Transmitter with quantization noise compensation
A technology for quantizing noise and transmitter, applied in the field of transmitter, which can solve the problems of reducing transmitter power efficiency, increasing power consumption, large insertion loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 600
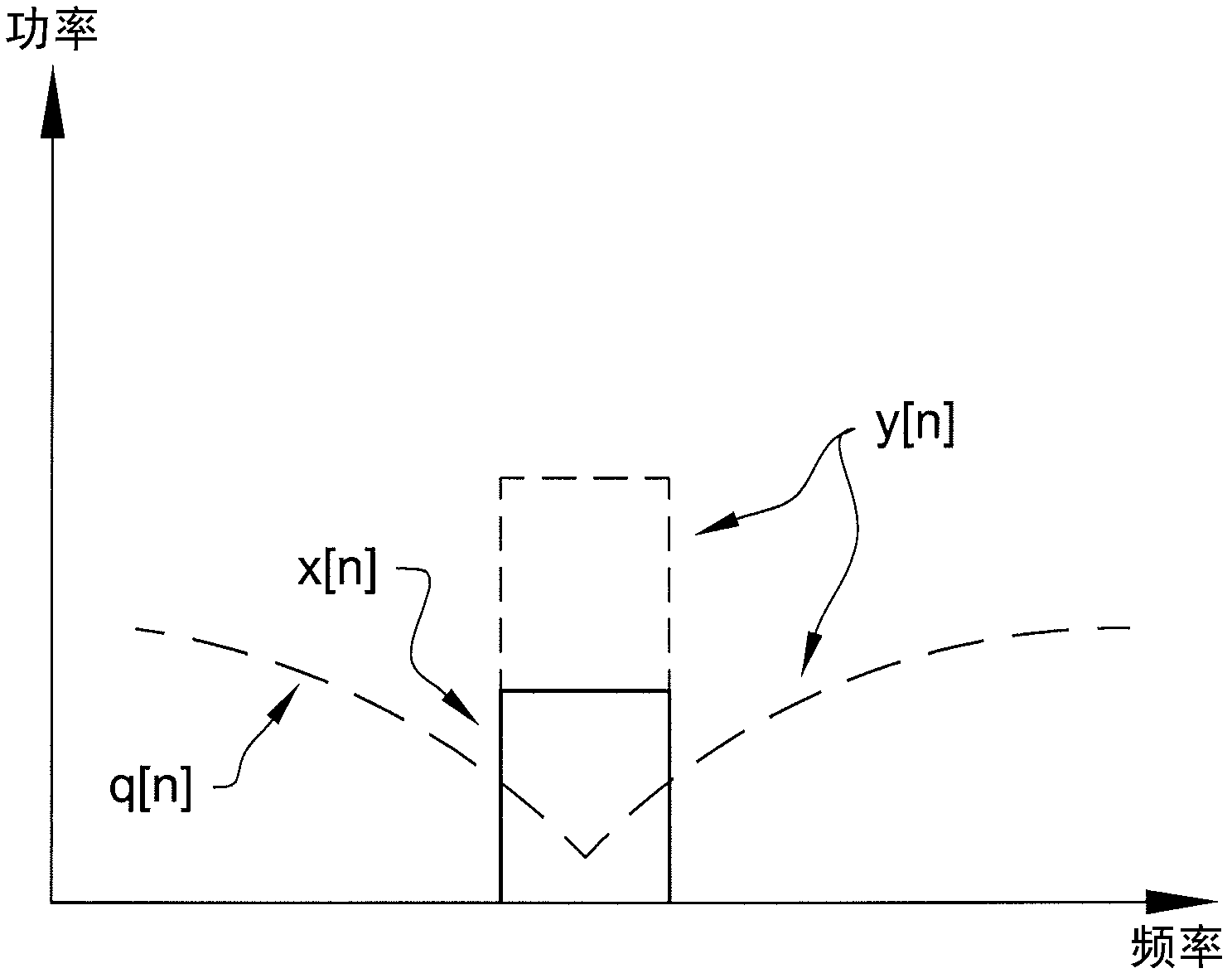
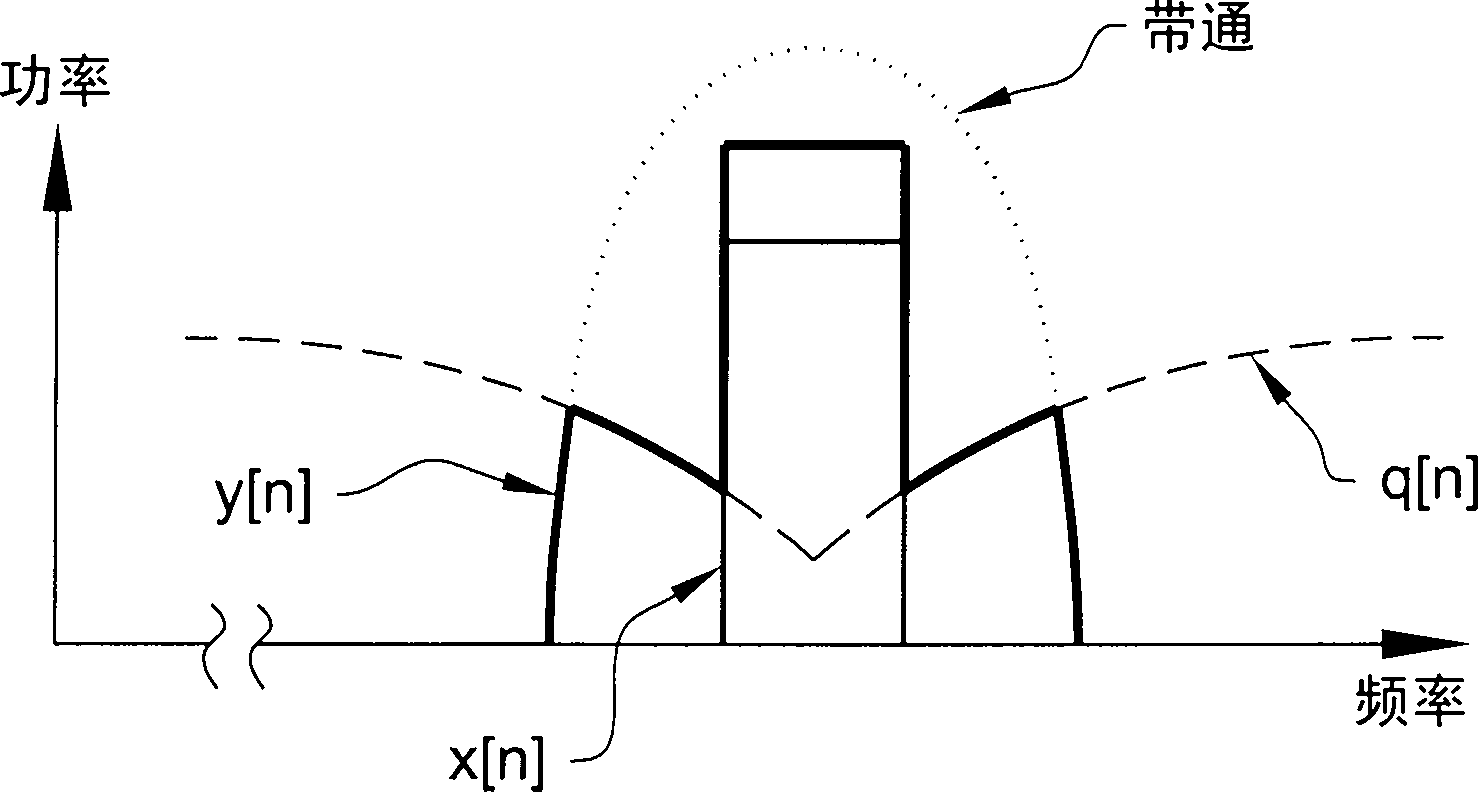
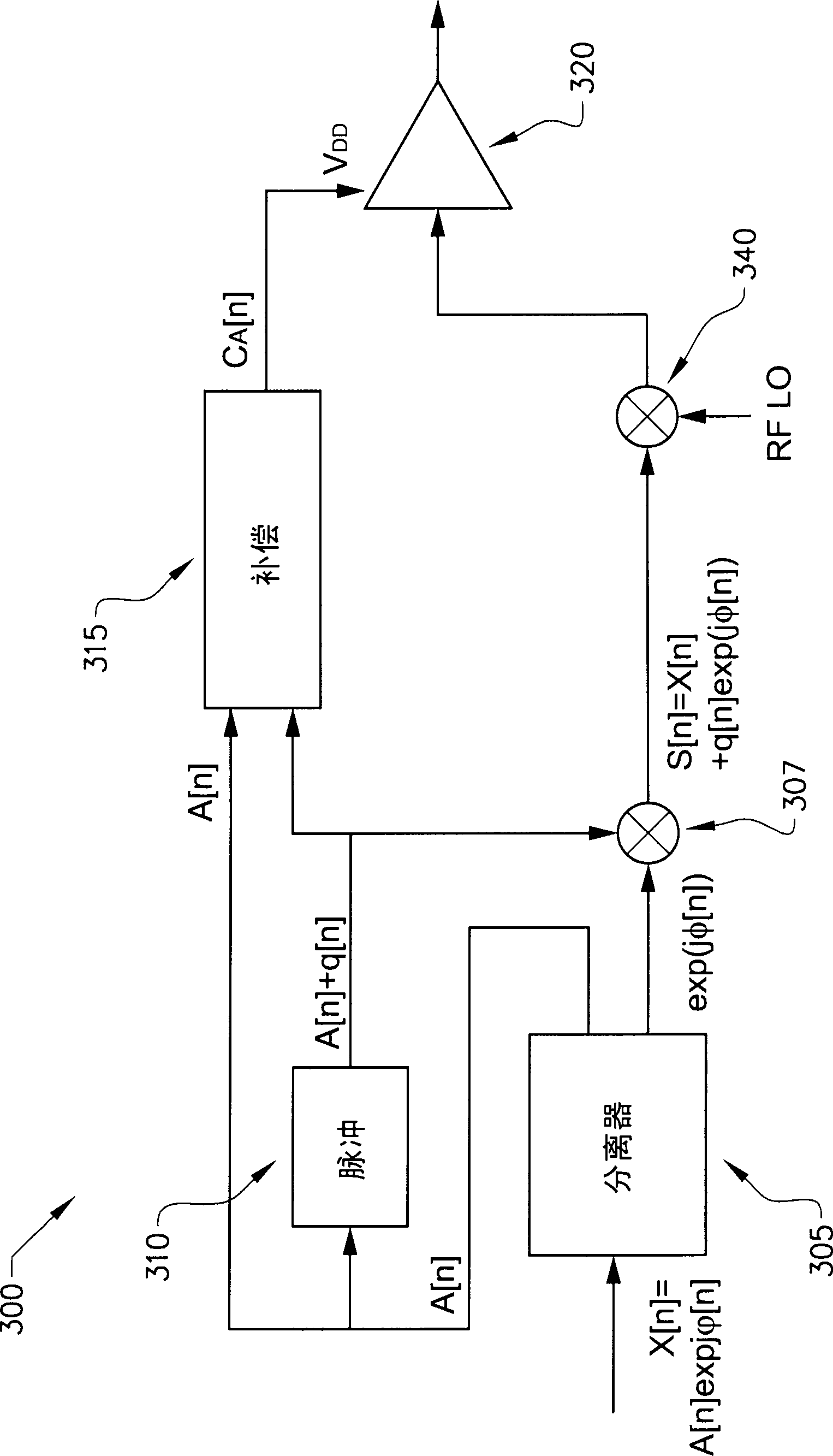
[0049] The compensation signal generator 315 of embodiment 600 has two input signals, one of which is the input signal x[n], and the other signal is the output from the mixer 307 (denoted S[n]). thus, Figure 5 The two input signals to the compensation signal generator 315 in are x[n] and Using the input signal x[n] as one of the input signals to the compensation signal generator 315 is achieved by "splitting" the input signal x[n] before the component separator 305, so that one "branch" of x[n] is related to the compensation The signal generator 315 is connected and the other "branch" of x[n] is used as the input signal to the signal component separator 305 .
[0050] As mentioned above, in Figure 5 In an embodiment of , the output S[n] from the mixer 307 is also split such that one "branch" of S[n] is used as an input to the compensation signal generator 315, and one "branch" of S[n] Used as an input to the first delay circuit 630 .
[0051] In contrast to the previo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com