Method for testing force characteristic of linear electric motor
A linear motor and characteristic testing technology, applied in the direction of motor generator testing, force/torque/power measuring instrument, measuring device, etc., to achieve the effect of complete functions, high reliability, and improved test accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
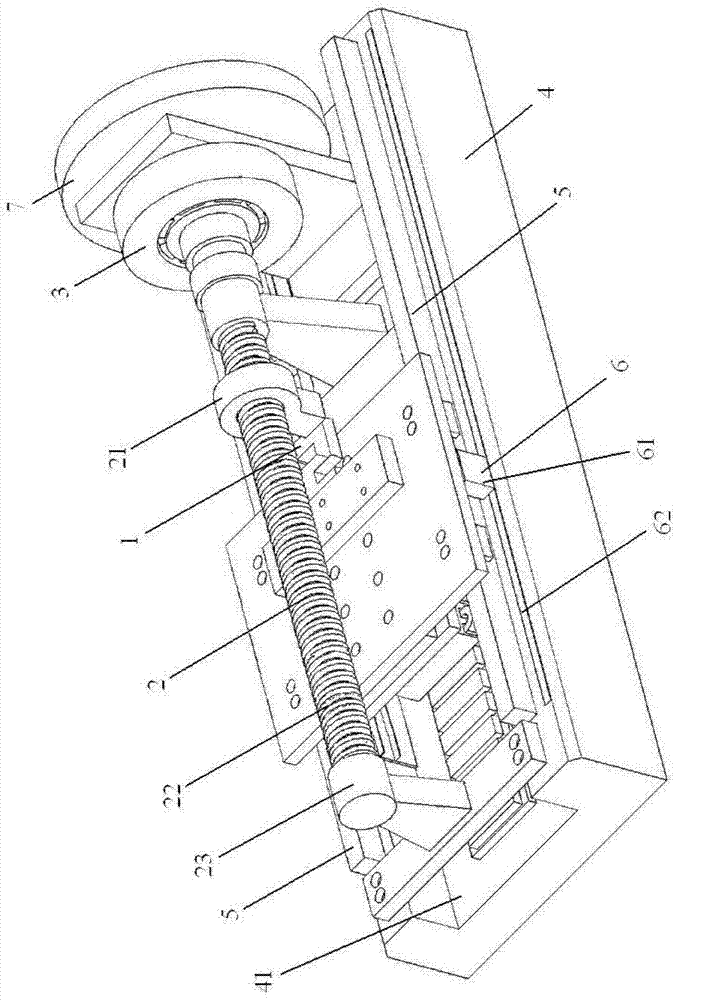
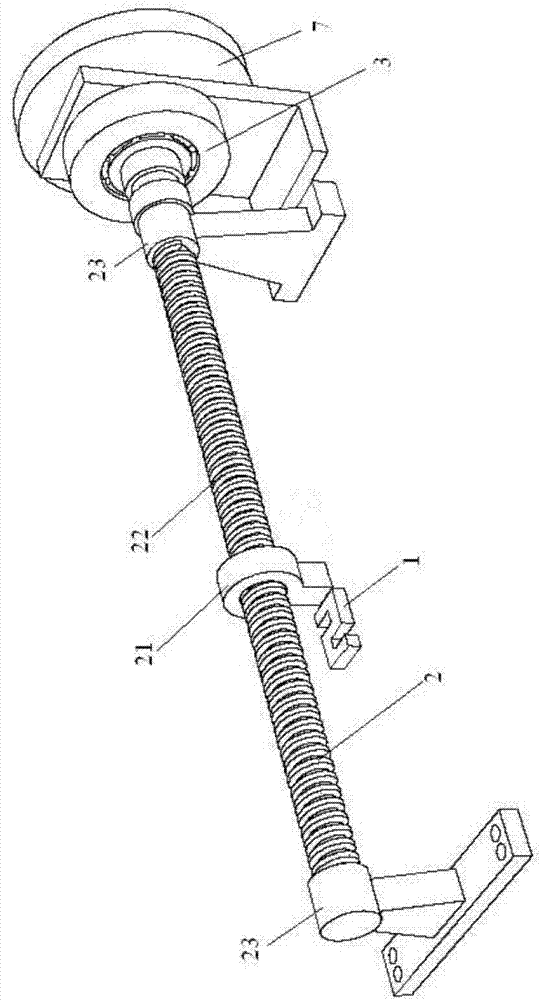
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 and figure 2 This embodiment is described. In this embodiment, the linear motor force characteristic test device includes a tension pressure sensor 1, a ball screw 2, a loading servo motor 3, a base 4, a guide rail 5 and a displacement sensor 6;
[0022] Pull pressure sensor 1, the two ends of pull pressure sensor 1 are respectively connected between the nut 21 of ball screw 2 and the mover of the linear motor under test, for testing the force applied to the mover of the linear motor under test, namely Test the output force of the linear motor under test;
[0023] The ball screw 2 is used to convert the rotary motion of the loaded servo motor 3 into the linear motion of the mover of the linear motor under test; the screw 22 of the ball screw 2 is coaxially connected with the rotor of the loaded servo motor 3, and the ball screw 2 Including nut 21, screw rod 22 and fixed bracket 23;
[0024] The servo motor 3 is loa...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment is that it also includes an inertia flywheel 7, and the inertia flywheel 7 is located on the loading servo motor 3 to reduce the speed fluctuation during mechanical operation. The inertia flywheel 7 is installed on the rotating shaft of the screw rod 22 of the ball screw 2 and the rotor of the loading servo motor 3, and an electromagnetic clutch, magnetic coupling or torque limiter is arranged between the inertia flywheel 7 and the loading servo motor. When the rotational speed increases, the kinetic energy of the flywheel increases and the energy is stored; when the rotational speed decreases, the kinetic energy of the flywheel decreases and the energy is released. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that the base 4 has a rectangular groove 41, the stator of the linear motor to be tested is fixed in the rectangular groove 41, and the platforms on both sides of the rectangular groove 41 Guide rails 5 are respectively arranged on the shoulders, and the guide members of the guide rails 5 are arranged at the bottom of the mover of the linear motor under test. The guide rail used by the mover of the tested linear motor is an air bearing guide rail, a magnetic bearing guide rail or a linear rolling guide rail. Other compositions and connection modes are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com