Semiconductor Element And Manufacturing Method Thereof
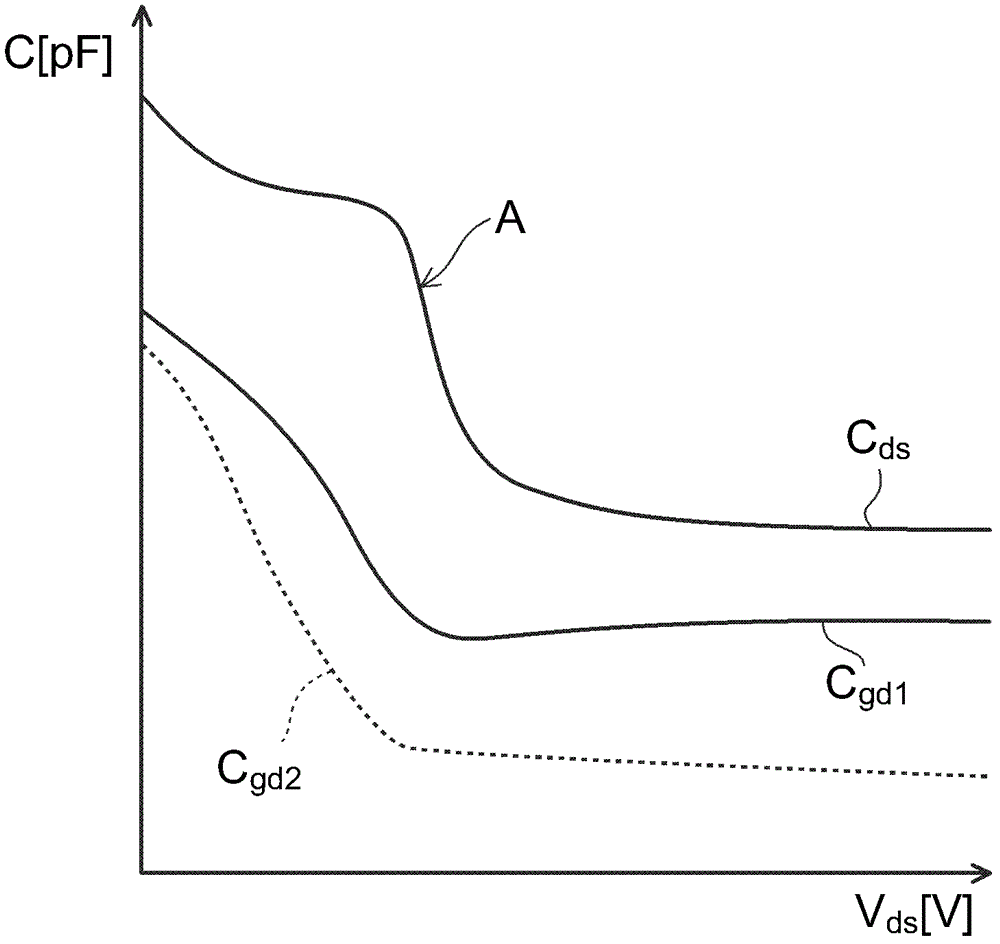
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of semiconductor device output capacitance change, capacitance reduction, high switching noise, etc., to increase output capacitance and reduce switching noise effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
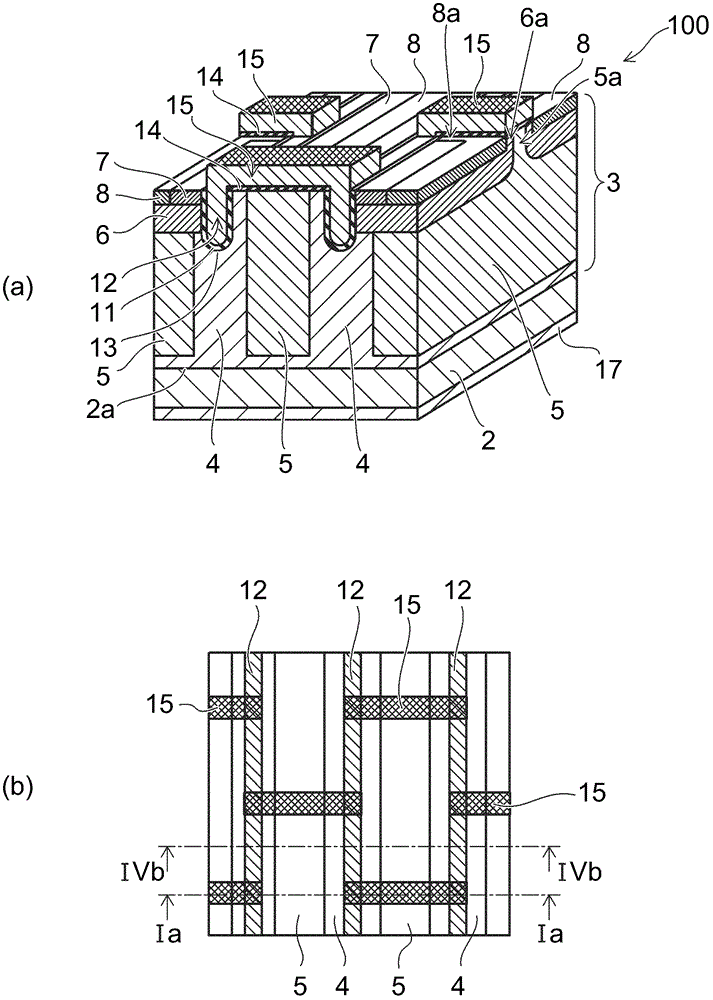
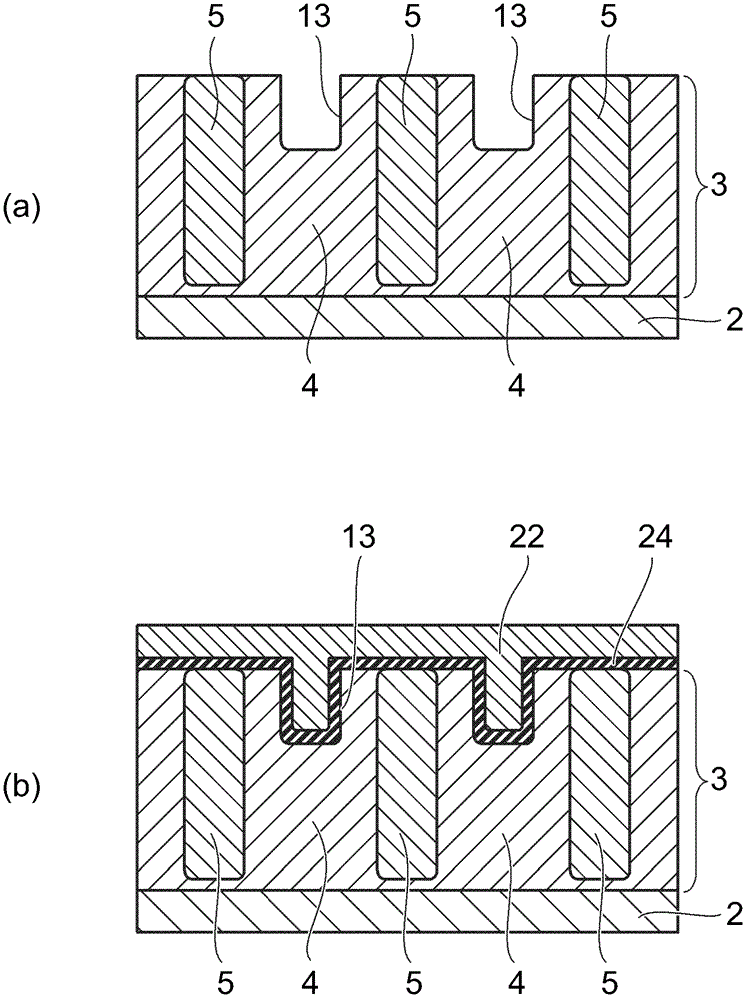
[0019] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing the semiconductor element 100 of this embodiment. figure 1 (a) is a perspective view showing a cross-sectional structure, figure 1 (b) is a plan view showing the arrangement of the gate electrodes 12 and 15 . figure 1 (a) In order to show the gate electrodes 12 and 15 and the n-type source regions 7 and p + The arrangement relationship between the contact regions 8 is shown in a state where the interlayer insulating film 23 and the source electrode 19 are removed (see Figure 8 ).
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown in (a), the semiconductor element 100 includes: the n-type drain layer 2 as the first semiconductor layer; the drift layer 3 as the second semiconductor layer; the gate electrode 12 as the first control electrode, buried in the The surface of the layer 3 faces the inside of the trench 13 arranged in the direction of the n-type drain layer; and the gate electrode 15 as the second control electrode is arranged on ...
no. 2 approach
[0085] Figure 13 It is a schematic diagram showing the structure of the semiconductor element 500 of the second embodiment. Figure 13 (a) shows the source electrode 19 and the interlayer insulating film 23 (refer to Figure 8 ) is a plan view of a part of the chip surface of the semiconductor element 500 other than ). Figure 13 (b) is a perspective view schematically showing the structure of the semiconductor element 500 .
[0086] In the semiconductor element 500 , the gate electrode 12 is provided on the surface of the n-type pillar 4 along the direction in which the n-type pillar 4 extends. Furthermore, the gate electrode 15 is formed on substantially the entire surface of the region of the drift layer 3 where the n-type column 4 and the p-type column 5 are provided with the gate insulating film 11 interposed therebetween.
[0087] The p-type base regions 6 are provided scattered on the surface of the drift layer 3 when viewed in plan view parallel to the main surface...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com