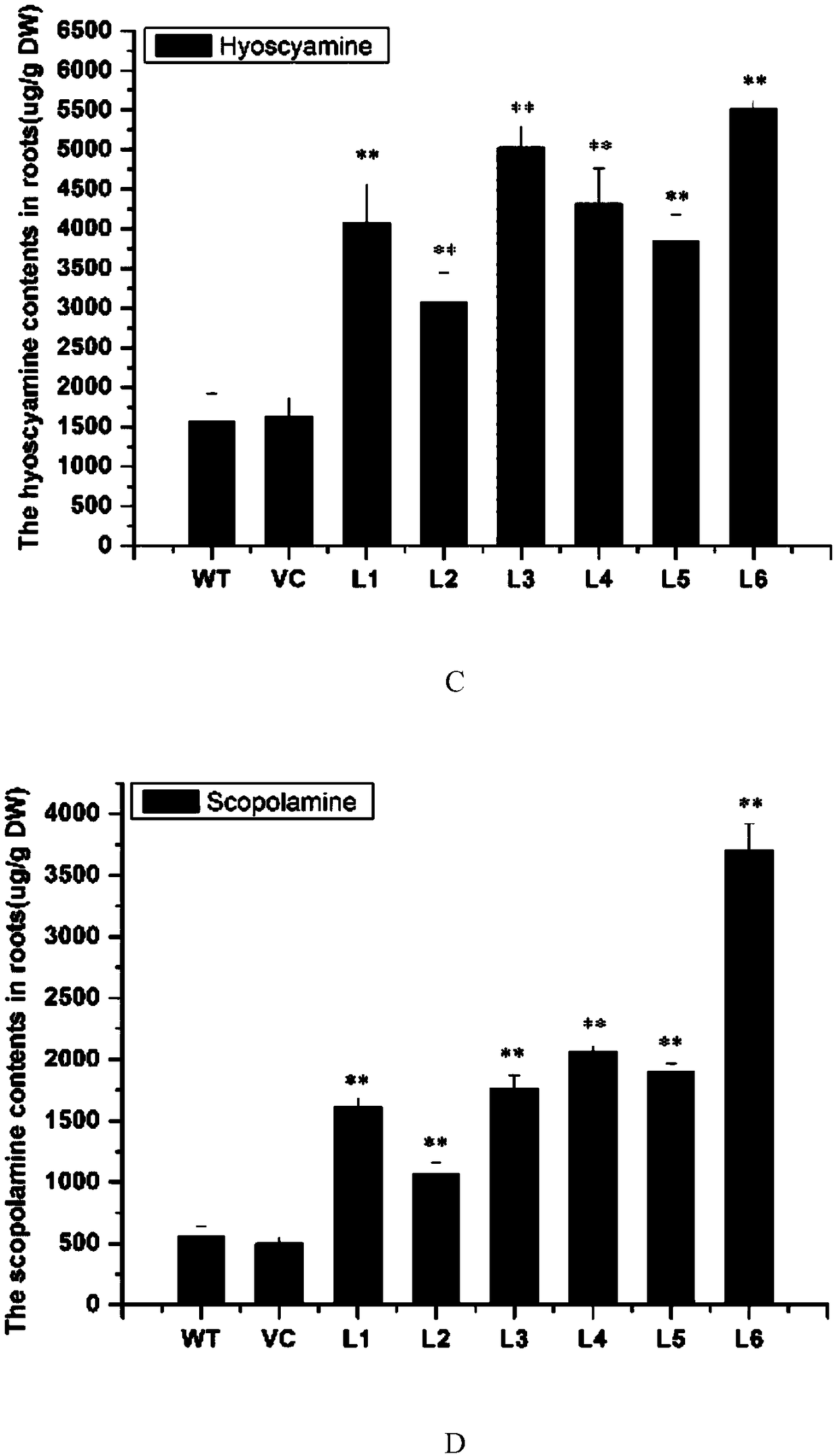
Anisodus luridus ornithine decarboxylase ALODC gene as well as recombinant expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN109022463AIncrease contentContent stability measurementFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTropane alkaloidTransgenic technology
The invention relates to an anisodus luridus ornithine decarboxylase ALODC gene as well as a recombinant expression vector and application thereof. By cloning the anisodus luridus ornithine decarboxylase ALODC gene, through an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation method, the gene is transferred into anisodus luridus, a transgenic plant is obtained, after ALODC over-expression is conducted, the contents of putrescine and tropane alkaloids in the anisodus luridus plant can be significantly improved, and an ideal method is provided for effectively producing hyoscyamine and scopolamine by means ofa transgenic technology.
Owner:TIBET AGRI & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY COLLEGE +1
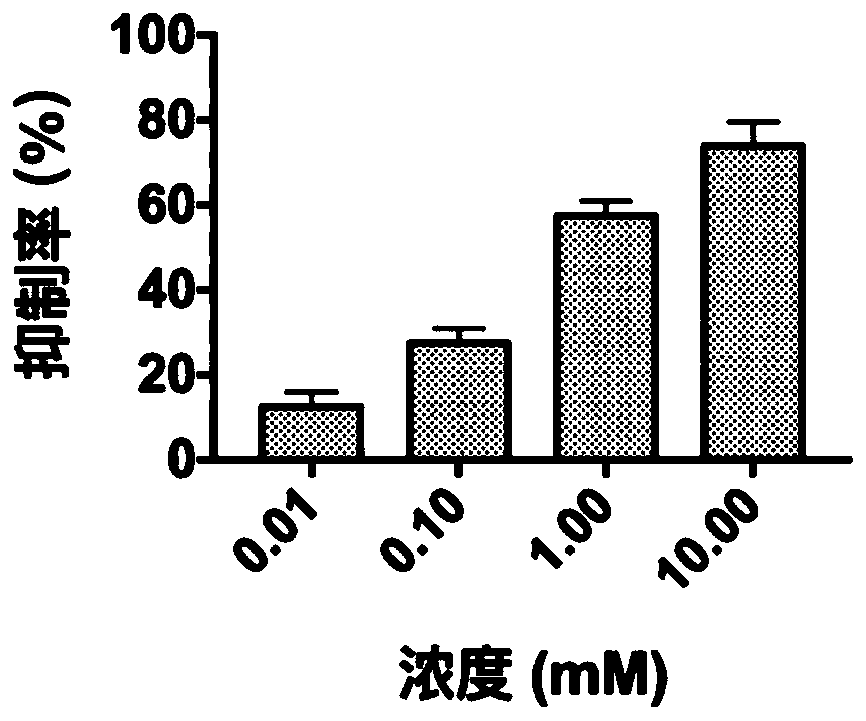
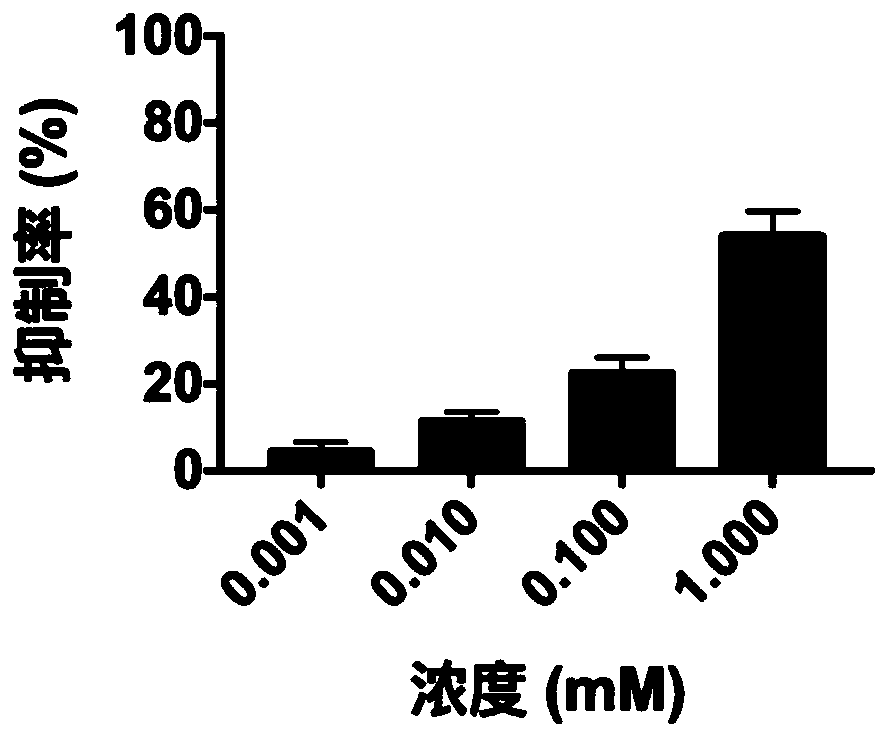
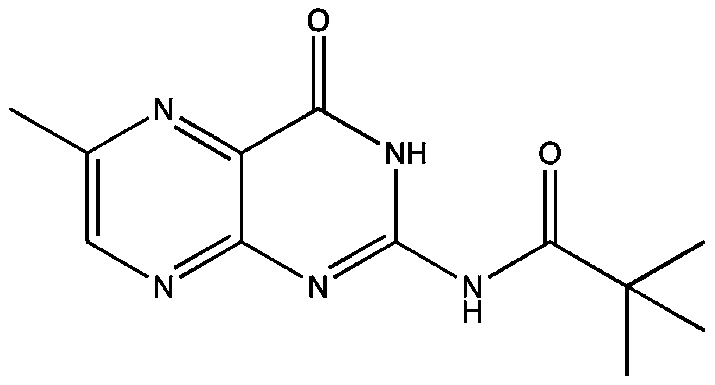
Small-molecule inhibitor containing dihydracridine and application of inhibitor in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (ODC)
ActiveCN109776541AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPathogenic microorganismStructural formula
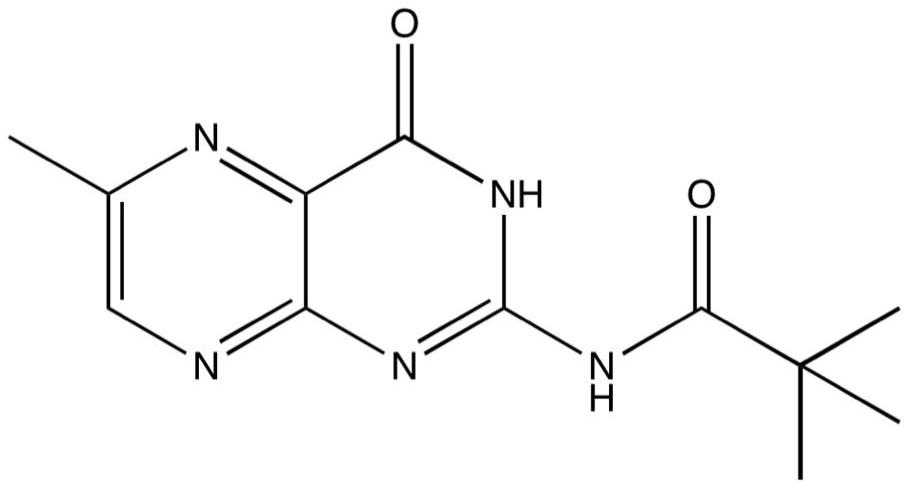
The invention provides a small-molecule inhibitor containing dihydracridine. The small-molecule inhibitor is 2, 2-dimethyl-N-(6-methyl-4-oxo-3, 4-dihydro-2-acridinyl) propanamide. The structural formula of the inhibitor is shown in the description. The small-molecule inhibitor containing the dihydracridine is applied to inhibiting the ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and preparing medicine used for treating tumors and medicine used for treating pathogenic microorganism infection, and significant effects are achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
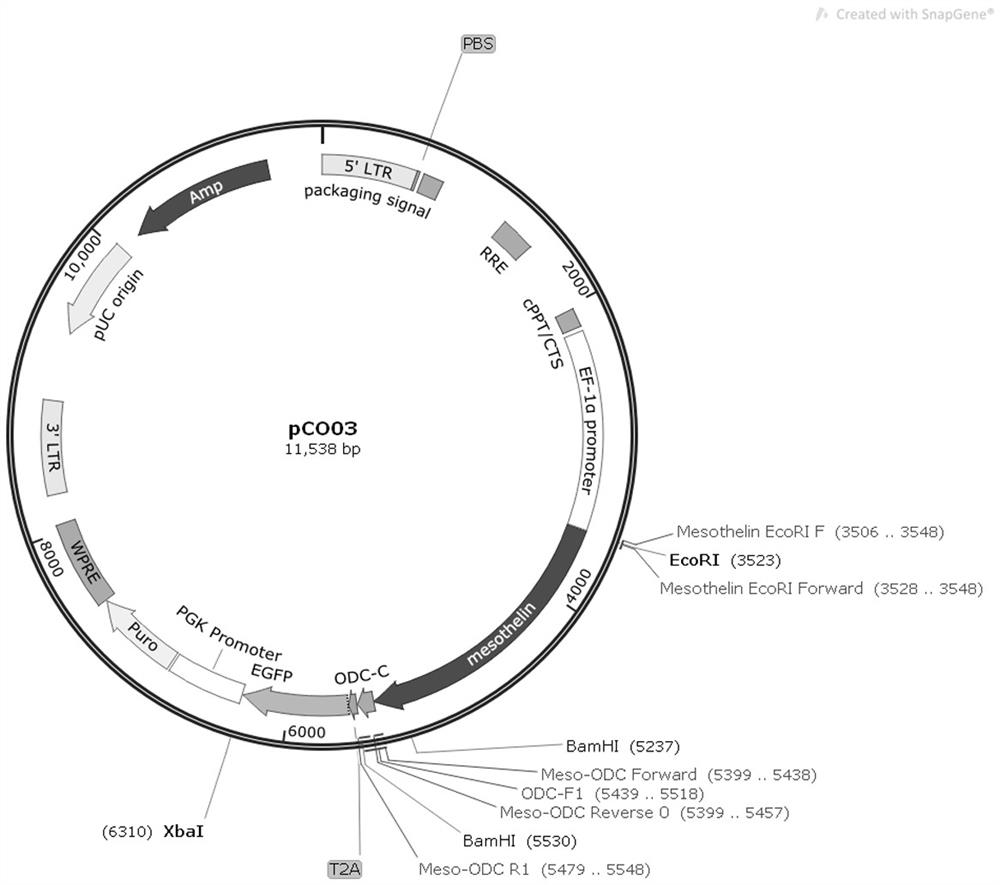
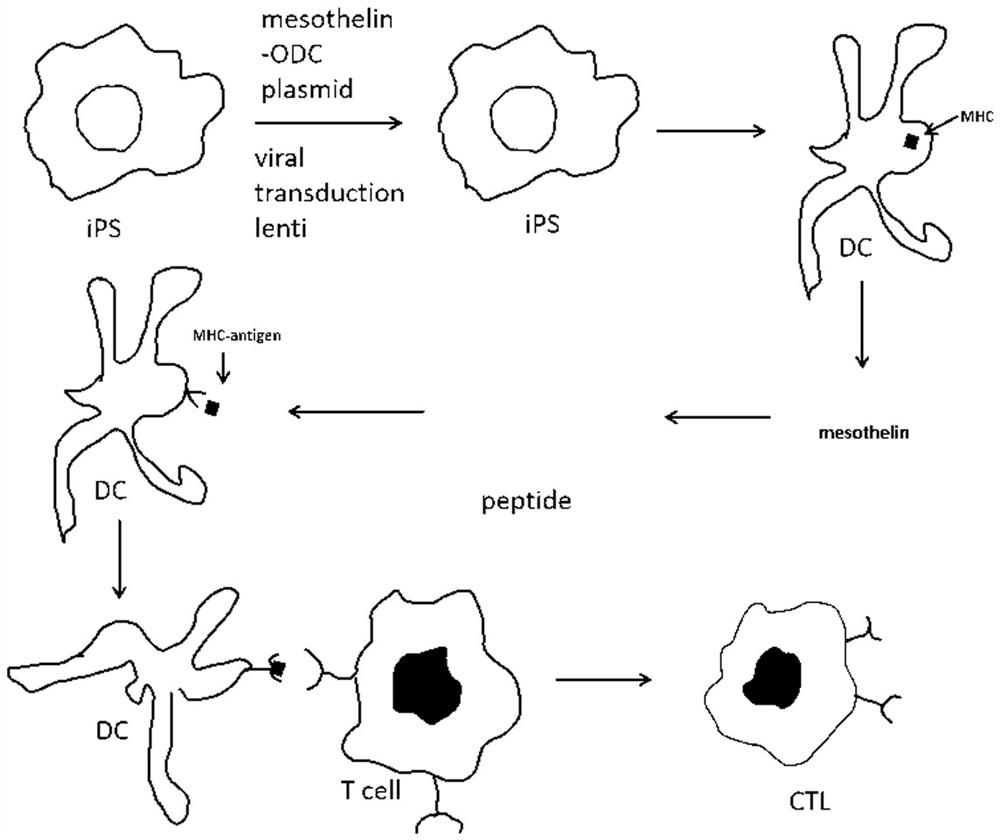
Mesothelin-ODC422-461 fusion protein expressed by DCs (dendritic cells) and application of mesothelin-ODC422-461 fusion protein
PendingCN113754779AShort half-lifeHelp with presentationVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDendritic cellTumor antigen
The invention discloses a mesothelin-ODC422-461 fusion protein expressed by DCs (dendritic cells) and application of the mesothelin-ODC422-461 fusion protein. The fusion protein is a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and is formed by fusing the mesothelin protein and amino acid at site C-422-461 of mouse ornithine decarboxylase, and the DCs are derived from DCs differentiated from monocyte in PBMCs, DCs differentiated from iPS / ES induction, and primary DC cells separated from blood. The fusion protein can be used for inducible expression in DC cells, tumor antigen presentation of the DCs is facilitated, the antigen presentation efficiency of in-vivo T cells is improved, the T cells are activated to kill tumor cells, and in addition, the fusion protein can be used for cell therapy since the half-life period of the fusion protein is very short, the fusion protein serving as medicine has small toxicity and small side effects, and can generate synergistic effects with immune cells.
Owner:赛元生物科技(杭州)有限公司
Chiral method for preparing D-ornithine and putrescine or derivatives thereof
InactiveCN101235403BEfficient Splitting EfficiencySuitable for industrial productionFermentationSalicylaldehydeSolvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of chiral compounds biological transformation separation, in particular relates to a method for preparing chiral organic coumounds and a method for preparing D-ornithine and putrescine, and is also suitable for preparing other D-ornithine compounds and aliphatic amine. The method for preparation comprises: mixing L-arginine or salt of the L-arginine with salicylal or derivant of the salicylal according to proportion, dissolving in alkaline or acidic dissolvant, obtaining DL-ornithine after racemization reaction, taking the DL-ornithine, biotransforming with microorganism or enzyme which contains lysine decarboxylase or ornithine decarboxylase under the temperature from 25DEG C to 45DEG C, obtaining the D-ornithine and the putrescine, then, using an isoelectric point crystallization method or a cation exchange resin separation method to separate the D-ornithine and the putrescine, and obtaining optically pure D-ornithine and putrescine. A chemical racemization method of the invention main takes water as the dissolvant, the catalyst consumption is little, the dissolvant which is used does not have poison and has low cost, the microorganism is easily cultured, and the invention is suitable for large scale industrial production.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
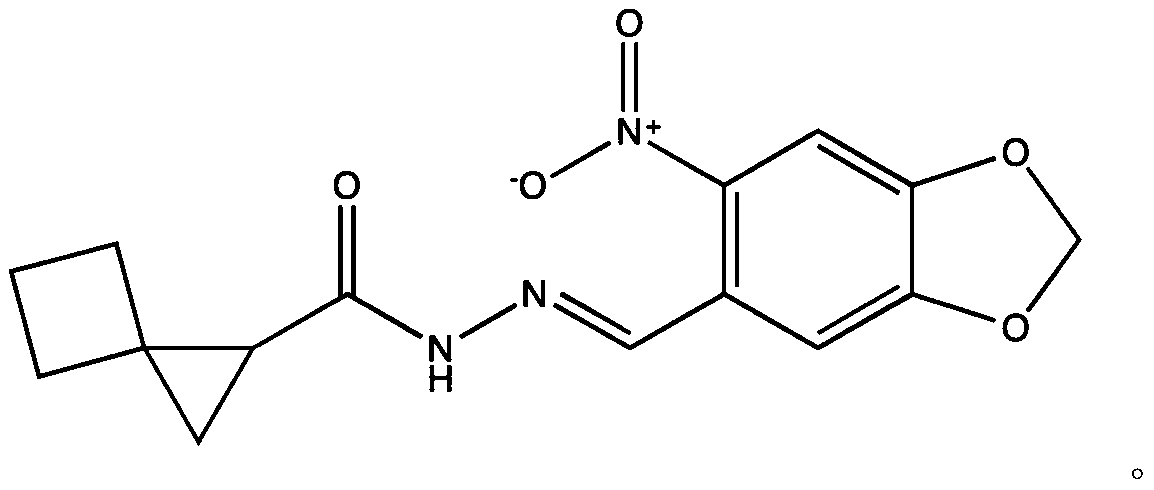
Small-molecule inhibitor containing benzo dioxole and application of inhibitor in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (ODC)
The invention provides a small-molecule inhibitor containing benzo dioxole. The small-molecule inhibitor is N'-({6-nitro-1,3-benzo dioxole-5-radical} methylene) spiro [2.3] hexane-1-carbohydrazide, and the structural formula of the inhibitor is shown in the description. The small-molecule inhibitor containing the benzo dioxole is applied to inhibiting the ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and preparing medicine used for treating tumors and medicine used for treating pathogenic microorganism infection, and significant effects are achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
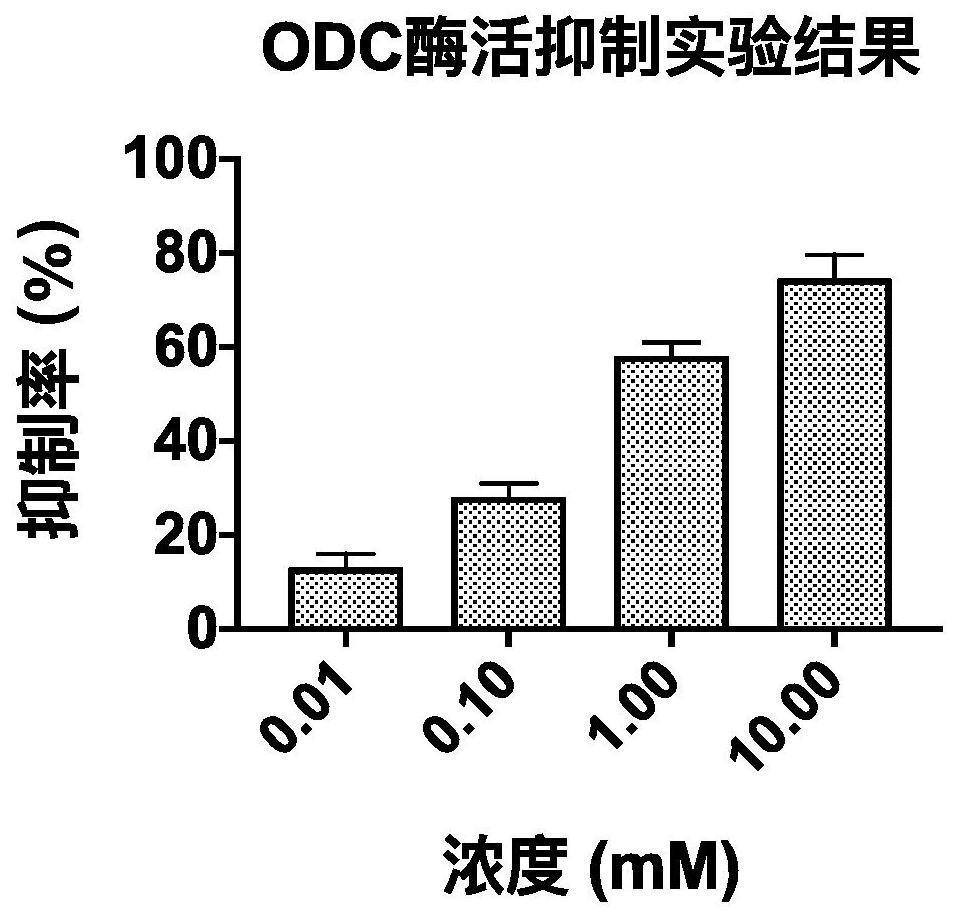
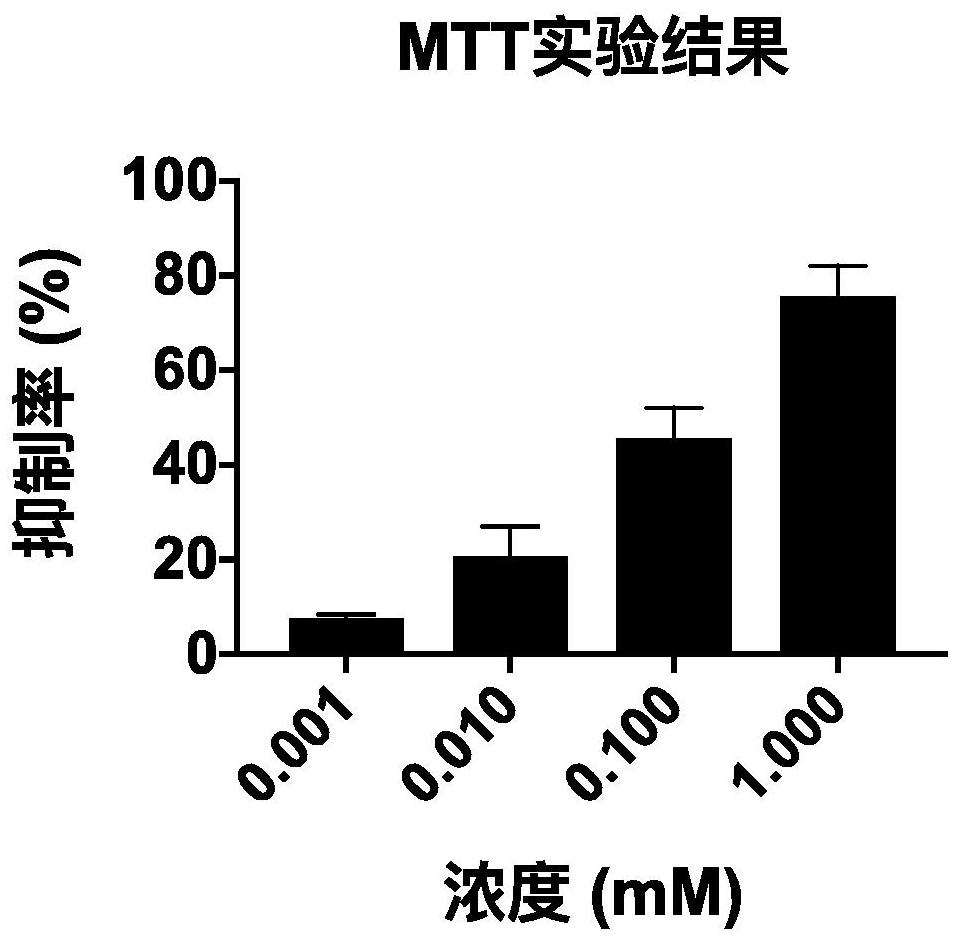
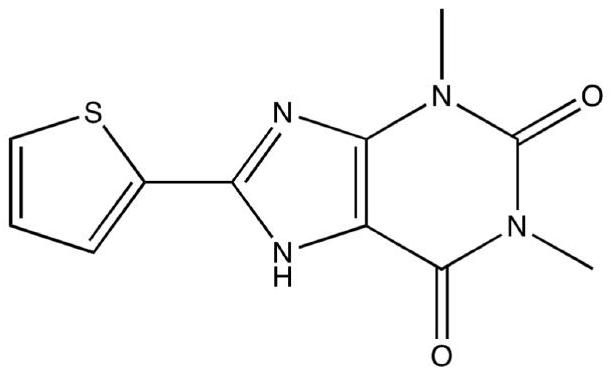
A small molecule inhibitor containing 2,6-dihydroxypurine and its application in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (odc)
The invention provides a small molecule inhibitor containing 2,6-dihydroxypurine, the small molecule inhibitor is 1,3-dimethyl-8-(2-thienyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H- Purine-2,6-diketone, its structural formula is: the present invention will contain the 2,6-dihydroxypurine small molecule inhibitor in the application of inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), and in the preparation of the drug for treating tumor application, and in the preparation of medicines for the treatment of pathogenic microorganism infections, and achieved remarkable results.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Engineering bacterium, treatment method of ornithine-containing solution and kit
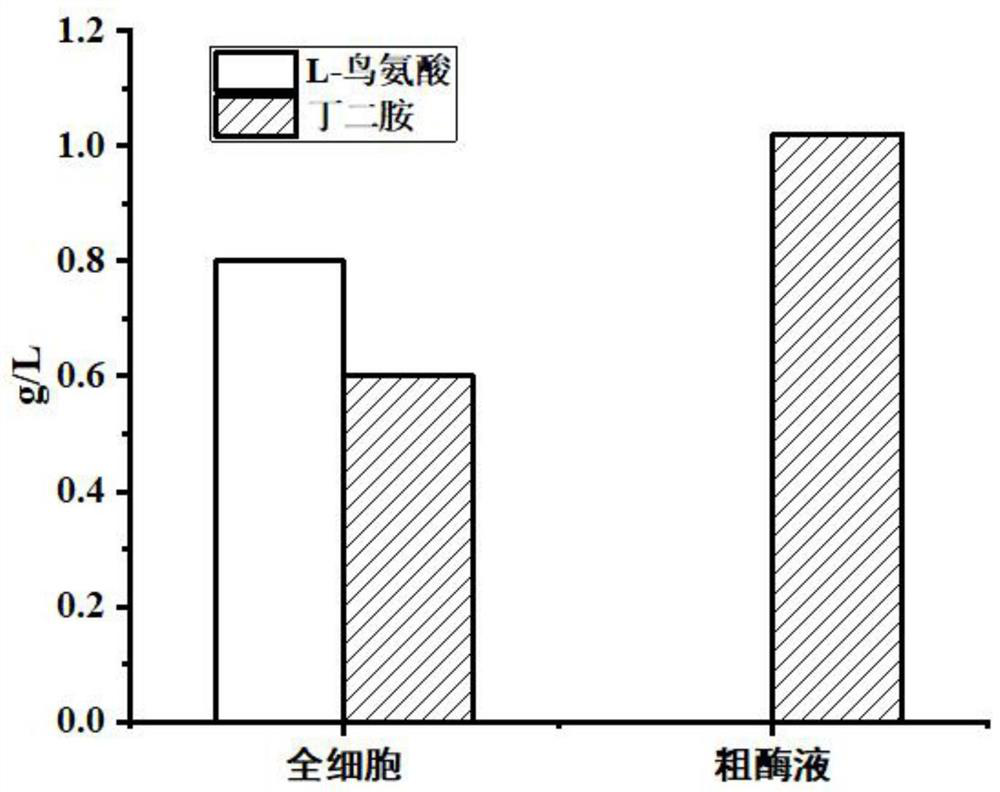
PendingCN112522171AHigh expressionImprove processing efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides an engineering bacterium capable of expressing ornithine decarboxylase, a treatment method of an ornithine-containing solution and a kit. The engineering bacterium comprises a nucleotide sequence for encoding ornithine decarboxylase. The treatment method of the ornithine-containing solution comprises the following steps: obtaining the ornithine-containing solution which comprises D-ornithine and L-ornithine; culturing engineering bacteria capable of expressing ornithine decarboxylase to obtain an ornithine decarboxylase crude enzyme solution; and conducting enzyme treatment: adding the ornithine decarboxylase crude enzyme solution and pyridoxal phosphate into the ornithine-containing solution, and reacting to generate a final product which contains D-ornithine and / orbutanediamine. The kit contains the ornithine decarboxylase crude enzyme solution. According to the treatment method of the ornithine-containing solution, DL-ornithine is converted into butanediamineand D-ornithine, the butanediamine and the D-ornithine are easy to separate, the product purity and the optical purity are improved, the product yield is increased, and the separation cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGSHAN CHEM IND GRP
Correlation between ornithine decarboxylase 1 gene and primary hypertension
InactiveCN1654677AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFhit geneEssential hypertension
The present invention discloses method of detecting primary hypertension susceptibility. The detection includes detecting individual ornithine decarboxylase 1 gene ODC1, transcript and / or protein, comparing with normal items to find the existing variation, which shows the greater attack probability of the individual in primary hypertension. The present invention also discloses the corresponding detection kit.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
A small molecule inhibitor containing dihydroacridine and its application in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (odc)
The invention provides a small molecule inhibitor containing dihydroacridine, the small molecule inhibitor is 2,2-dimethyl-N-(6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2 ‑acridinyl) propionamide, the structural formula is the application of the small molecule inhibitor containing dihydroacridine in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) of the present invention, and the application in the preparation of drugs for treating tumors, and in The application in the preparation of medicines for the treatment of pathogenic microorganism infections has achieved remarkable results.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Rapidly degrading GFP-fusion proteins and methods of use
InactiveUS20050158833A1Improve developmentAvoiding toxic levelFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeMutant
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is widely used as a reporter in determining gene expression and protein localization. The present invention provides fusion proteins with a half life of ten hours or less with several embodiments having half lives of 4 hours or less. Such proteins may be constructed by fusing C-terminal amino acids of the degradation domain of mouse ornithine decarboxylase (MODC), which contains a PEST sequence, to the C-terminal end of an enhanced variant of GFP (EGFP). Fluorescence intensity of the fusion protein in transfected cells is similar to that of EGFP, but the fusion protein, unlike EGFP, is unstable in the presence of cycloheximide. Specific mutations in the MODC region have resulted in mutants with varying half lives, useful for a variety of purposes.
Owner:CLONTECH LAB
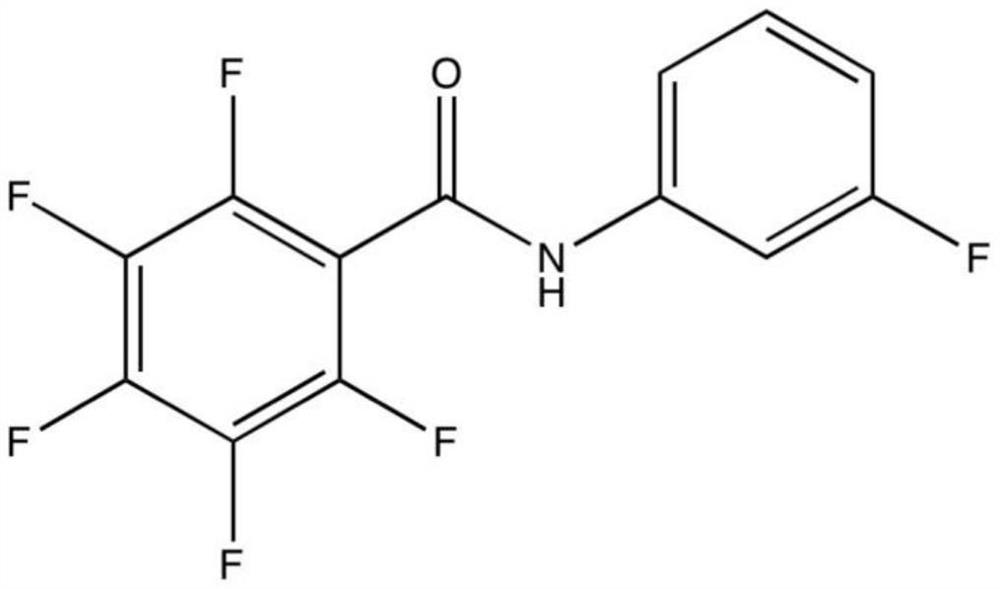
A kind of benzamide small molecule inhibitor and its application in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase
ActiveCN109875987BOrganic active ingredientsAntiinfectivesPathogenic microorganismPharmaceutical drug
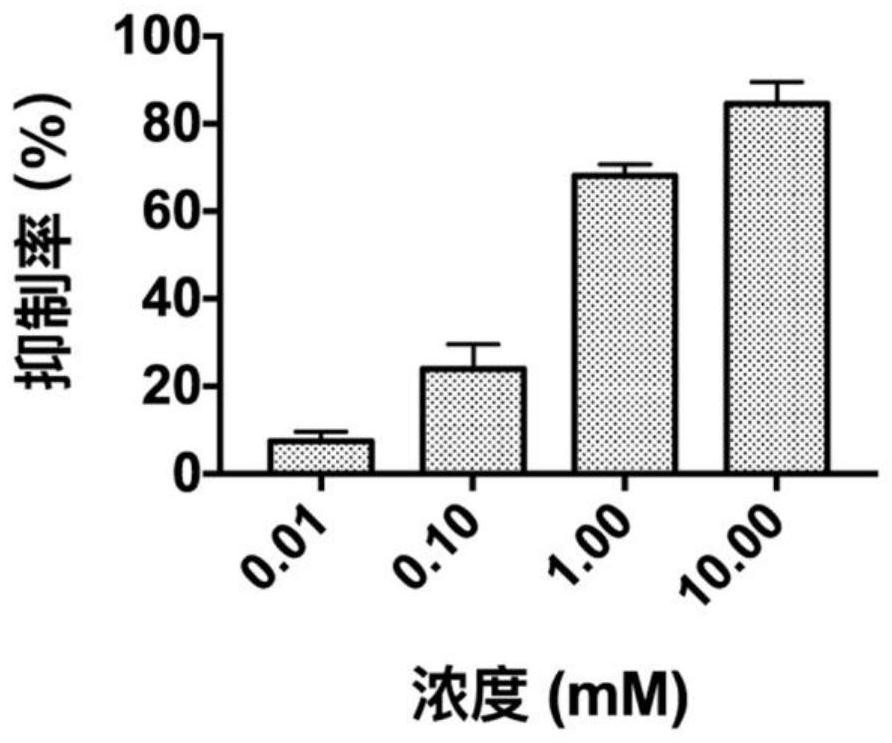
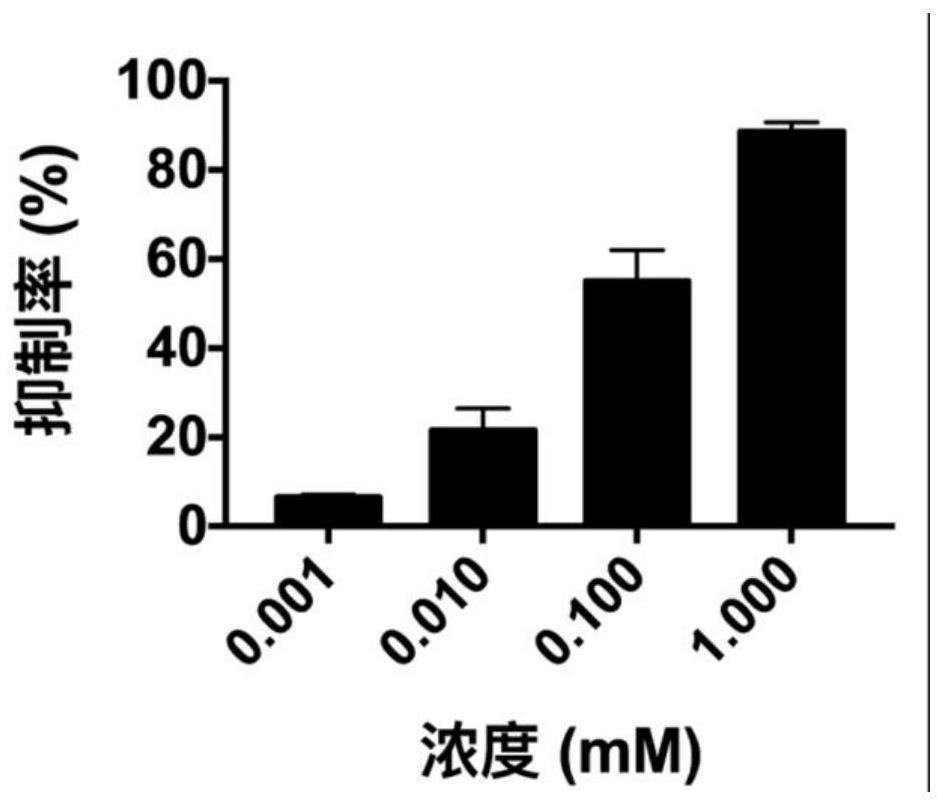
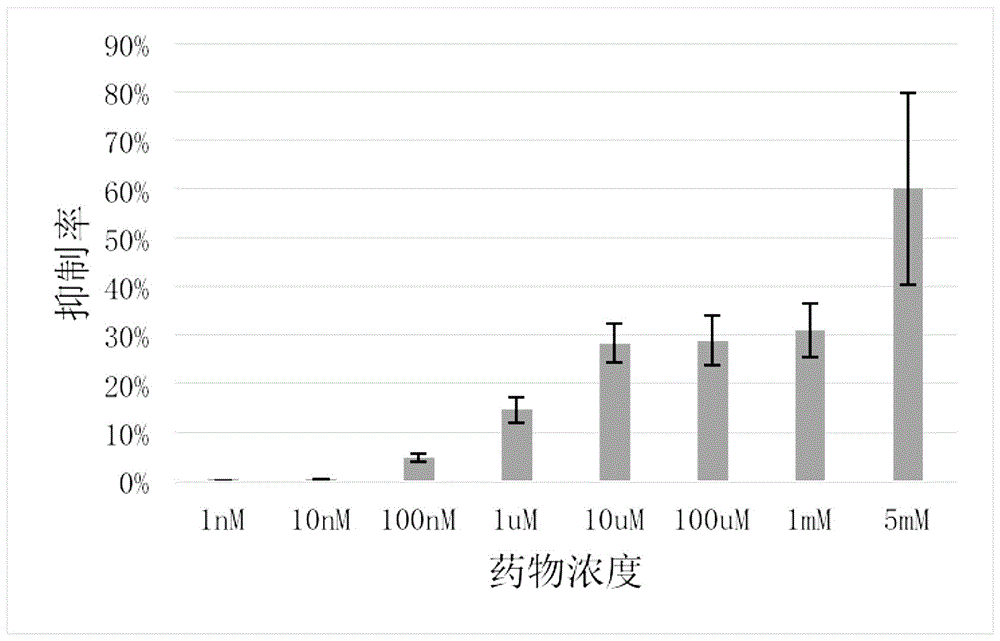
The present invention provides a kind of benzamide small molecule inhibitor, and this small molecule inhibitor is 2,3,4,5,6-pentafluoro-N-(3-fluoroalkenyl) benzamide, and structural formula is as follows: The present invention The application of the benzamide small-molecule inhibitor in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), in the preparation of a drug for treating tumors, and in the preparation of a drug for treating pathogenic microorganism infection has achieved remarkable effects.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
A kind of small molecule inhibitor and its application
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
A kind of small molecule inhibitor and its application in inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and relates to a small molecule inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and an application thereof. A novel small molecule inhibitor aiming at ODC is found through computer-aided high-throughput medicine screening. Verification of the effects of the novel small molecule inhibitor finds that the novel small molecule inhibitor has good inhibiting effects on ODC and can be especially used for inhibiting human-derived ODC, preventing, treating and diagnosing tumor diseases and pathogenic microorganism infection and developing and preparing tumor medicines or medicines against pathogenic microorganism infection.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
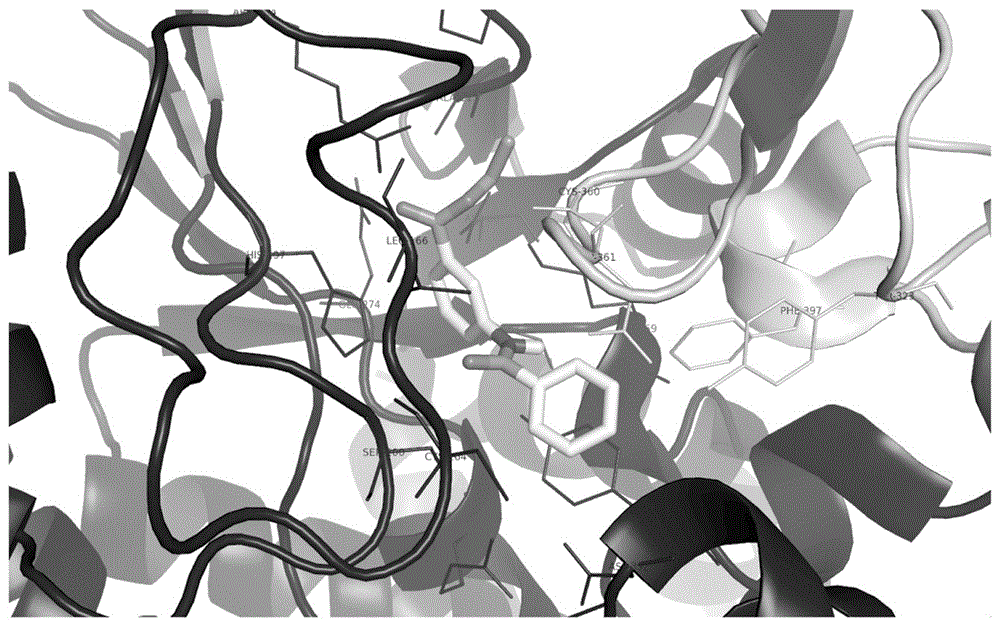
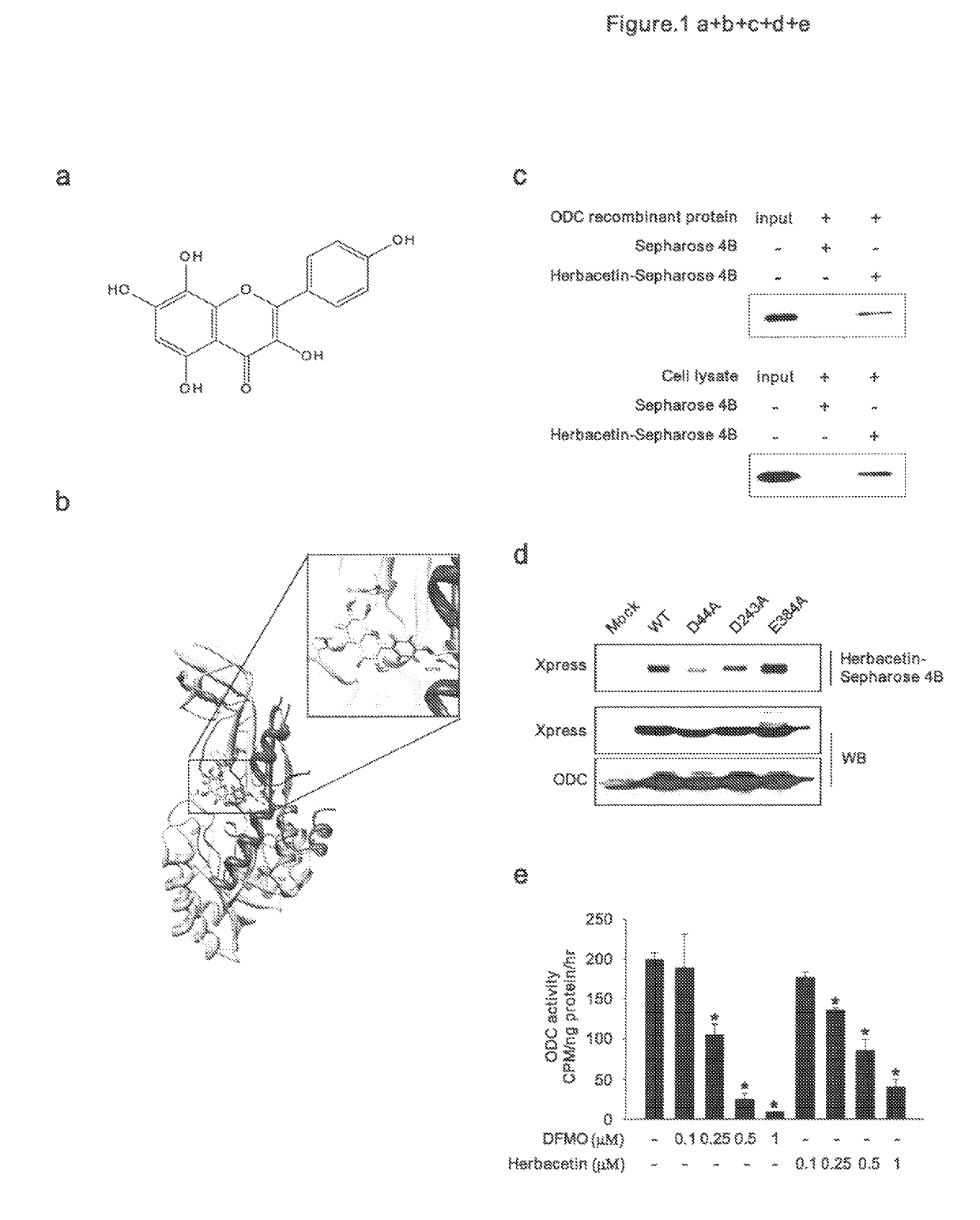
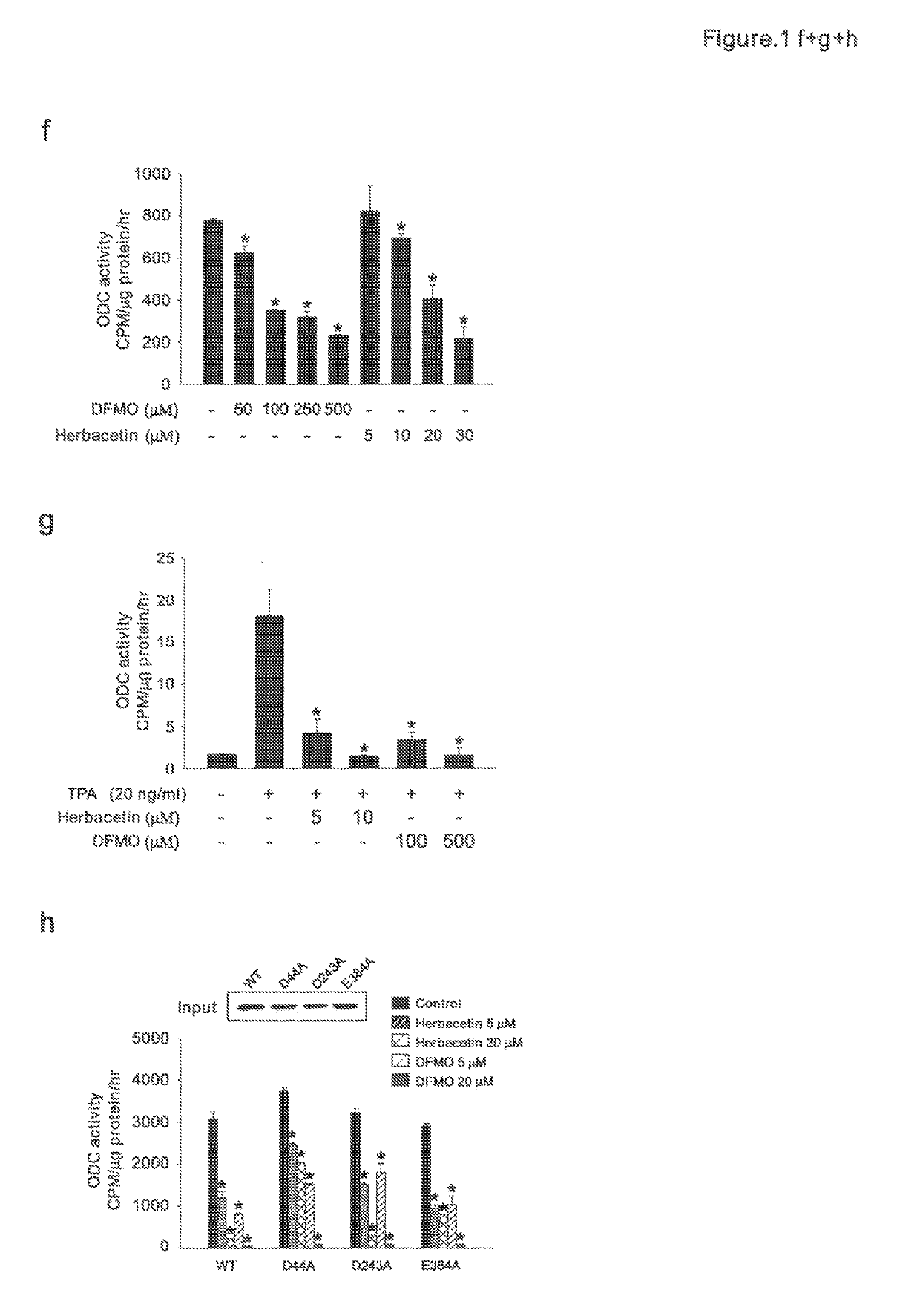
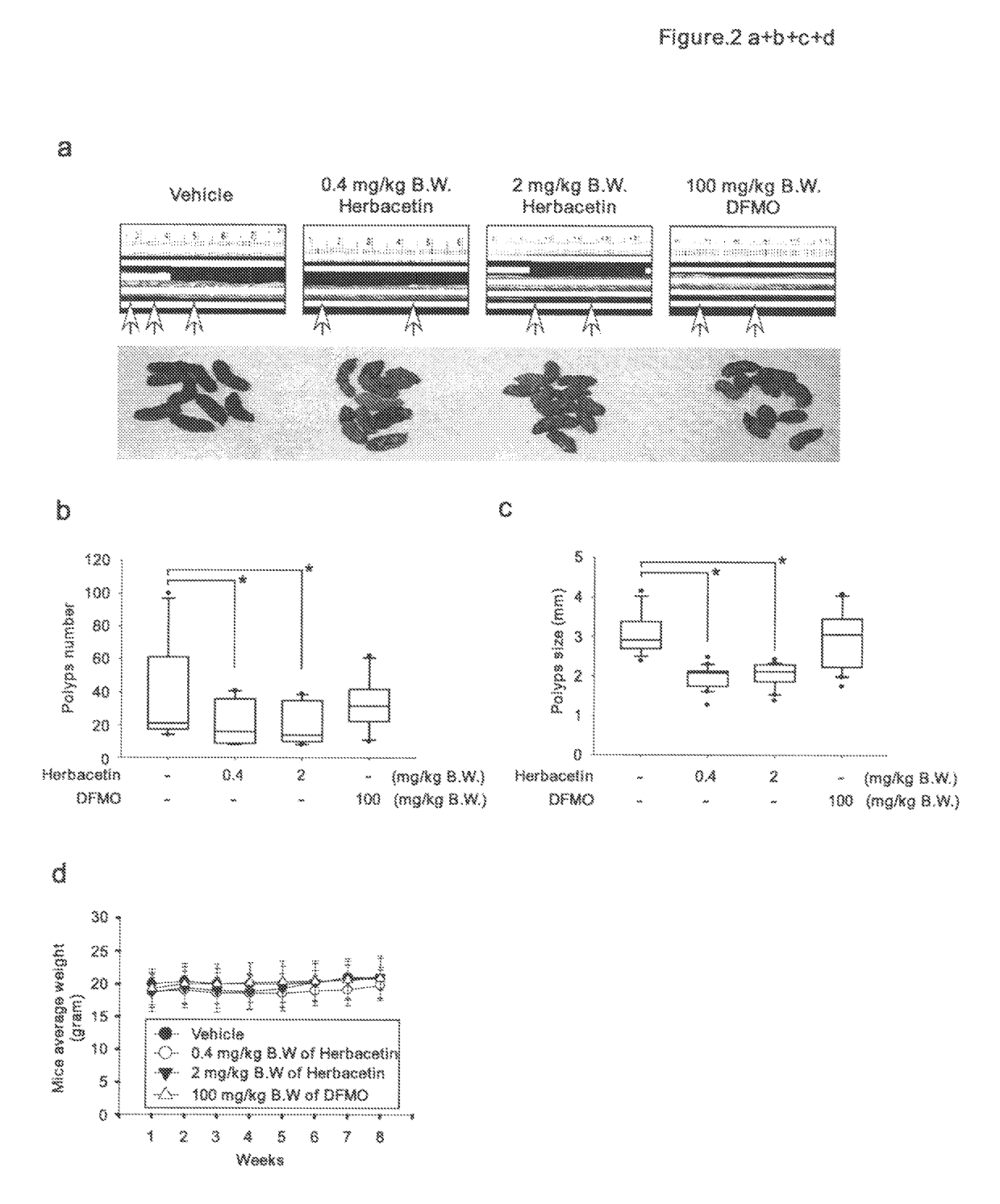
Methods of treating cancer with herbacetin
The invention provides methods, uses and compounds for treating cancers. For example, certain embodiments provide a method for treating cancer in a mammal comprising administering to the mammal an effective amount of 3,5,7,8,4′-Pentahydroxyflavone, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Certain other embodiments of the invention provide methods for inactivating ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) in a cell comprising contacting the cell in vitro or in vivo with an effective amount of 3,5,7,8,4′-Pentahydroxyflavone, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The invention also provides a dermal product comprising 3,5,7,8,4′-Pentahydroxyflavone, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein the product prophylactically or therapeutically treats sunburn or other sun exposure and / or skin cancer in a mammal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com