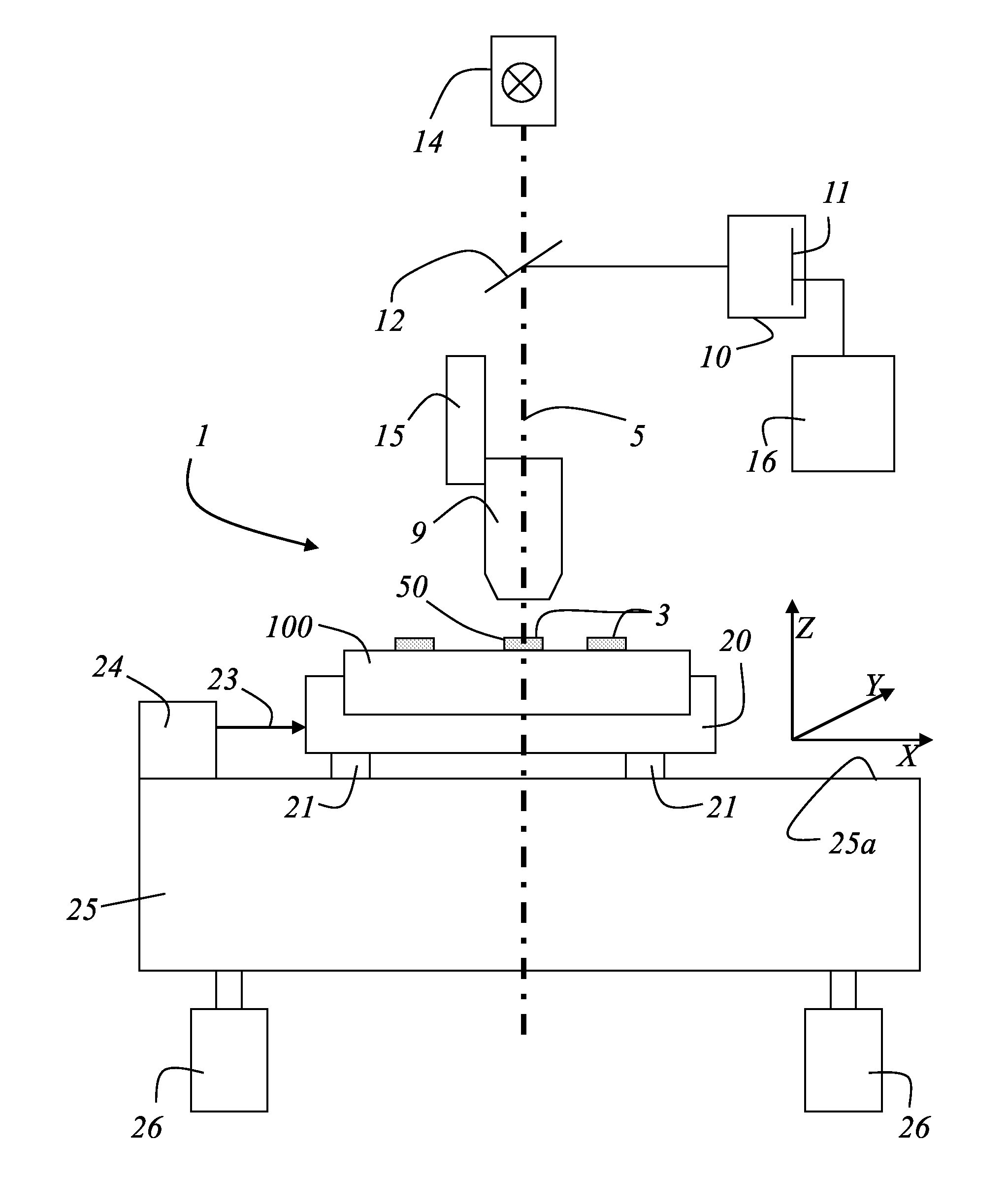
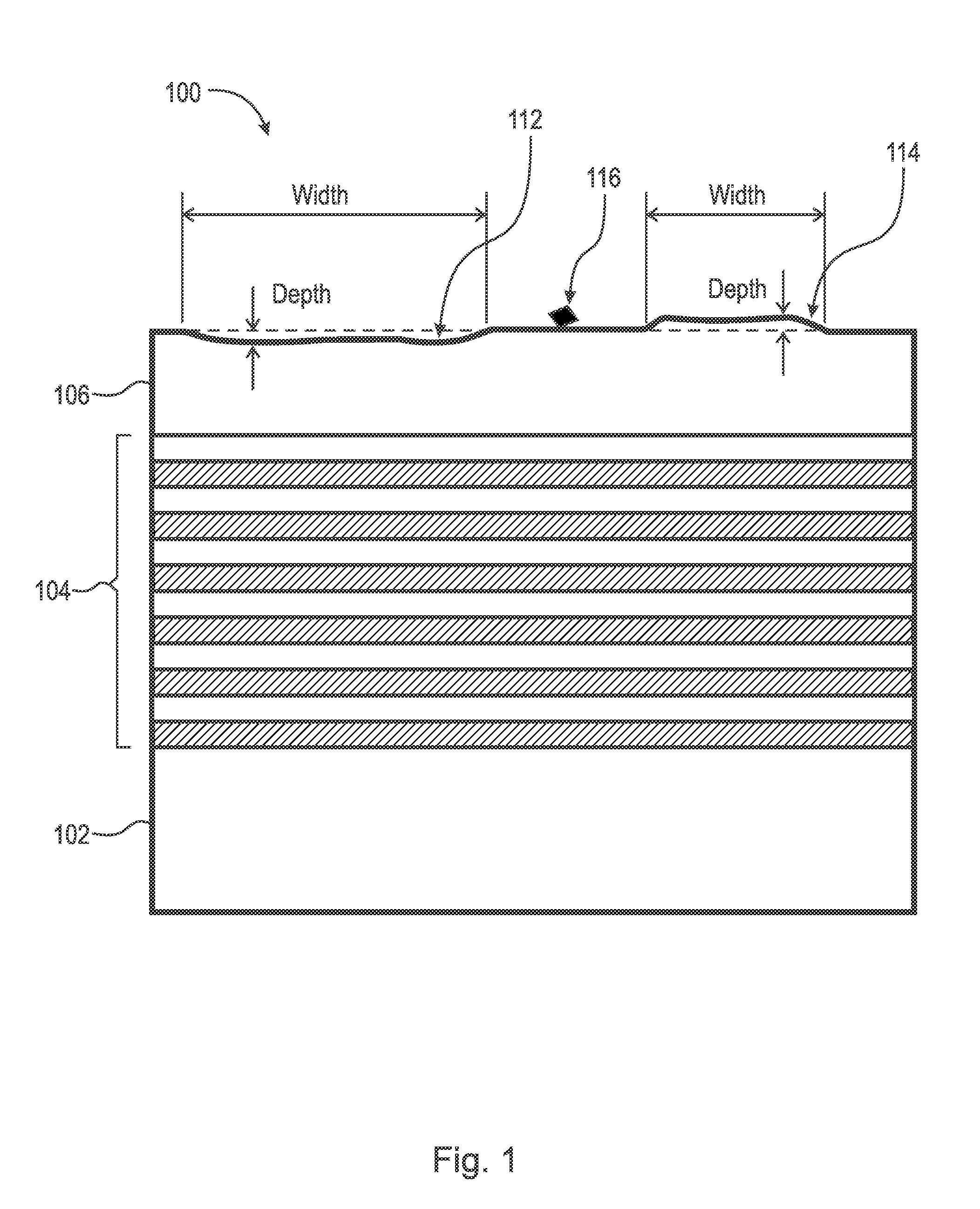
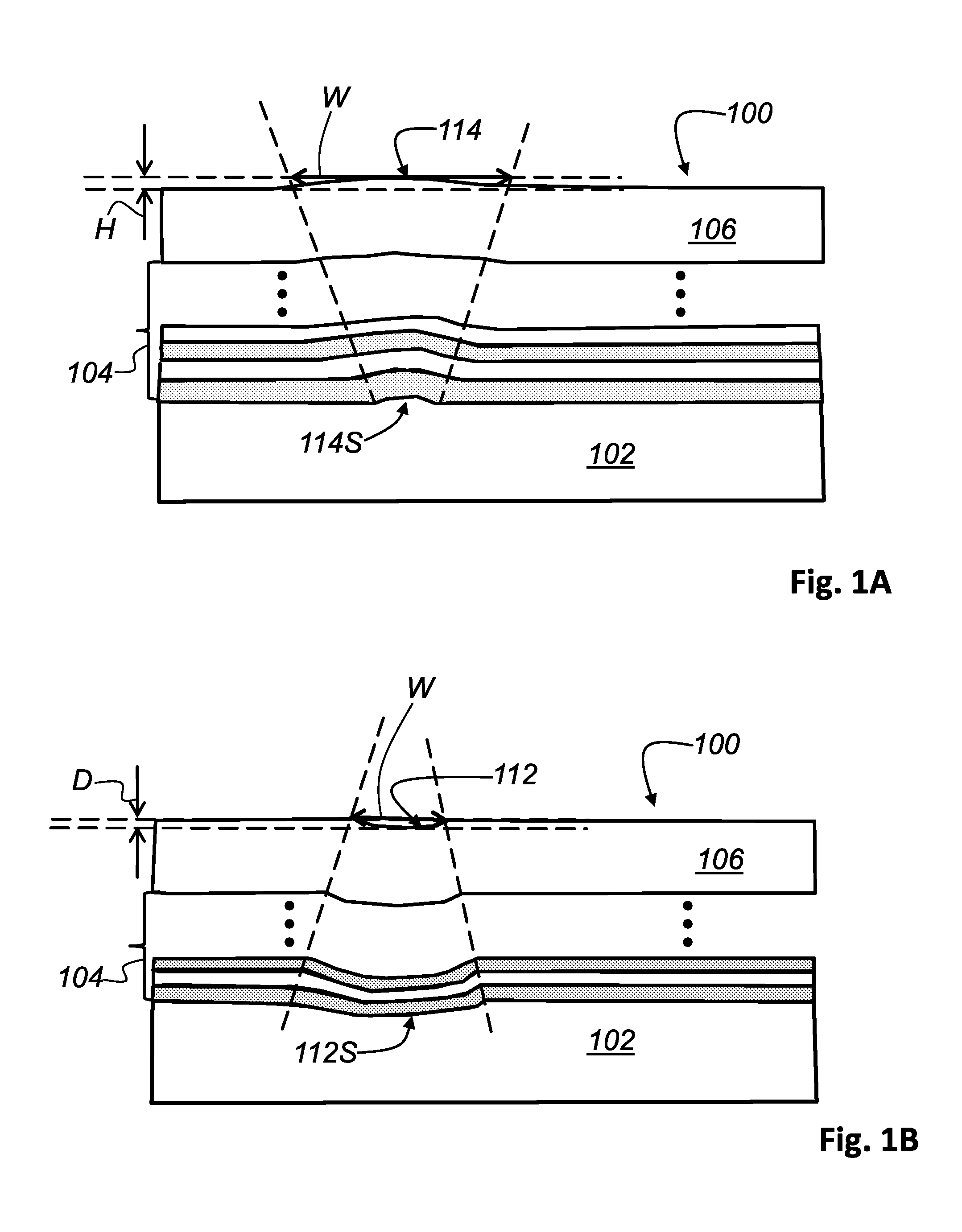
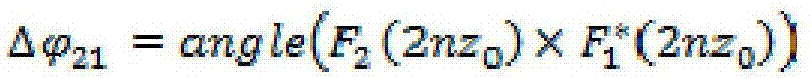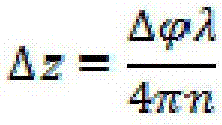Patents
Literature
950results about How to "Reduce vibration effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Imaging system for vehicle
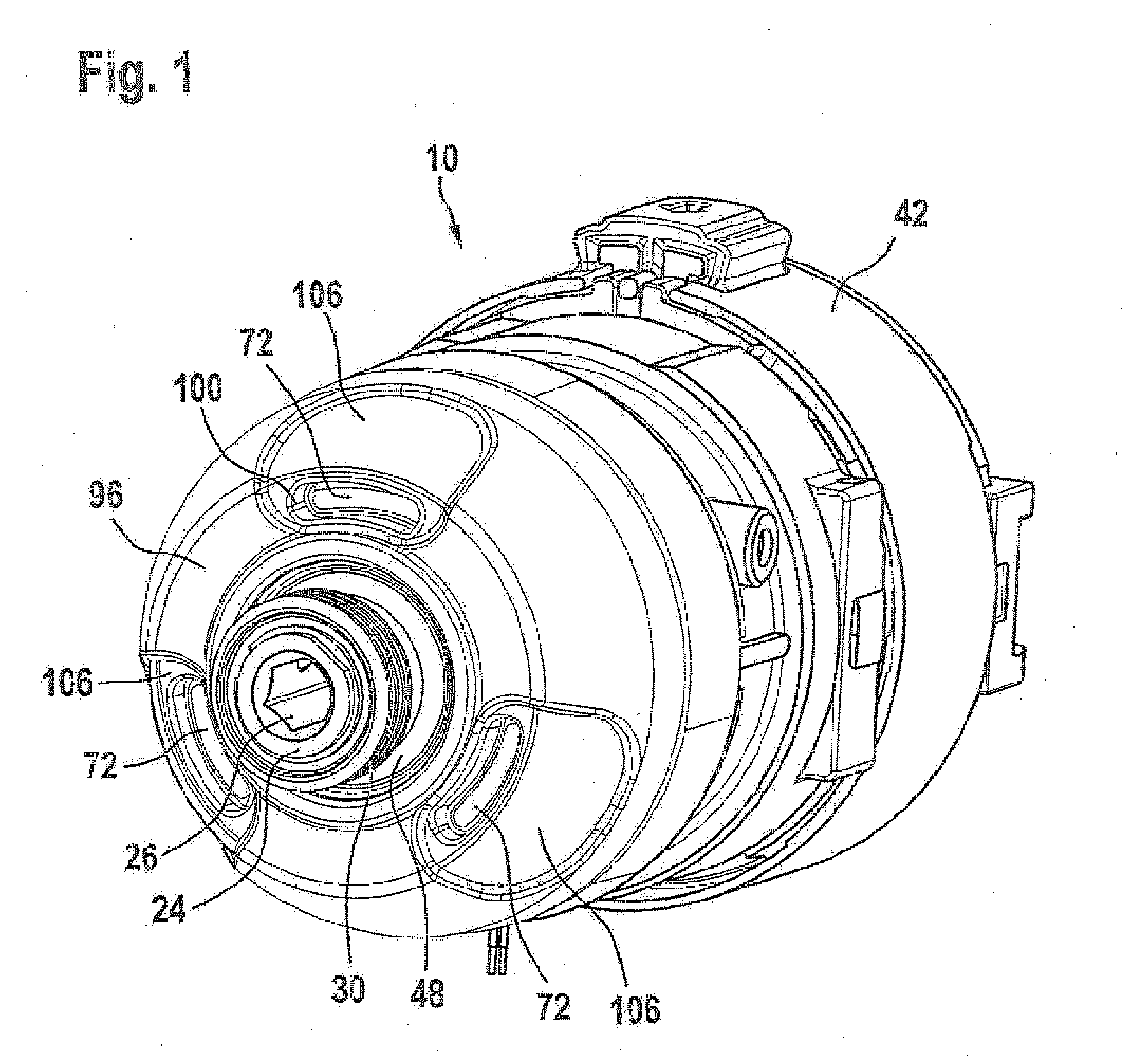
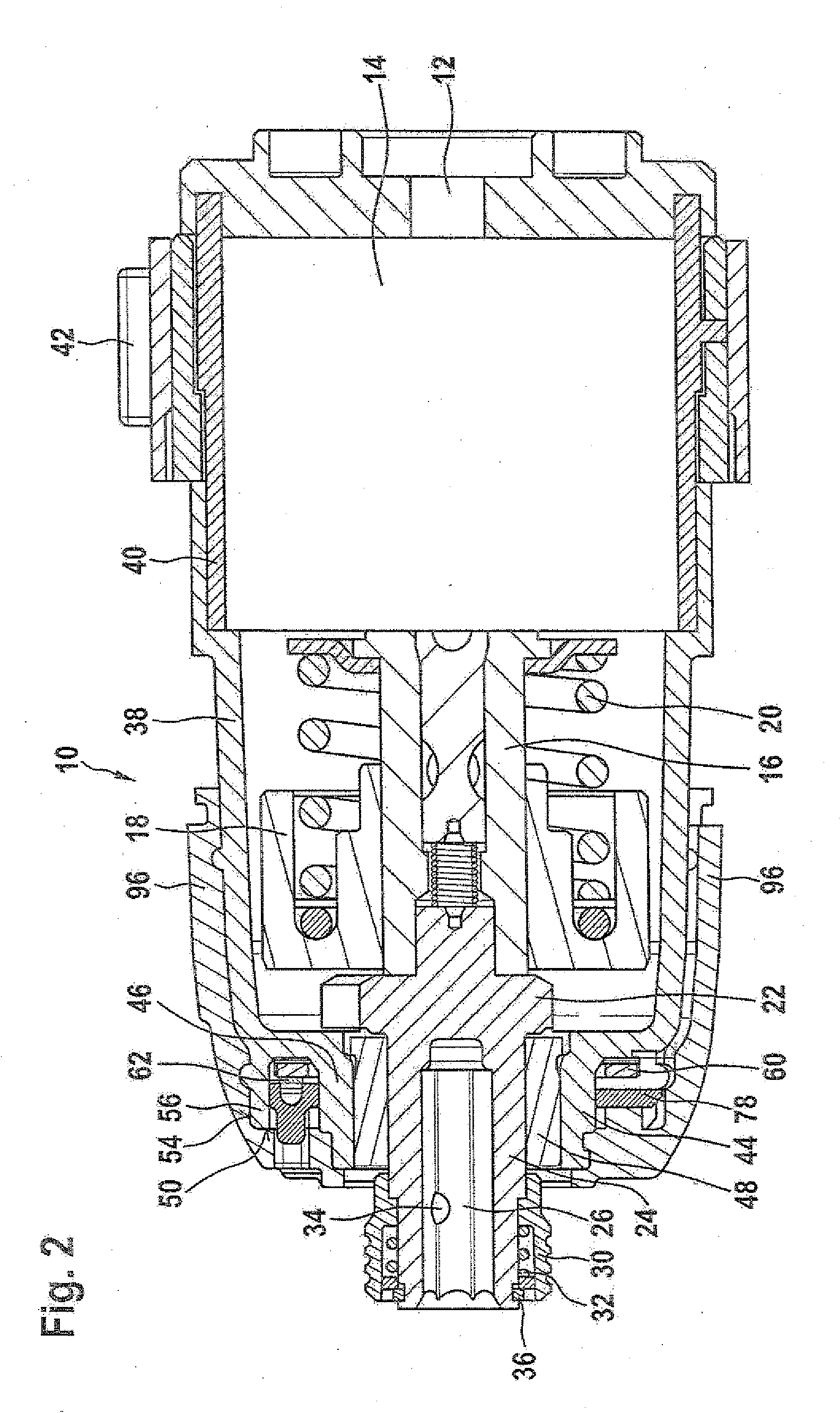
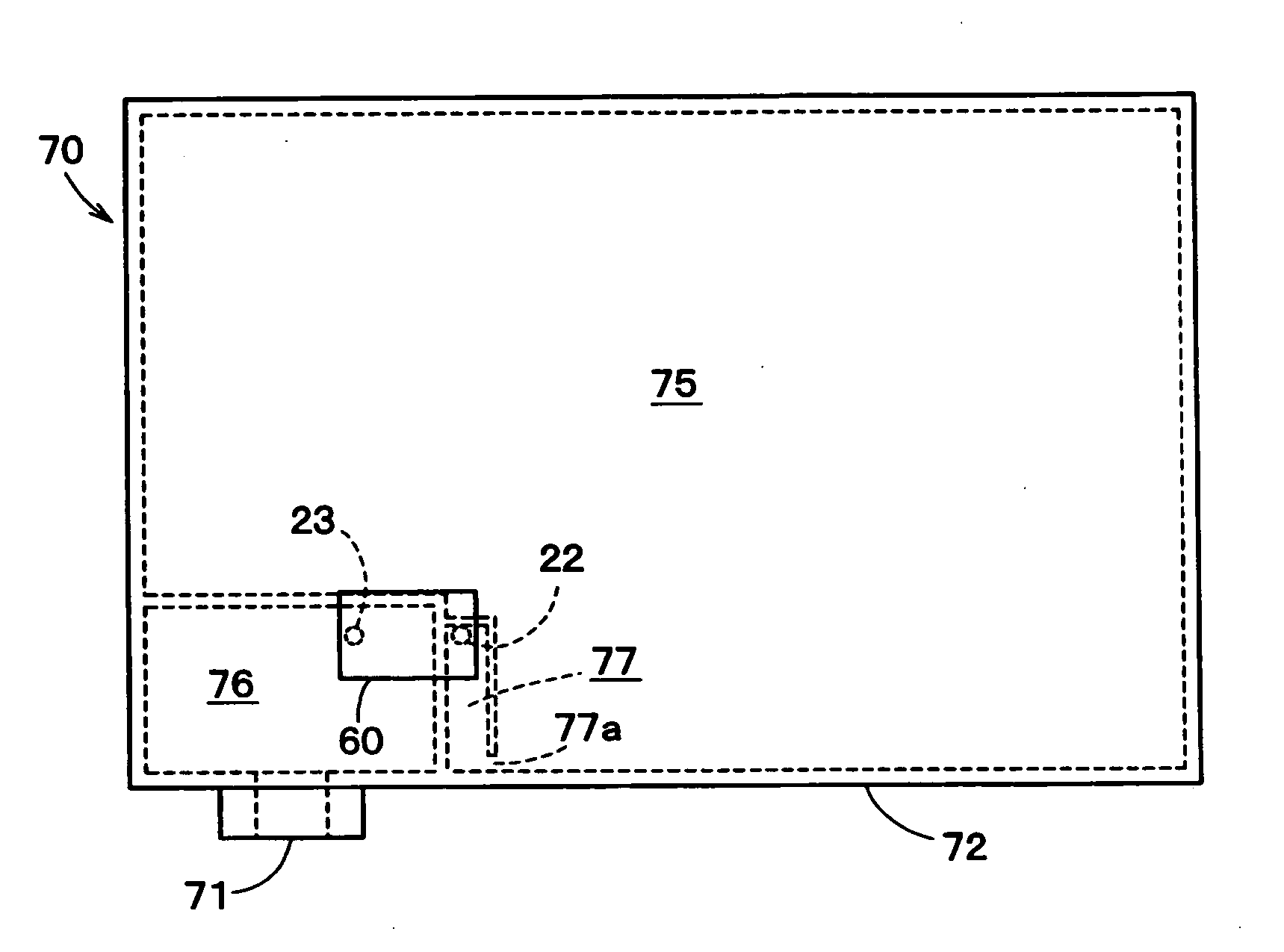
ActiveUS7965336B2Reduce vibration effectsReduce foggingTelevision system detailsPrintersWater vaporCamera module
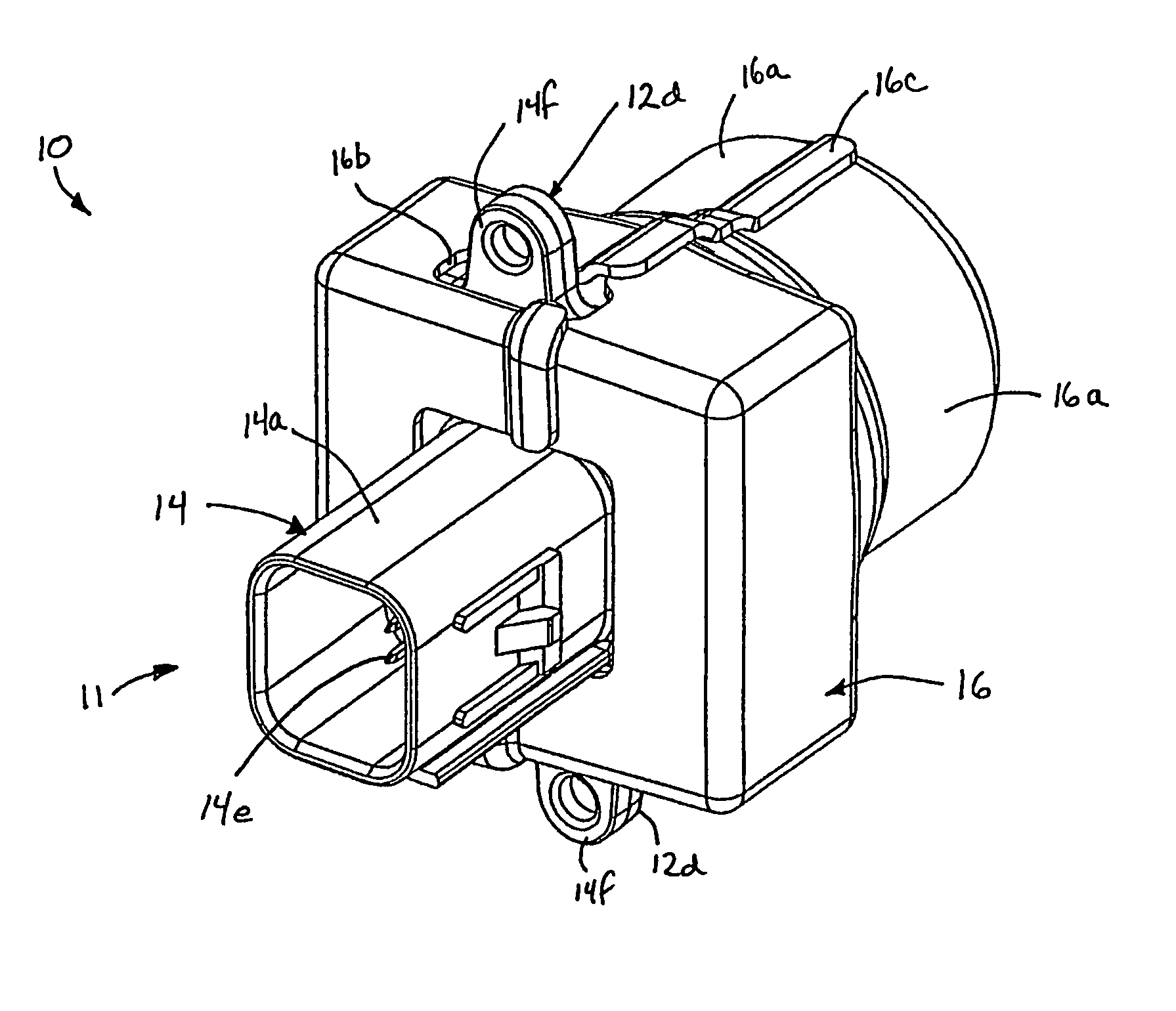
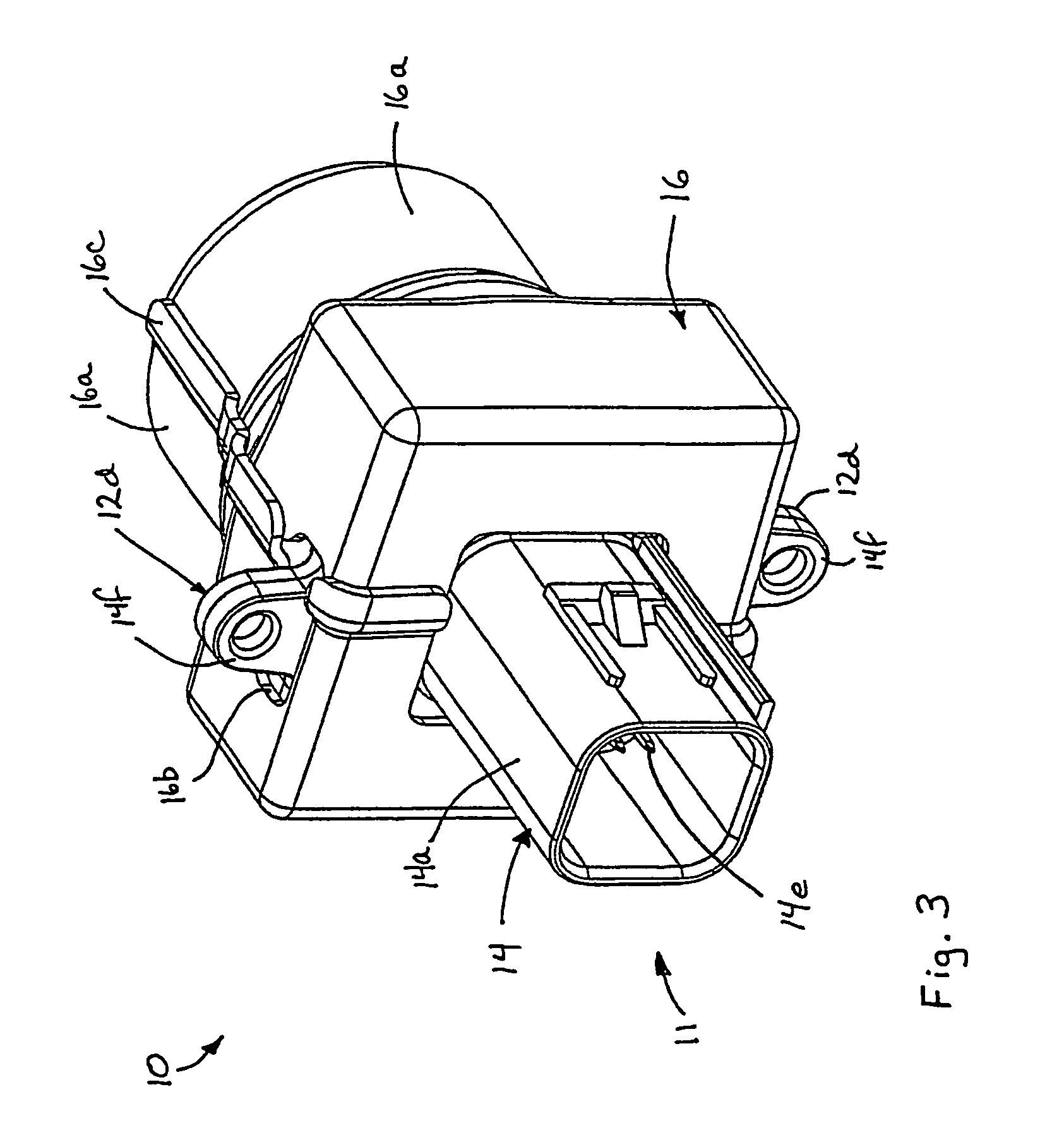
An imaging system for a vehicle includes a camera module positionable at the vehicle and a control. The camera module includes a plastic housing that houses an image sensor, which is operable to capture images of a scene occurring exteriorly of the vehicle. The control is operable to process images captured by the image sensor. The portions of the housing may be laser welded or sonic welded together to substantially seal the image sensor and associated components within the plastic housing. The housing may include a ventilation portion that is at least partially permeable to water vapor to allow water vapor to pass therethrough while substantially precluding passage of water droplets and / or other contaminants. The housing may be movable at the vehicle between a stored position and an operational position, where the image sensor may be directed toward the exterior scene.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
Noise reduction for analyte detection systems
InactiveUS20070258083A1Improve accuracyReduce contentCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysicsMicrophonics
Methods and apparatus are provided for determining the concentration of an analyte in a sample, such as an analyte in a sample of bodily fluid. Some embodiments use a synchronous demodulator and digital filter to reduce microphonic signal content. Some embodiments monitor the microphonic signal content and “hold off” on making a measurement until vibrations subside. Monitoring can be performed using an accelerometer or other vibration sensor. An algorithm can be used to examine the detector output signal and detect excessive microphonic components, making an accelerometer unnecessary.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Contained environmental control system for mobile event data recorder
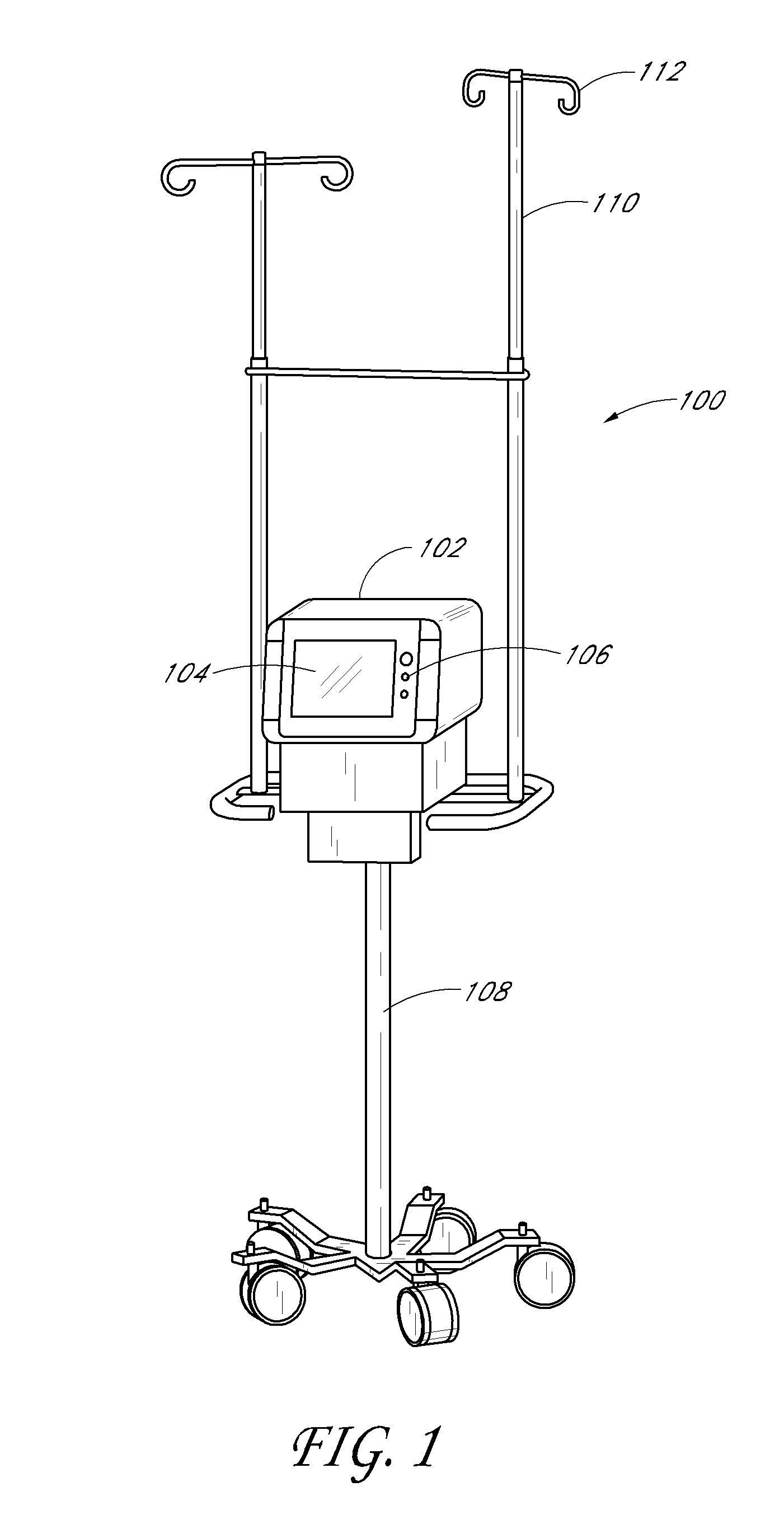
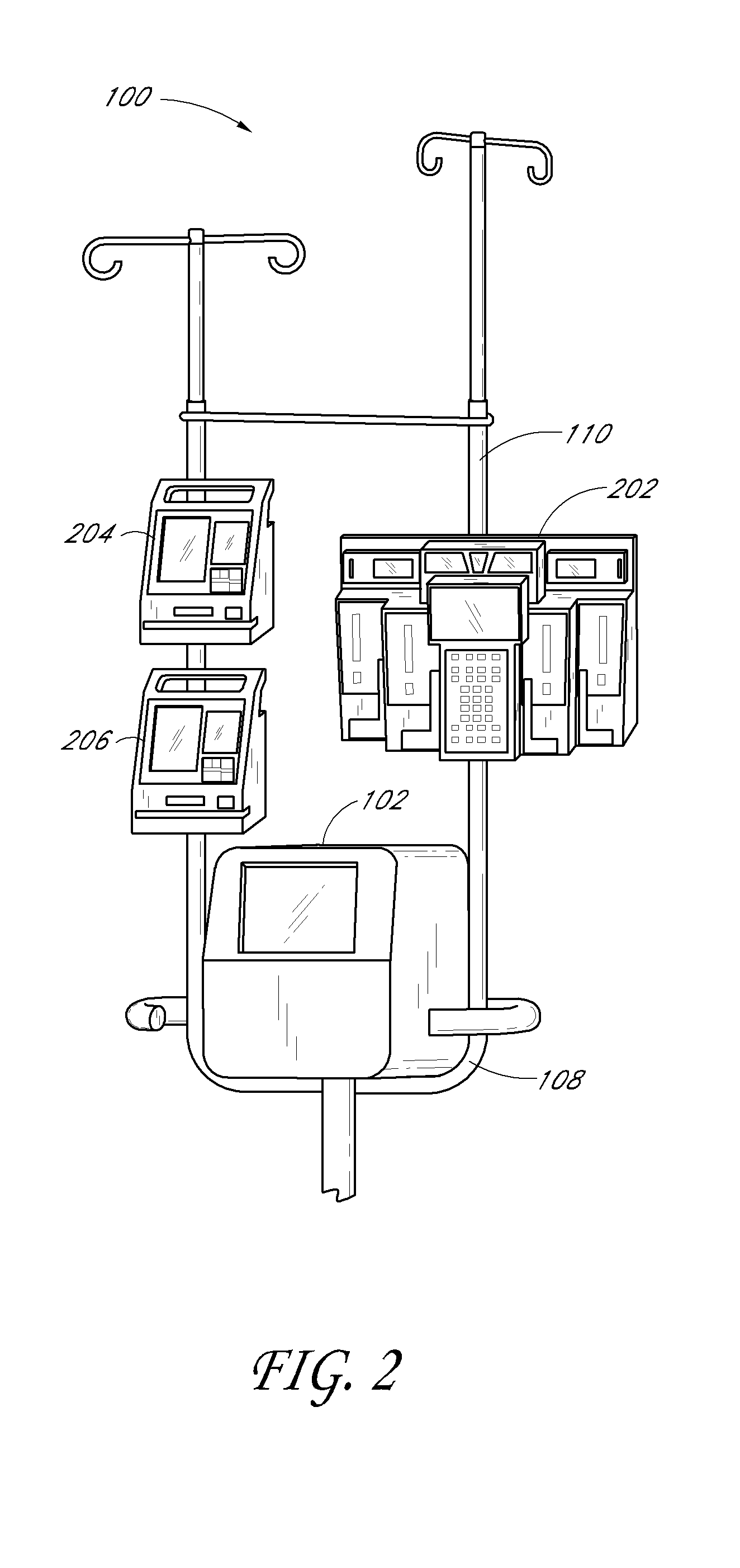
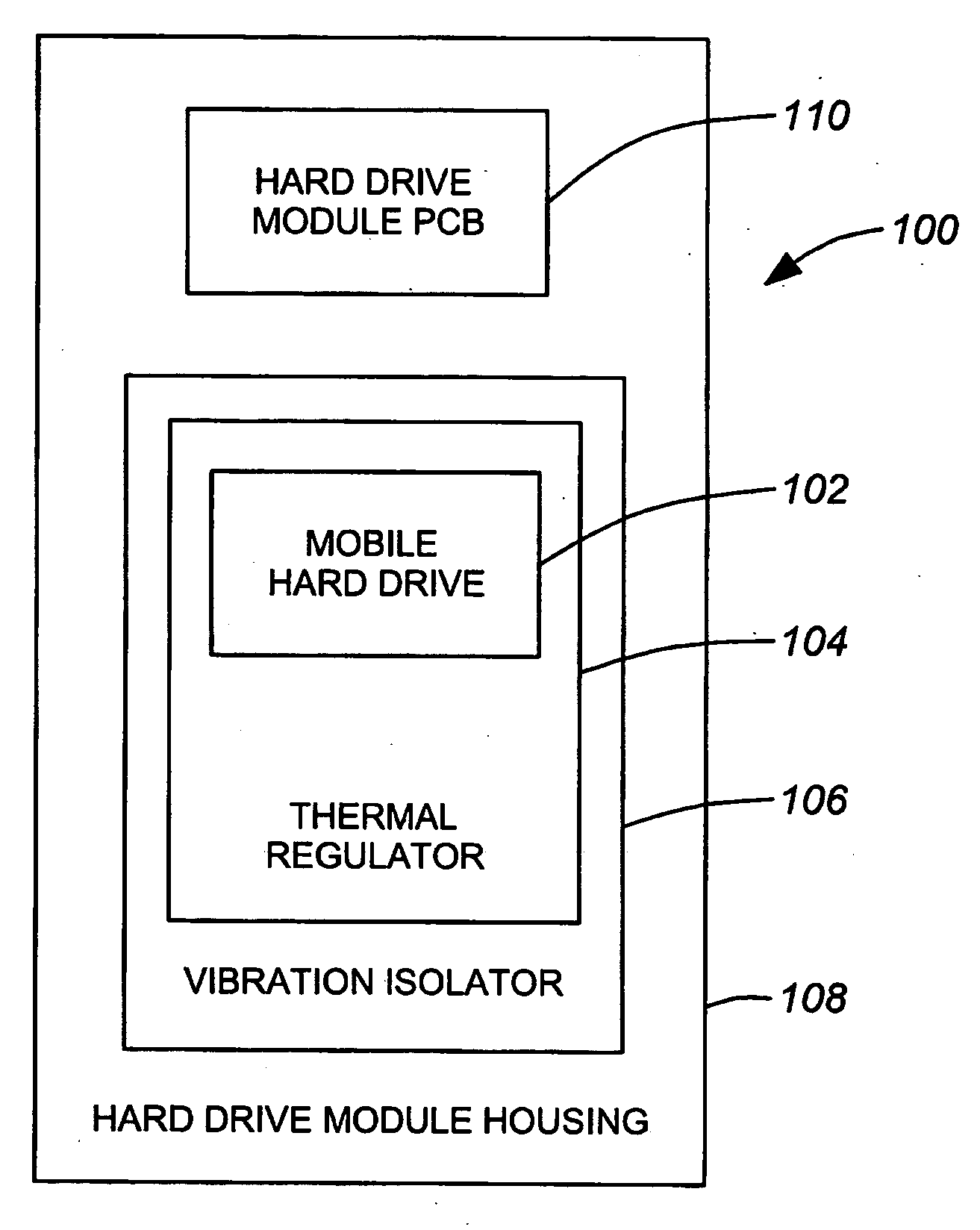
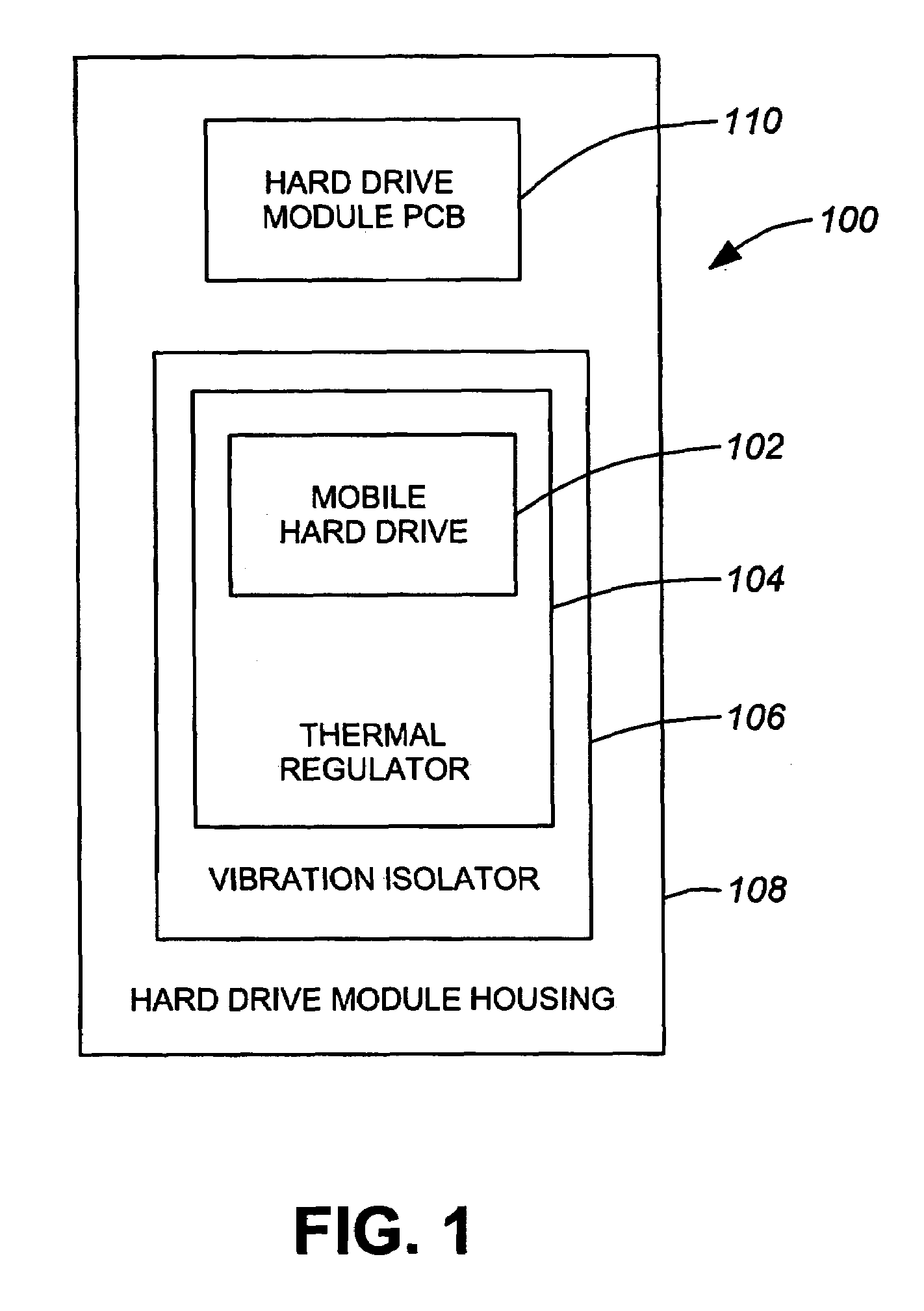
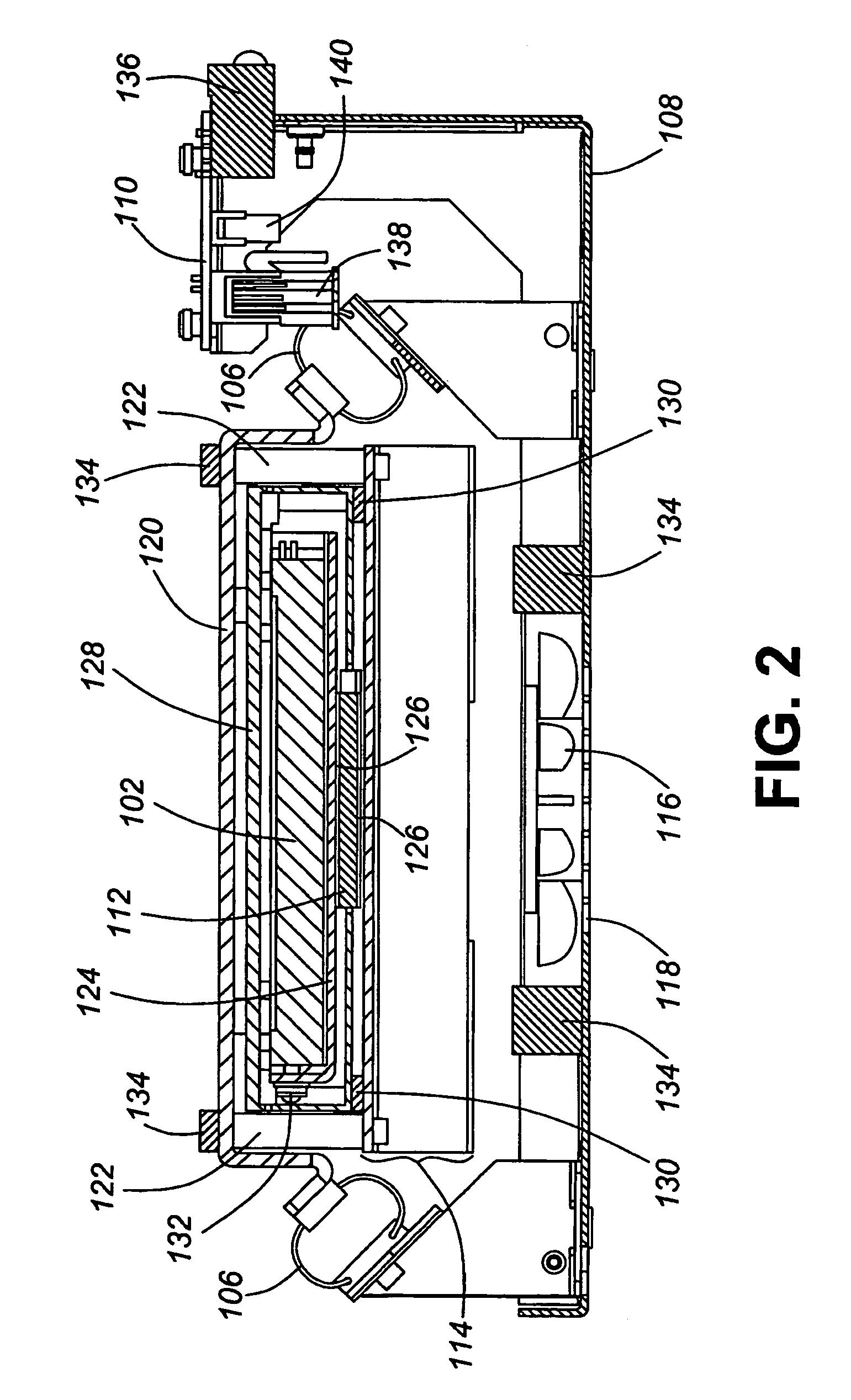
ActiveUS20060232891A1Reduce vibration effectsFast heat conductionReducing temperature influence on carrierDisposition/mounting of recording headsData packHard disc drive
An environmental control system, or data pack, is provided in accordance with embodiments of the present invention. The system allows for audio and video recording on hard drive media in situations where temperature, vibration and humidity would otherwise have prevented the use of such technology. The system can be used in conjunction with an event recorder for use in motor vehicles, trains and the like. The environmental control system includes a thermoelectric module connected to the hard drive and to a housing. The thermoelectric module is for transferring heat between the hard drive and the housing in response to an applied voltage in order to maintain a hard drive temperature within a hard drive operable temperature range. The vehicle operating temperature range includes temperatures outside the hard drive operable temperature range.
Owner:MARCH NETWORKS
Image processing device, focal plane distortion component calculation method, image processing program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20100214423A1Quality improvementImprove frame qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingMotion vector
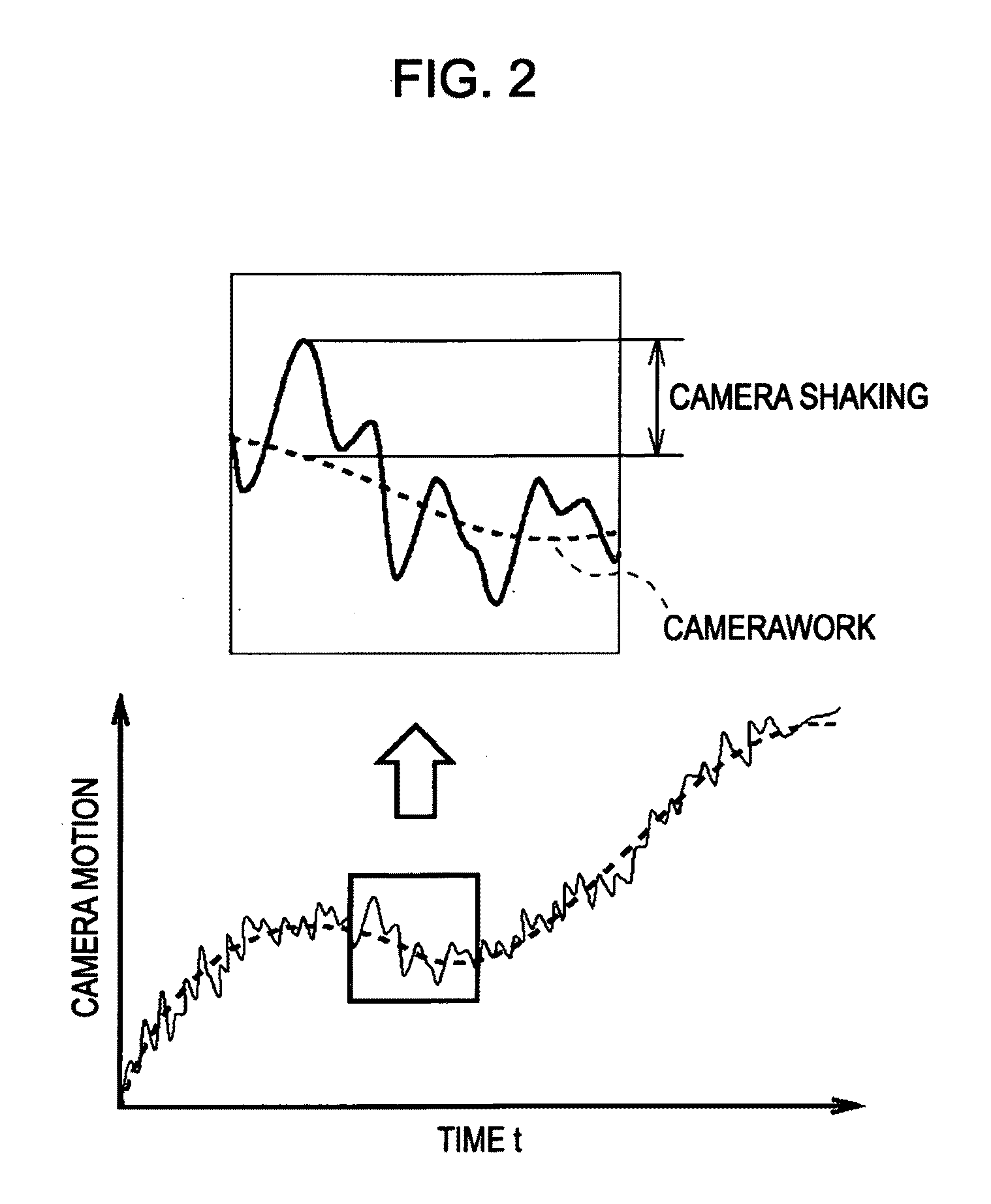
An image processing device includes: a motion vector receiving unit configured to receive, from frame image data made up of frame images, motion vectors representing motion of the frame images; a modeling unit configured to model the motion vector, received from the motion vector receiving unit, to a component separation expression in which a camera motion component and a focal plane distortion component are separated, using component parameters respectively representing camera motion which is motion of a camera, and the amount in change in focal plane distortion; and a component calculation unit configured to calculate the component parameters used in the component separation expression, thereby calculating the focal plane distortion component in the motion vector.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image processing device, camera motion component calculation method, image processing program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20100208087A1Avoid distractionReduce vibration effectsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingMotion vector
An image processing device, comprising:a motion vector detection unit configured to detect, from frame image data made up of frame images, motion vectors representing motion of the frame images;a modeling unit configured to model the motion vector, detected by the motion vector detection unit, to a component separation expression in which a camera motion component and a focal plane distortion component are separated, using unknown component parameters respectively representing camera motion which is motion of a camera, and the amount in change in focal plane distortion; anda component calculation unit configured to calculate the component parameters used in the component separation expression, thereby calculating the camera motion component in the motion vector.
Owner:SONY CORP
Contained environmental control system for mobile event data recorder
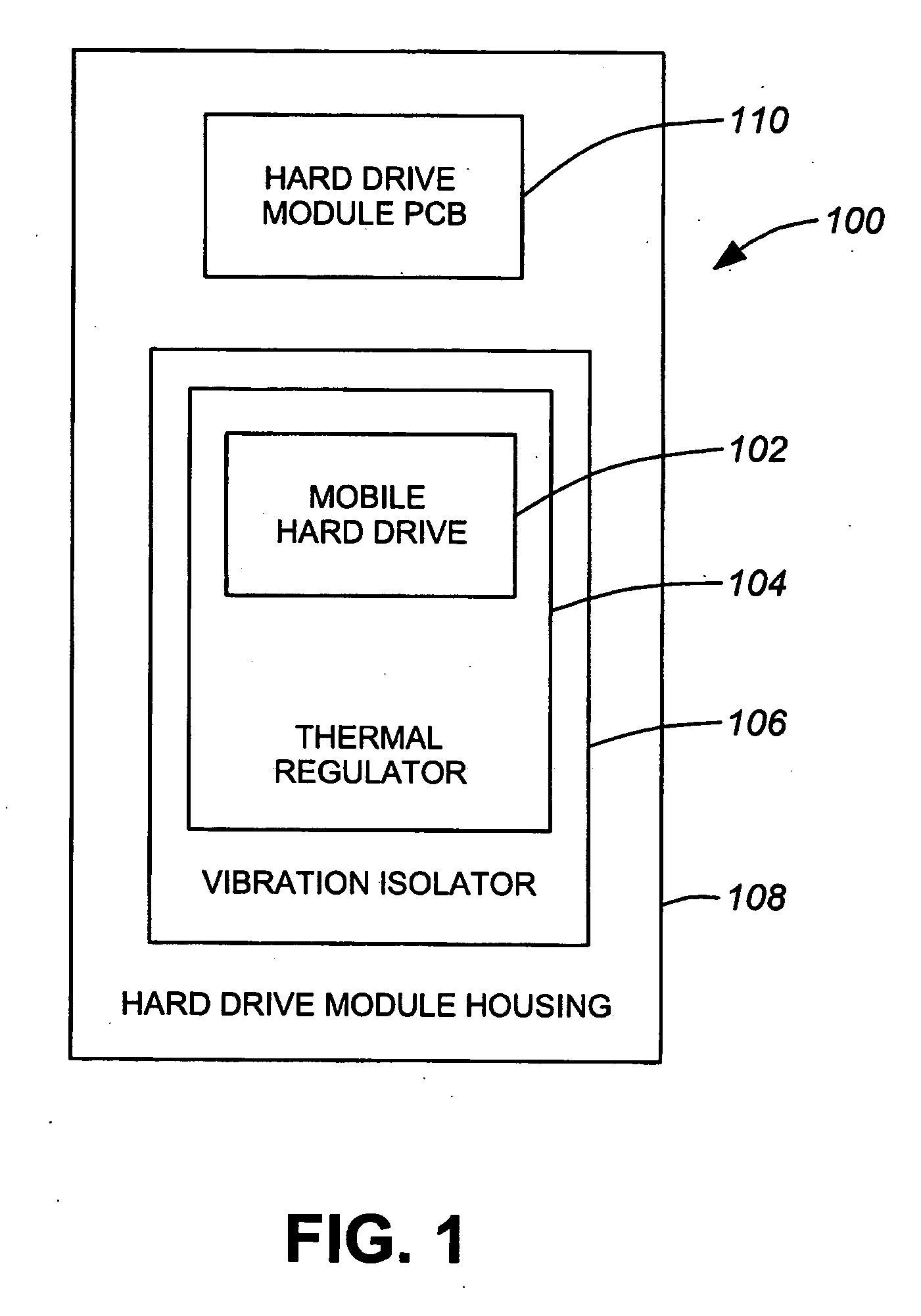
ActiveUS7703291B2Reduce vibration effectsFast heat conductionReducing temperature influence on carrierDisposition/mounting of recording headsHard disc driveMobile vehicle
An environmental control system, or data pack, is provided in accordance with embodiments of the present invention. The system allows for audio and video recording on hard drive media in situations where temperature, vibration and humidity would otherwise have prevented the use of such technology. The system can be used in conjunction with an event recorder for use in motor vehicles, trains and the like. The environmental control system includes a thermoelectric module connected to the hard drive and to a housing. The thermoelectric module is for transferring heat between the hard drive and the housing in response to an applied voltage in order to maintain a hard drive temperature within a hard drive operable temperature range. The vehicle operating temperature range includes temperatures outside the hard drive operable temperature range.
Owner:MARCH NETWORKS
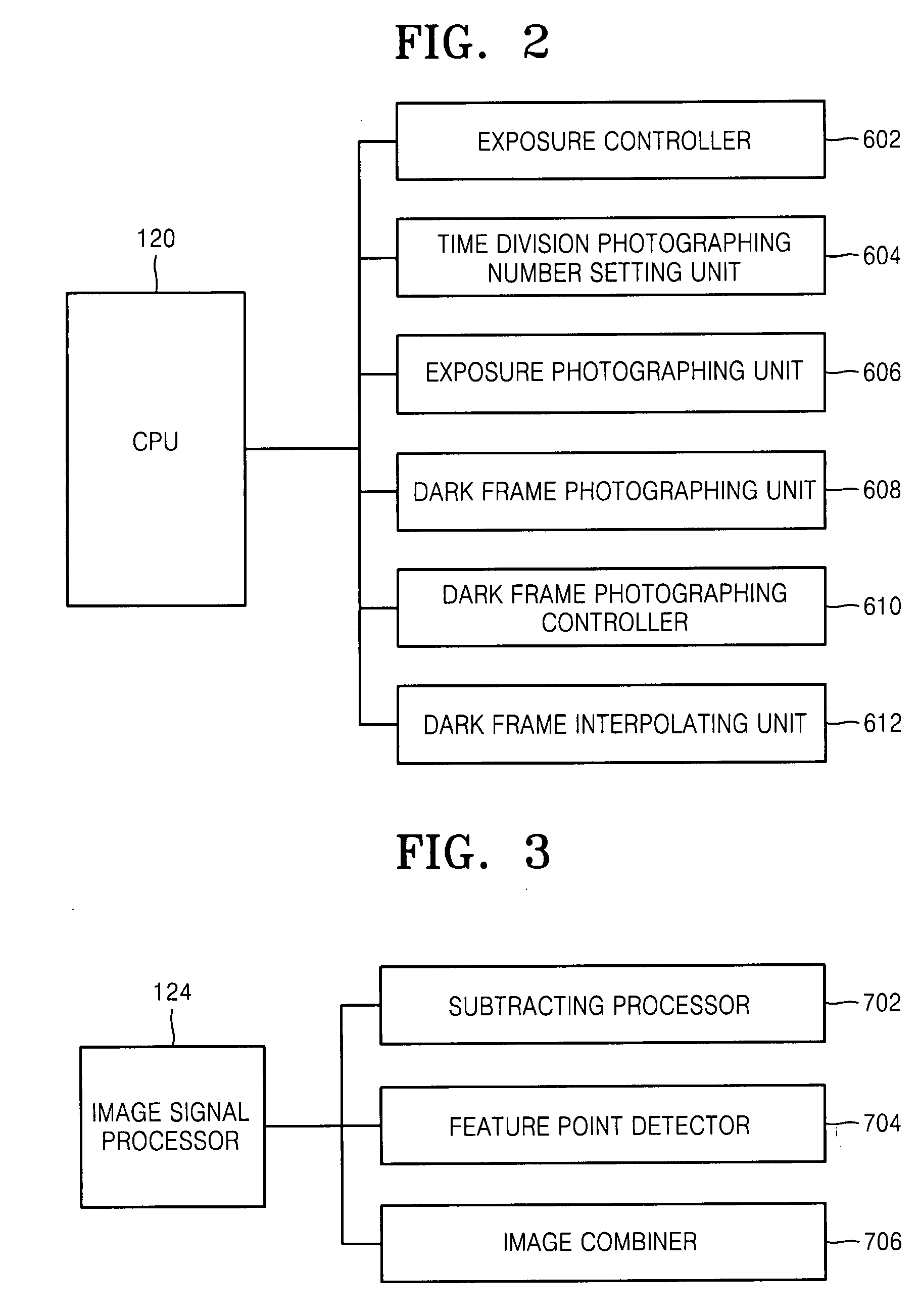
Apparatus and method for image pickup
InactiveUS20070230932A1Noise in imaged image can be reducedReduce noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHand movementsLight exposure
An apparatus and method for image pickup capable of reducing noise in the images to reduce the effect of shaking due to, for example, hand movement. The image pickup apparatus and method can employ an exposure photographing unit for photographing at least one exposure image at predetermined time intervals using time-division exposure in a light exposure state, a dark frame photographing unit for photographing at least one dark frame at predetermined time intervals using time-division exposure in a dark state, a subtracting processor for subtracting the dark frames from the exposure images to reduce noise in the exposure images, and an image combiner for combining the plurality of reduced noise exposure images.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
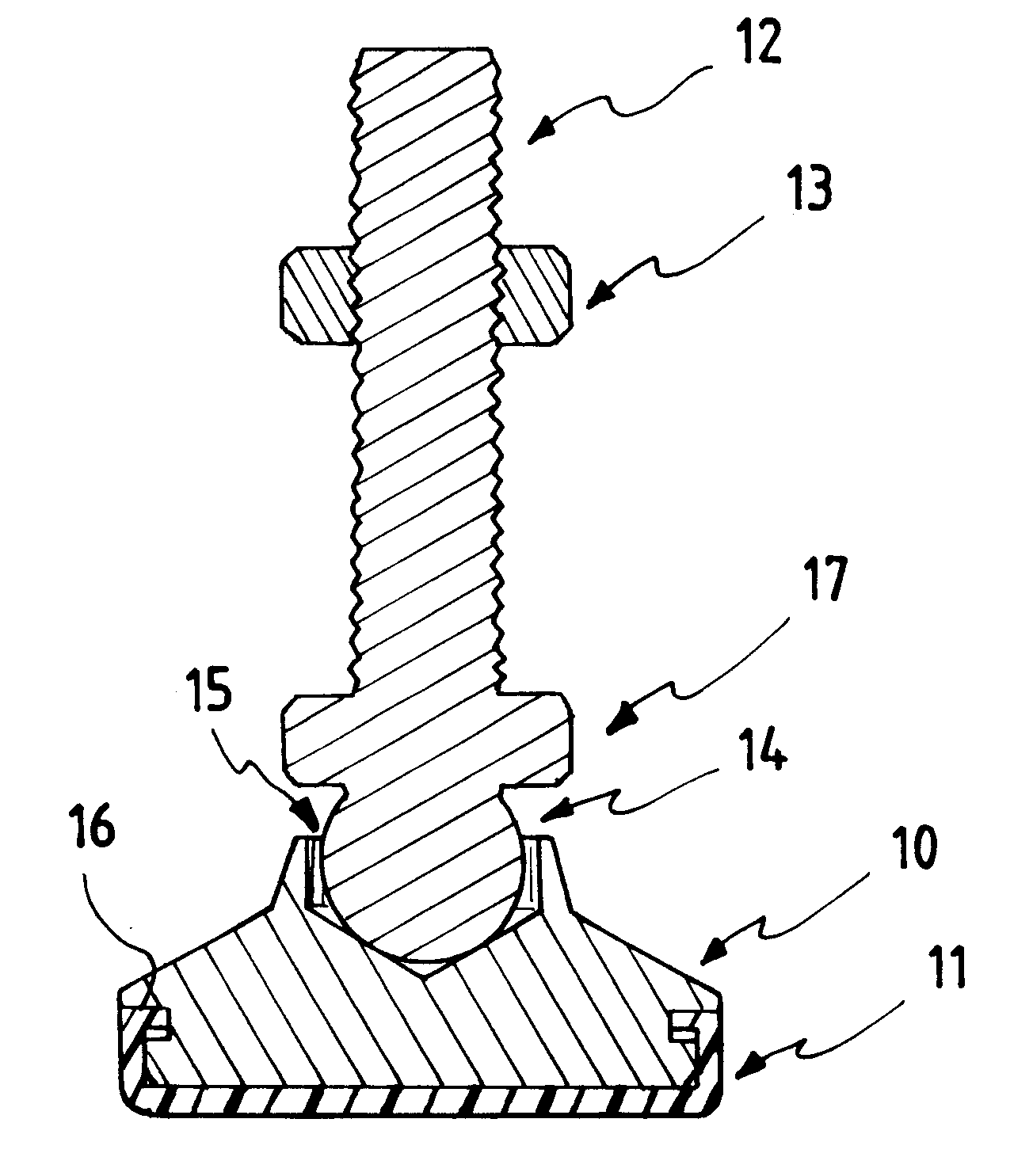
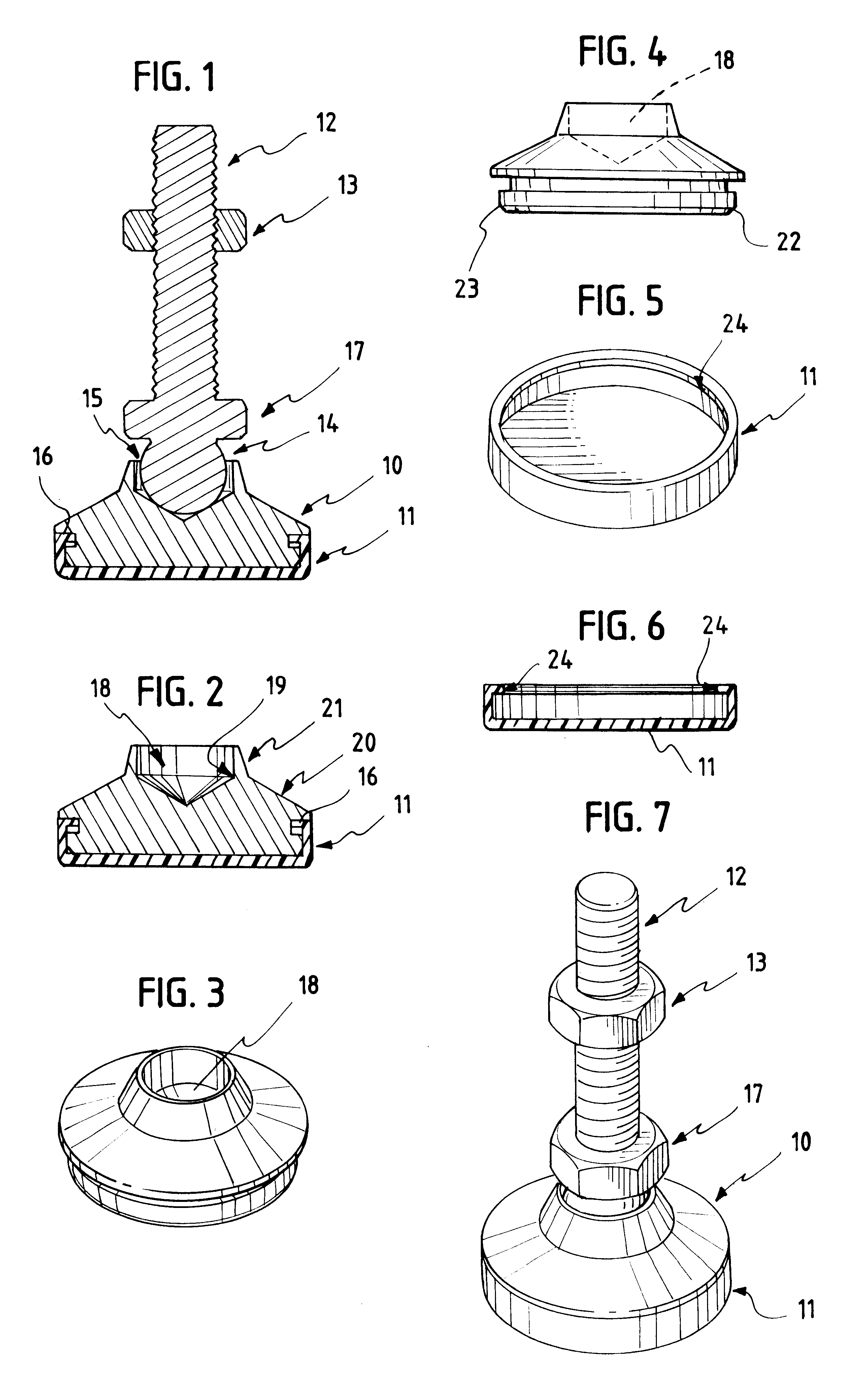
Leveling mount
InactiveUS6520459B2Easy and simple and efficientEasy to disassembleMachine framesStands/trestlesEngineeringSupport surface
A leveling mount is disclosed for equipment in temporary or permanent installations wherein the supporting surface can be a non-level planar surface. A ball and socket support stud provides a self-leveling adjustment of support. An elastomeric removable mount base pad provides non-skid means. Limited swivel and radial movement of the ball and socket support stud are maintained. The leveling mount base can engage a support stud affixed to the supported equipment.
Owner:S & W MFG
Impact tool
ActiveUS7861799B2Increased durabilityReduce weightSleeve/socket jointsReciprocating drilling machinesEngineeringLubricant
It is an object of the invention to provide a technique which is effective in improving the durability of an angular positioning device of a tool bit and in reducing weight of a tool body in an impact tool. A representative impact tool includes a tool body, a lubricant sealed in the housing space, a driving mechanism, a tool holder, an angular positioning device disposed on a tip end side of the tool body and serves to fix a position of the tool bit around the axis with respect to the tool body. The angular positioning device includes first and second locking members. The first locking member is disposed between the tool body and the tool holder. The second locking member is disposed opposite to the first locking member. One end of the first locking member in the axial direction of the tool bit extends into the housing space of the tool body and is connected to the tool body within the housing space.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
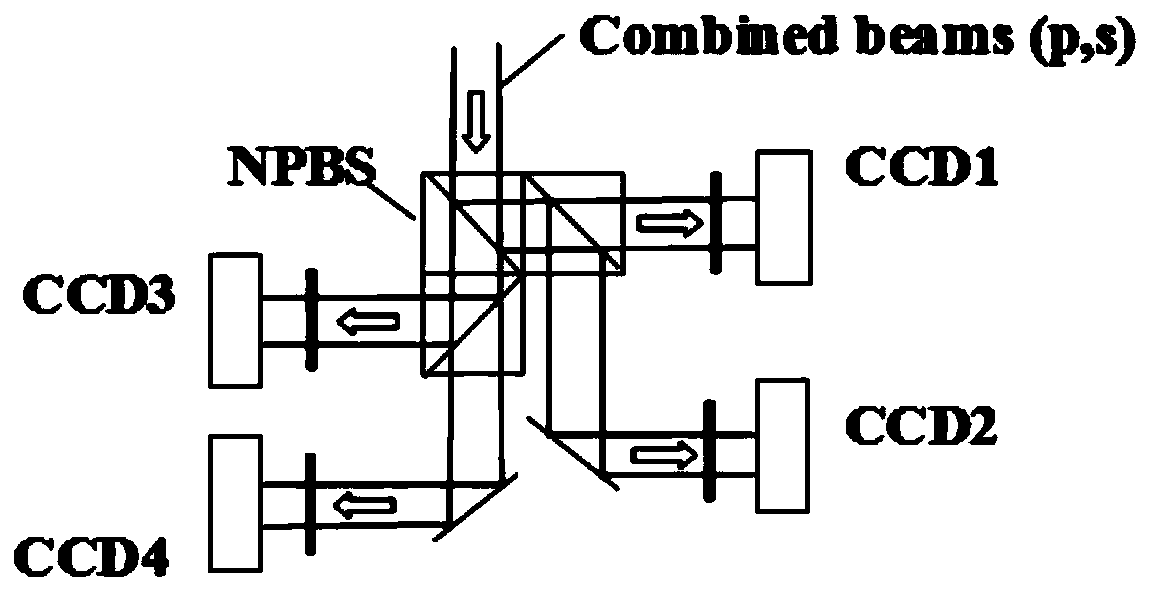
Device and method for measuring synchronous phase shifting interference of Fizeau quasi-common optical path structure
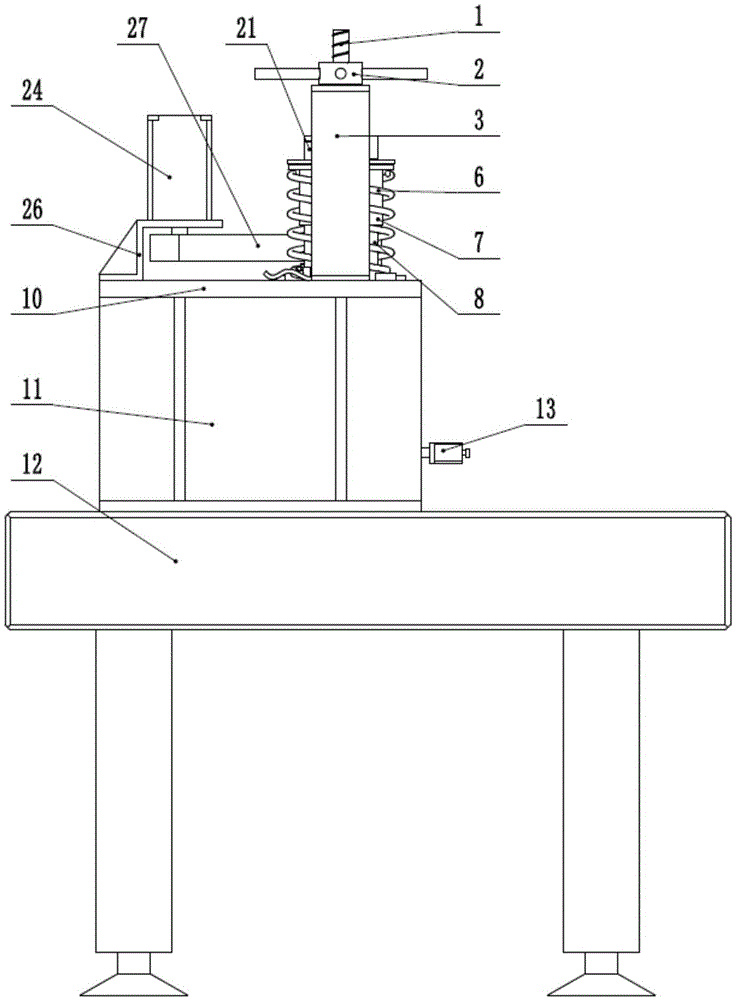
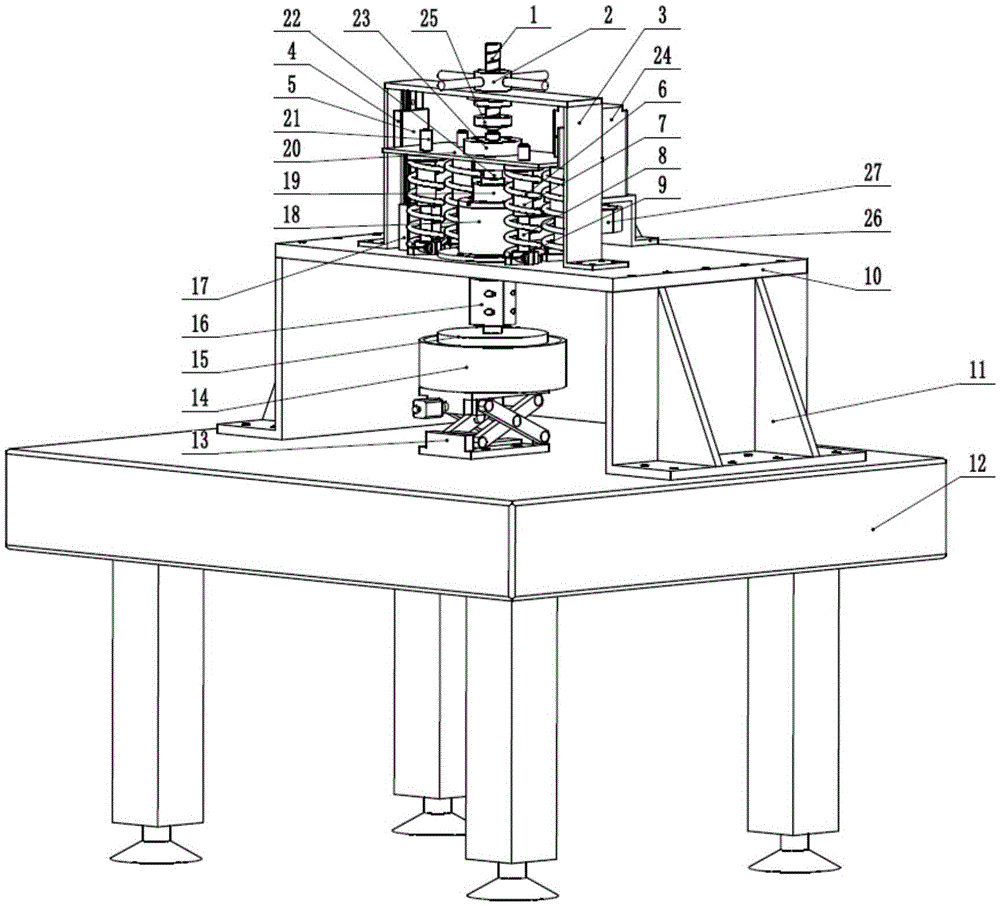
ActiveCN104034257AReduce vibration effectsHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansImaging lensCcd camera
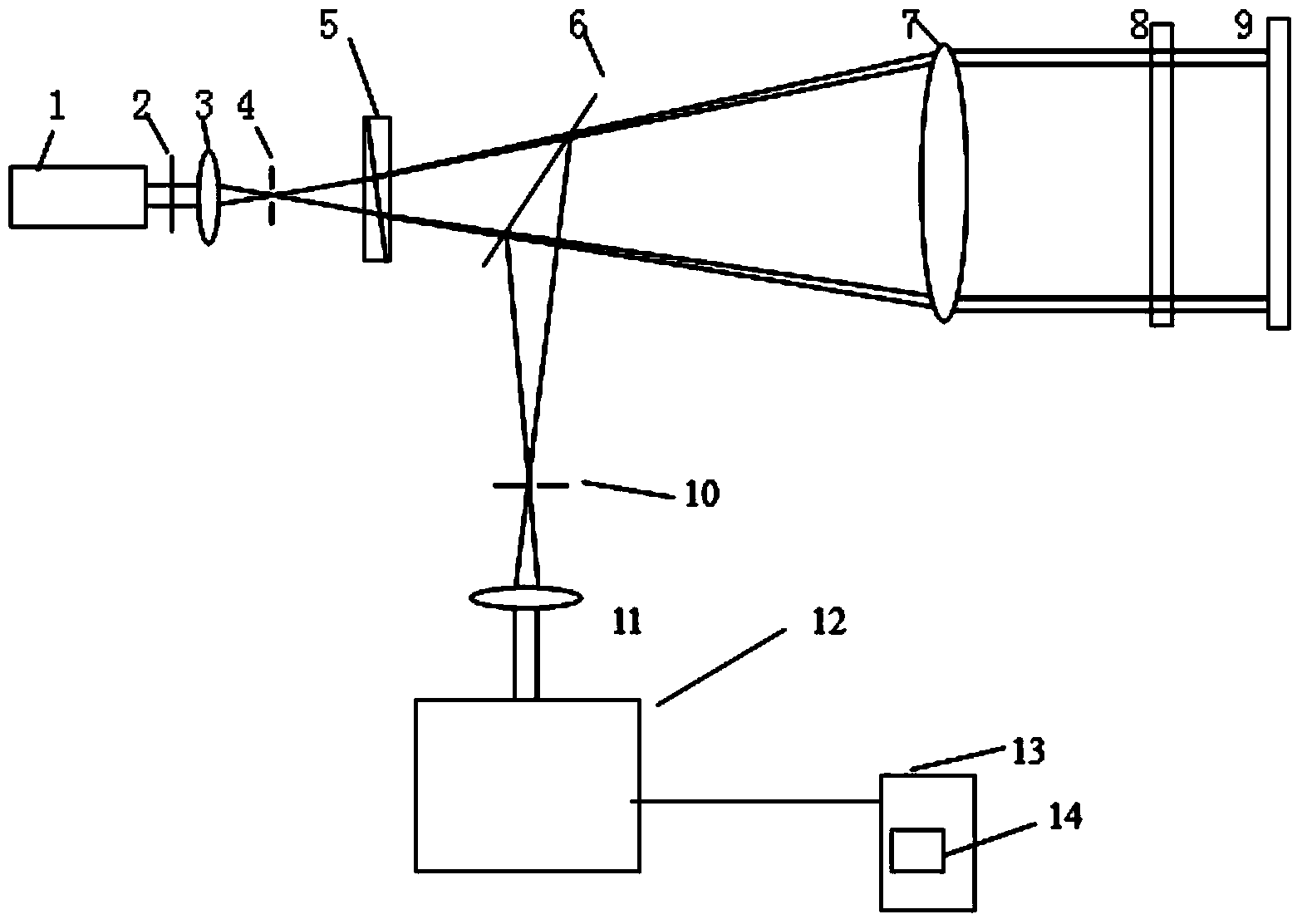
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring synchronous phase shifting interference of a Fizeau quasi-common optical path structure. The device comprises a laser, a half wave plate, a focusing lens, a spatial filter, a circularly polarized light beam splitter (an optically active crystal), a spectroscope, a collimating lens, a reference mirror, a pin-hole diaphragm, an imaging lens, a light splitting and phase shifting system, a computer control system and a CCD camera. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, a synchronous phase shifting technology is combined with a Fizeau interference method, so that technical difficulties of a conventional interferometer in poor stability and disability of realizing dynamic measurement are solved; the device and the method are characterized by utilizing an optical rotation effect of the crystal and adding the circularly polarized light beam splitter with a very small splitting angle in the Fizeau interfering structure, so as to realize orthogonally polarized separation of reference lights and test lights in a common optical path. The device and the method disclosed by the invention avoid utilization of a high-quality quarter wave plate in a synchronous phase-shifting interference system, and also greatly decrease a phase measurement error caused by a stress birefrigent effect which exists in an optical element of the system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
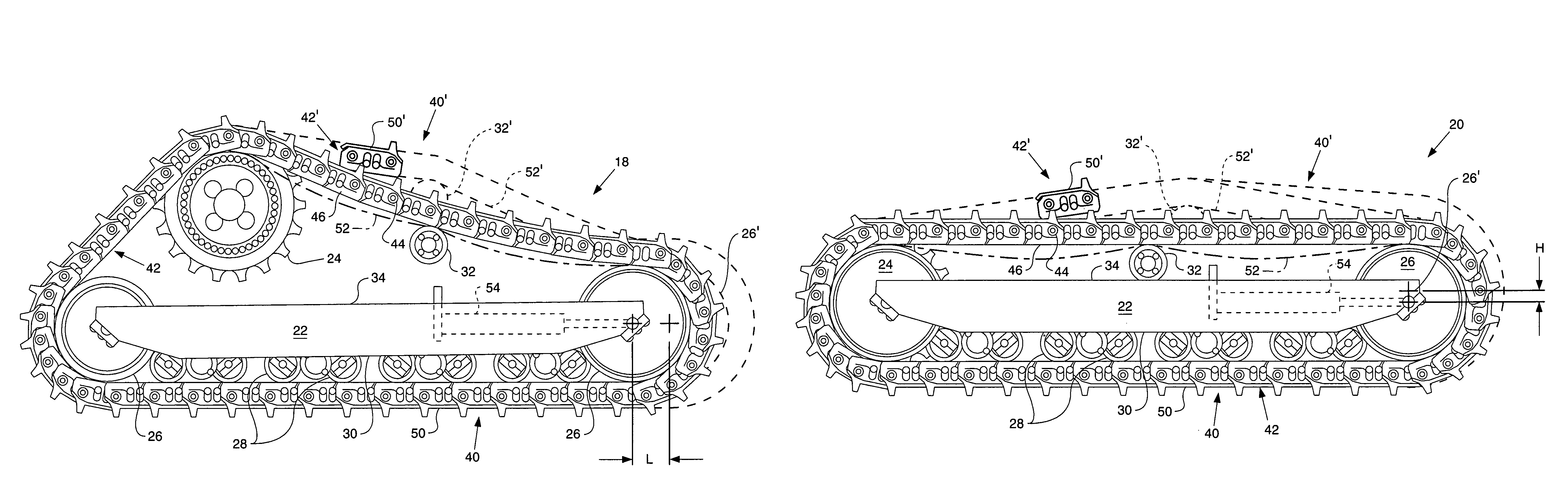
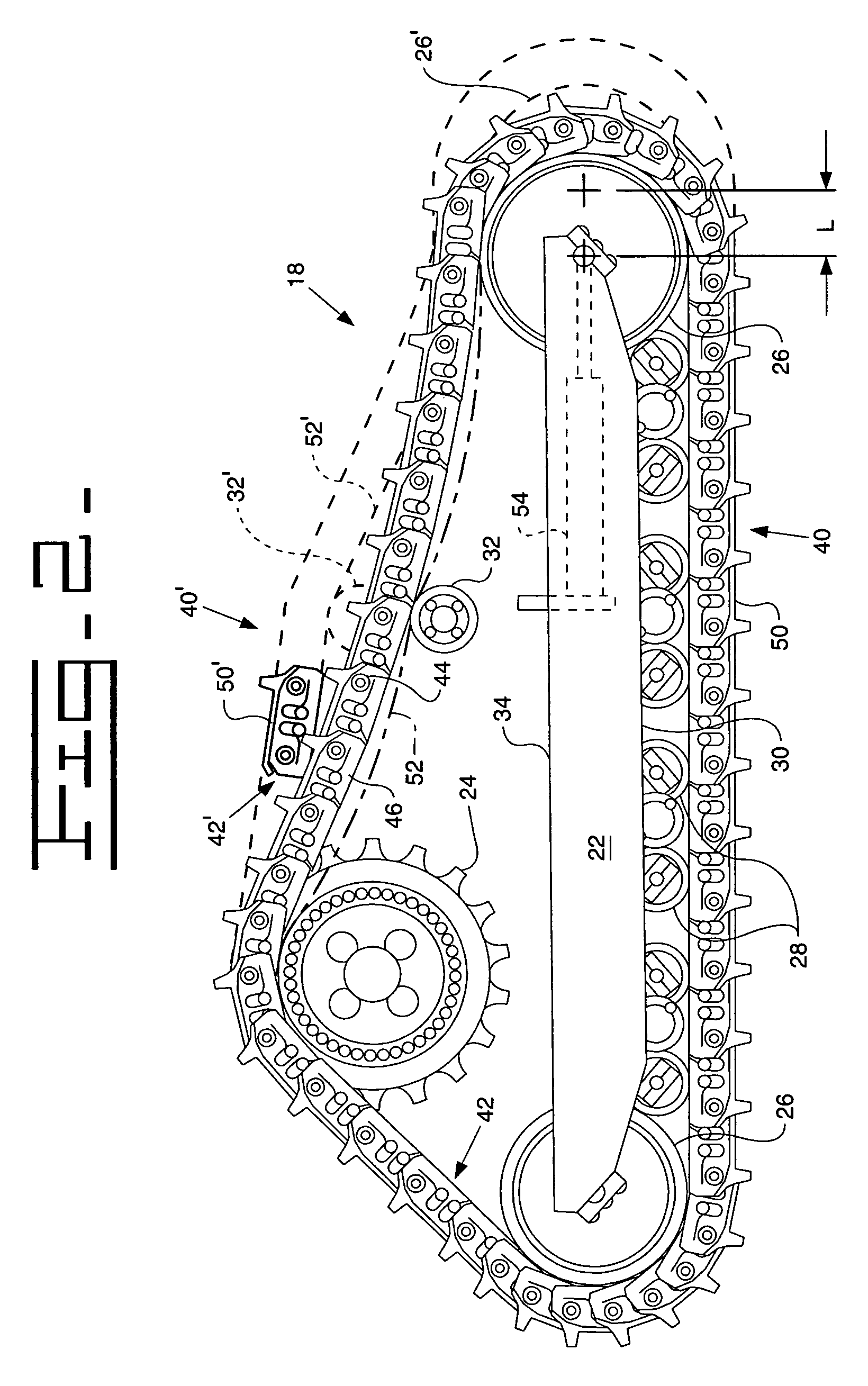
Apparatus and method to reduce vibrations on a tracked work machine
ActiveUS7806209B2Reduce vibration effectsGearingEndless track vehiclesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus and method for reducing vibrational effects of track chain assembly catenary hang is disclosed. A work machine includes a pair of track roller assemblies one positioned on each side of the work machine. The vibration reducing apparatus and method includes repositioning undercarriage components to vary the catenary hang from one side of the work machine to the other.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
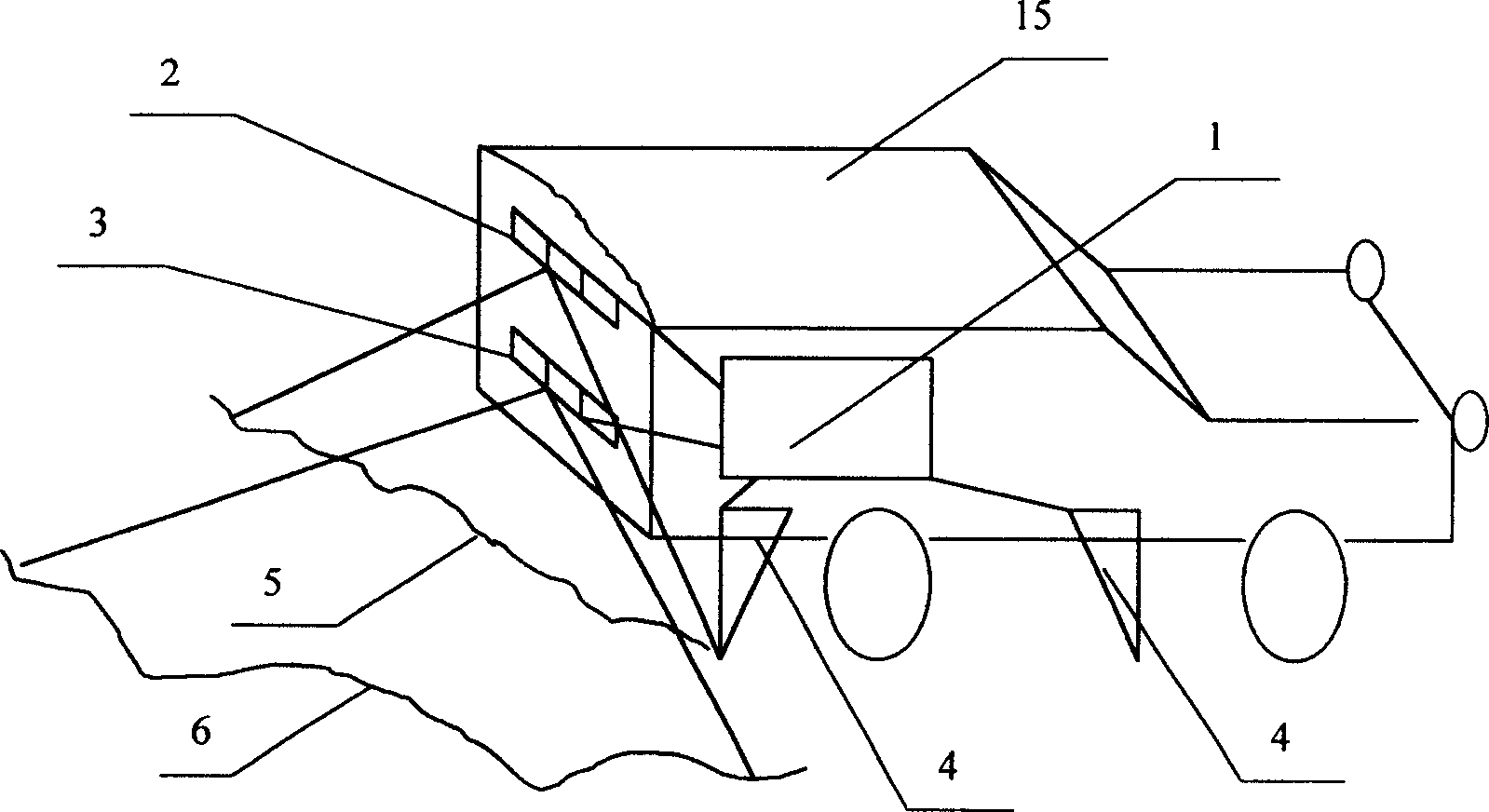
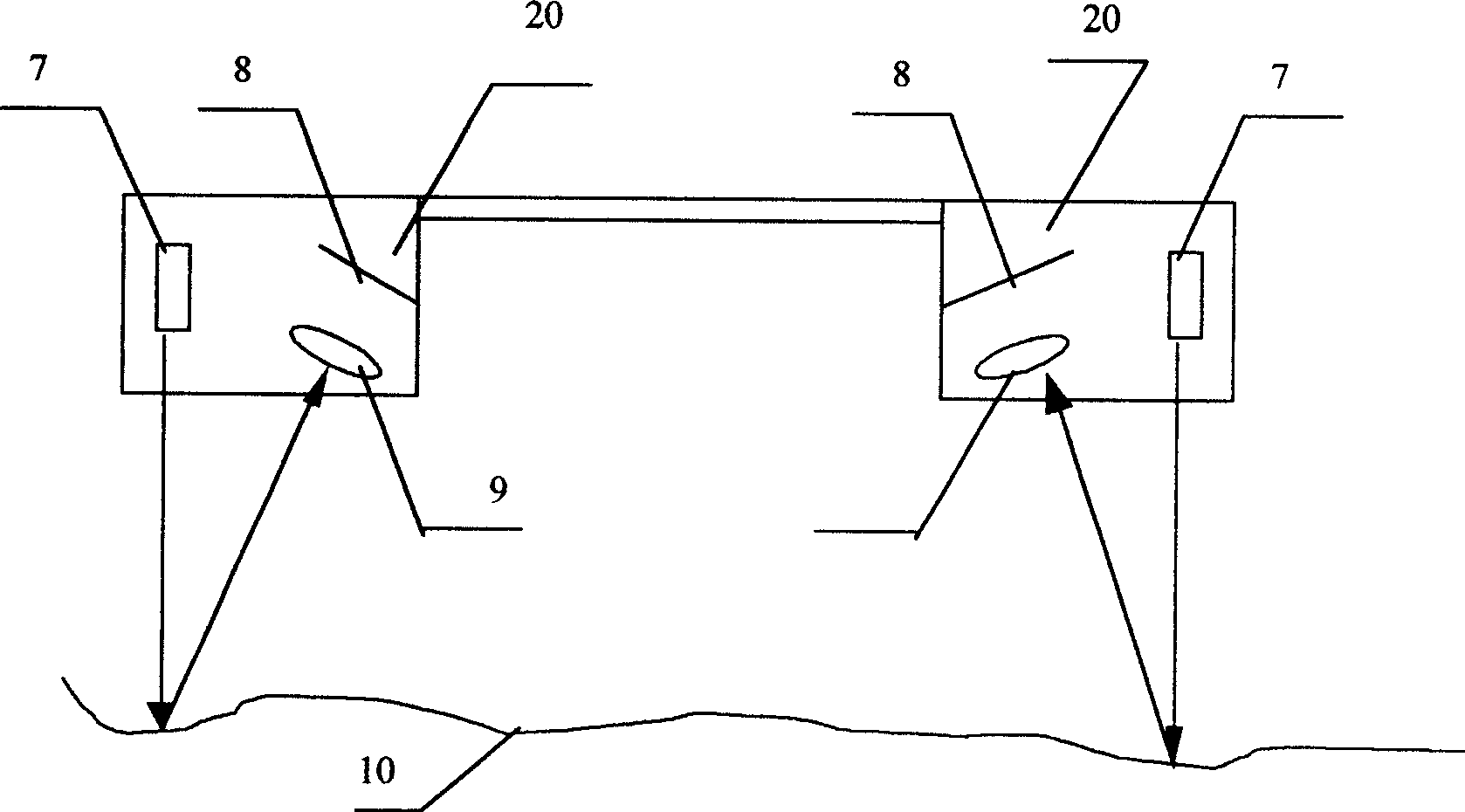
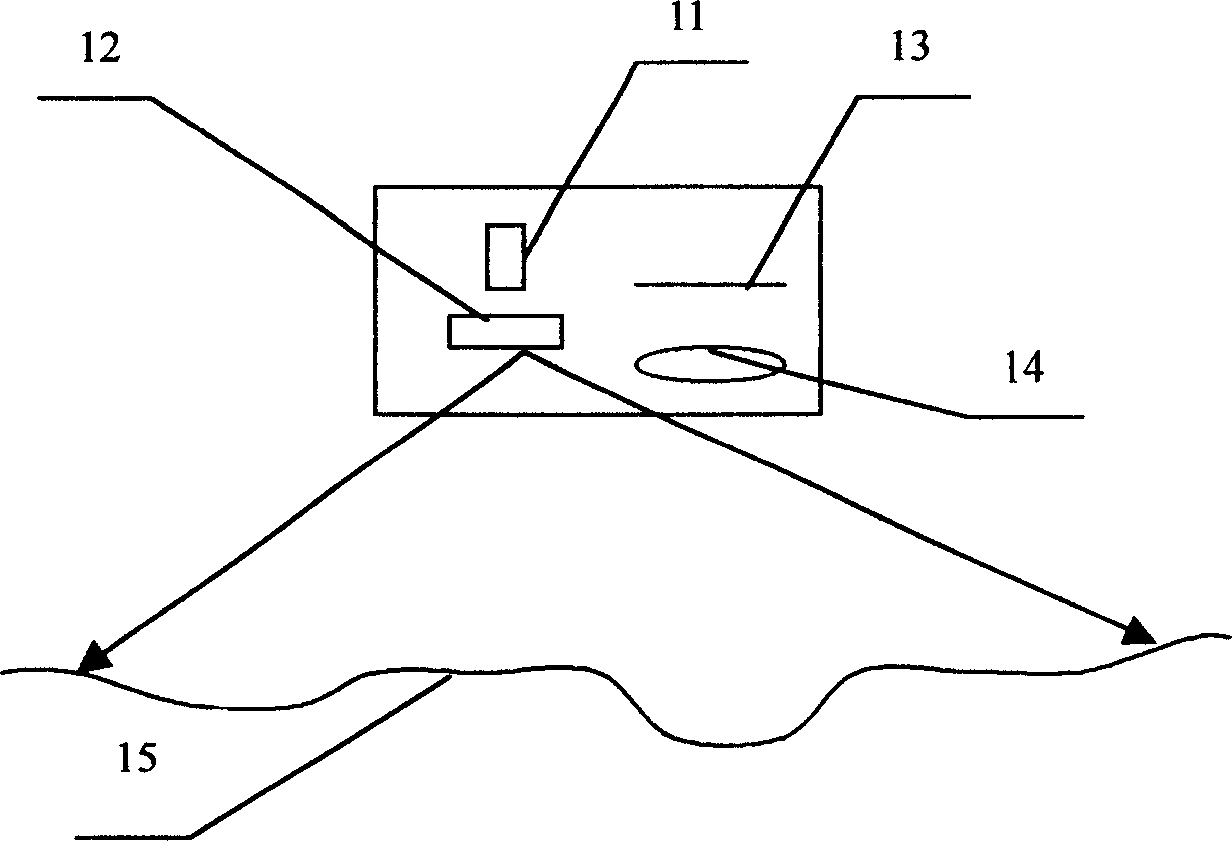
Intelligent 3D laser road state detecting vehicle
InactiveCN1548653AReduce vibration effectsRealize vehicle-mounted high-speed intelligent detectionRoads maintainenceRoad surfaceInformation processor
The intelligent 3D laser road state detecting vehicle includes vehicle body, rideograph set on one side below the vehicle body, laser road disease instrument, wheel track and road form instrument, laser power supply and central information processor inside the vehicle body and connected to the fore said instruments. The rideograph consists of two elevation meters with shared beam; the road disease instrument consists of area light source lighting the road and linear CCD detector array; and the wheel track and road form instrument consists of one or several small area light source and area CCD detector array. The present invention can realize fast road detection to obtain various road surface parameters and 3D data in high precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
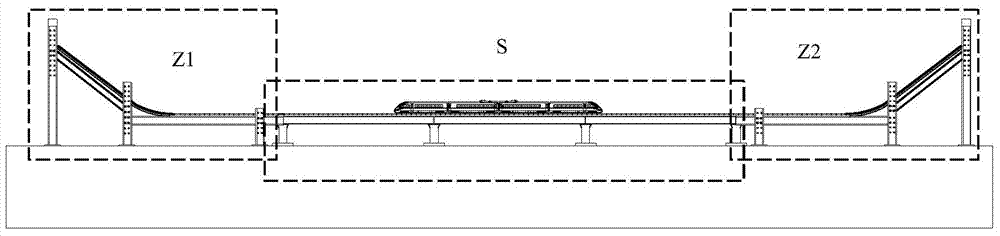
Dynamic simulation test system for ensuring running safety of train on railway bridge under earthquake
InactiveCN103698140AEnable Hybrid SimulationEnsure the bridge speedRailway vehicle testingVibration testingBridging modelCoupling vibration
The invention discloses a dynamic simulation test system for ensuring running safety of a train on a railway bridge under an earthquake. The dynamic simulation test system comprises a bridge model and a train model, wherein a supporting frame component for supporting the bridge model and adjusting an inclination angle and a horizontal position of the bridge model is arranged at the bottom of the bridge model; track boards are paved on the bridge surface of the bridge model; train tracks for guiding a running route of the train model and central tracks for preventing the train model from falling off are paved on the track boards; the train tracks are parallel to the central tracks; the bridge model comprises a first supporting section for adjusting a preset speed of the train model through the inclination angle, a test section for performing a train-bridge coupling vibration test and a second supporting section for stopping the running of the train model according to the inclination angle; the first supporting section and the second supporting section are respectively connected to two ends of the test section. The weak action of the bridge, which is caused by the upper train, and strong action of bridge vibration, which is caused by a vibration table, are mutually coupled to realize a train and earthquake mixing simulation system.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Soft support bridge type silicon micro-piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer chip and prepration method thereof
InactiveCN101645484AHigh sensitivityGood process compatibilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionVertical projectionUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a soft support bridge type silicon micro-piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer chip which comprises a silicon substrate with a square conical hole which is small at the top andbig at the bottom in the center; a silicon layer and a first oxidation layer are sequentially covered on the front surface of the silicon substrate, and a second oxidation layer is covered on the backsurface; the corresponding silicon layer and the first oxidation layer above the square hole of the front surface of the silicon substrate constitute a square vibration membrane, one pair of oppositesides of the square vibration membrane respectively etch a vertical narrow slot, and the vertical projection of each narrow slot is positioned on the inner side of the hole edge above the front surface of the silicon substrate; a lower electrode, a piezoelectric membrane and an upper electrode are sequentially deposited on the square vibration membrane; a polyimide membrane is deposited on various parts on the front surface of the silicon substrate; and the square vibration membrane which is etched with the vertical narrow slots and the polyimide membrane commonly constitute a soft support anti-sound leakage bridge type vibration membrane. The anti-sound leakage bridge type structure is used on the vibration membrane of the transducer; in order to avoid sound leakage through the narrow slots, the soft polyimide membrane is deposited on the narrow slots, which has little effect on vibration of the vibration membrane and can still keep high sensitivity.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Physiological parameter detecting system with comb filter and monitoring system for depth of sleep
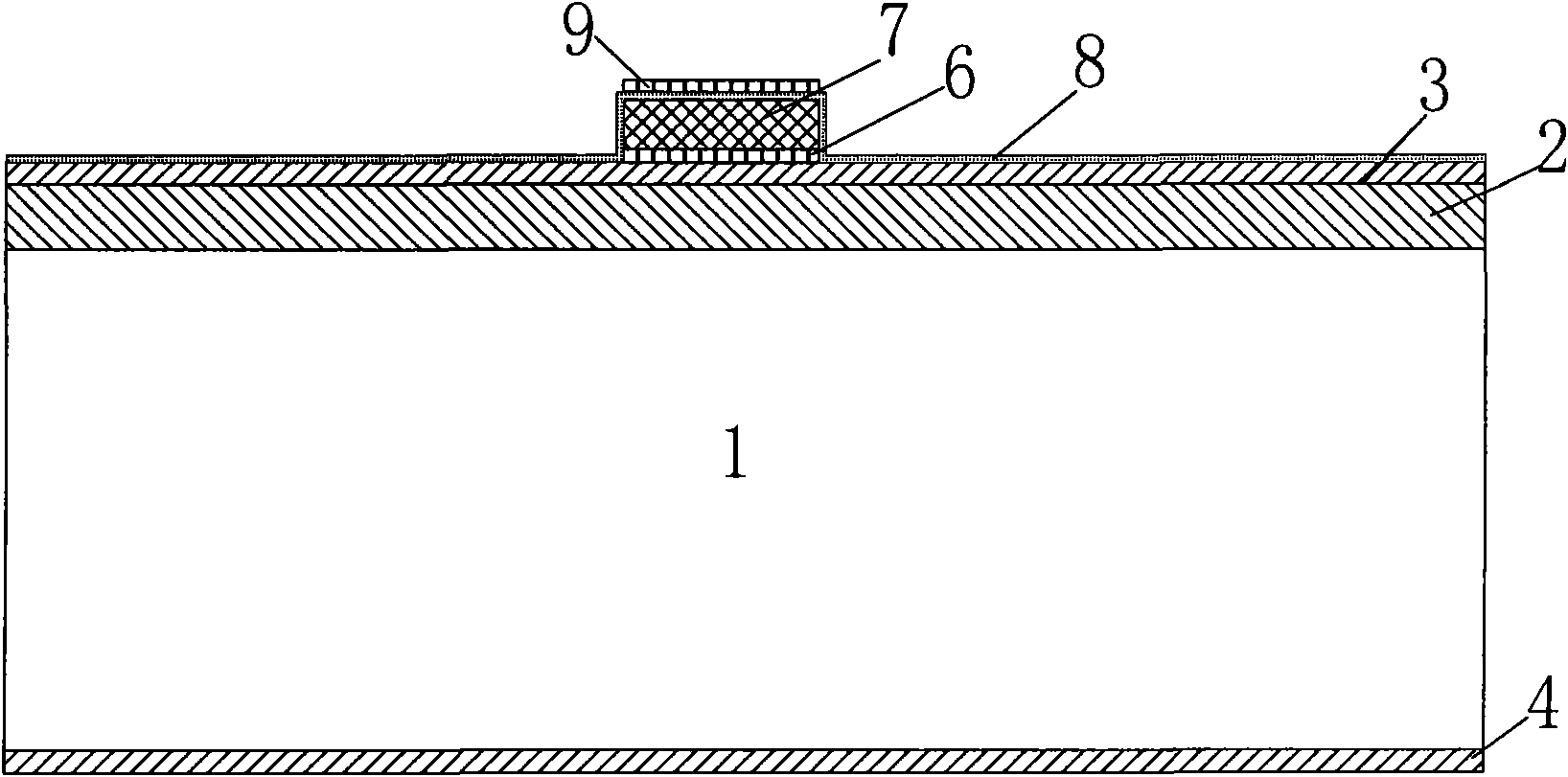
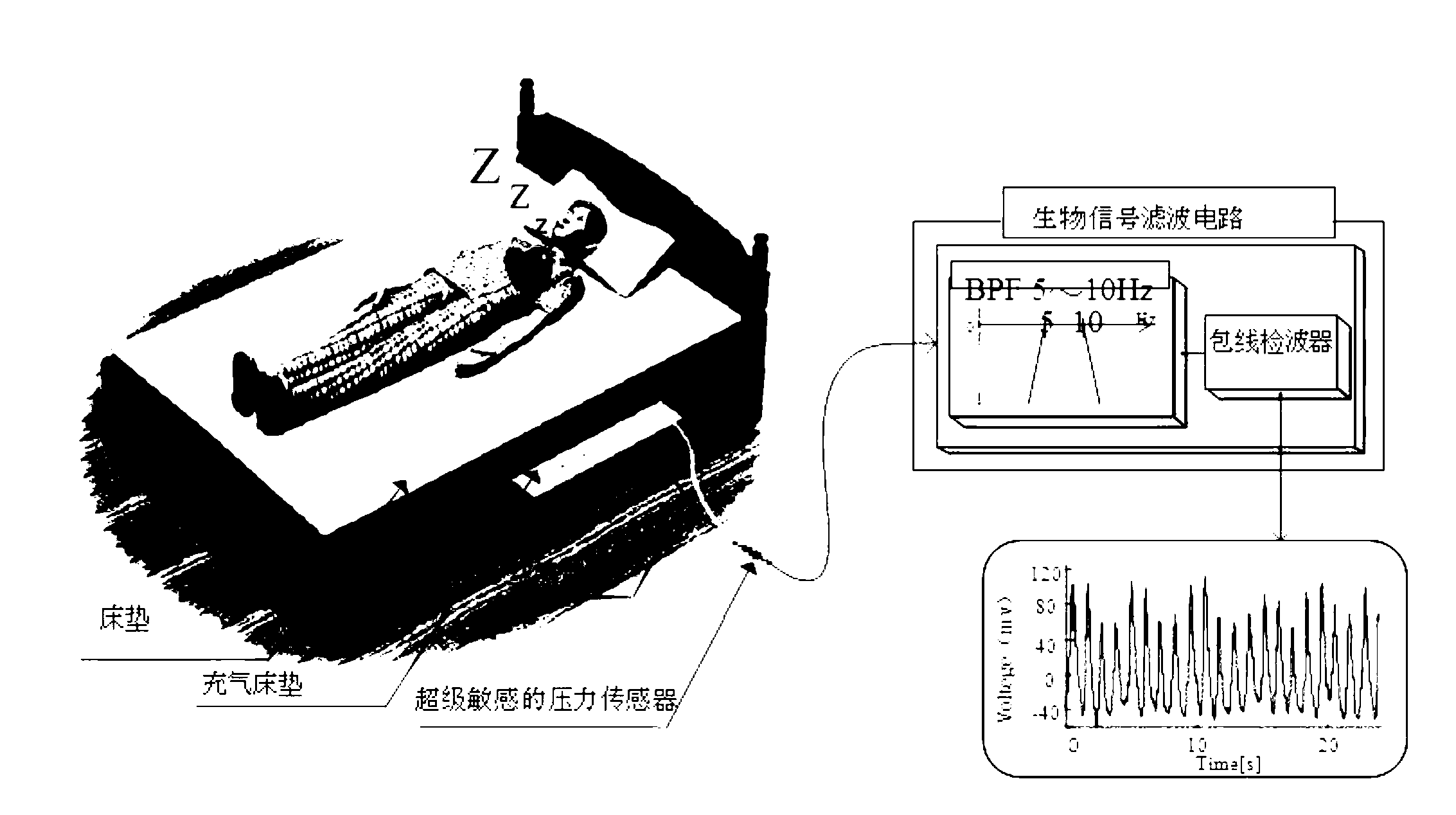
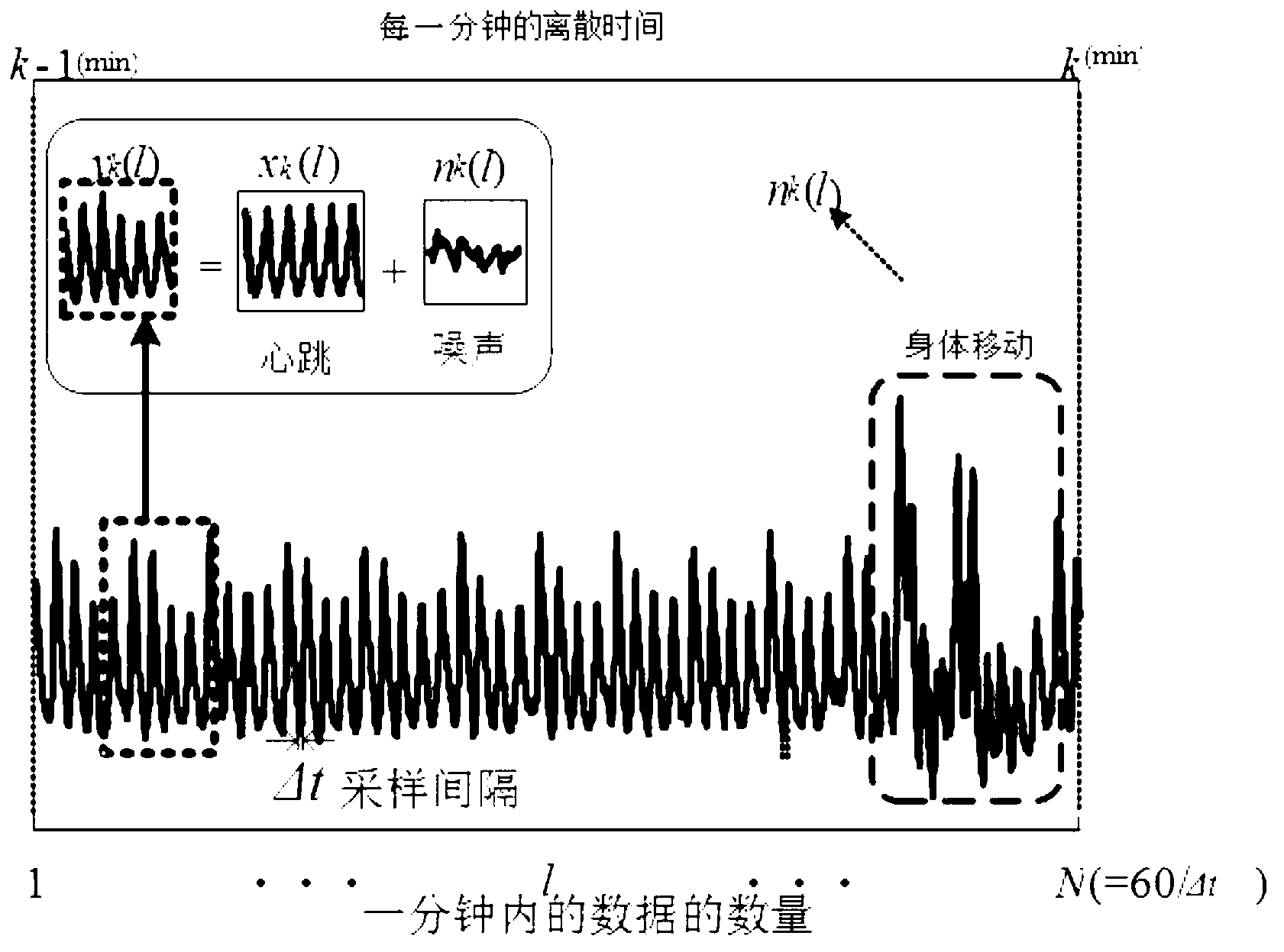
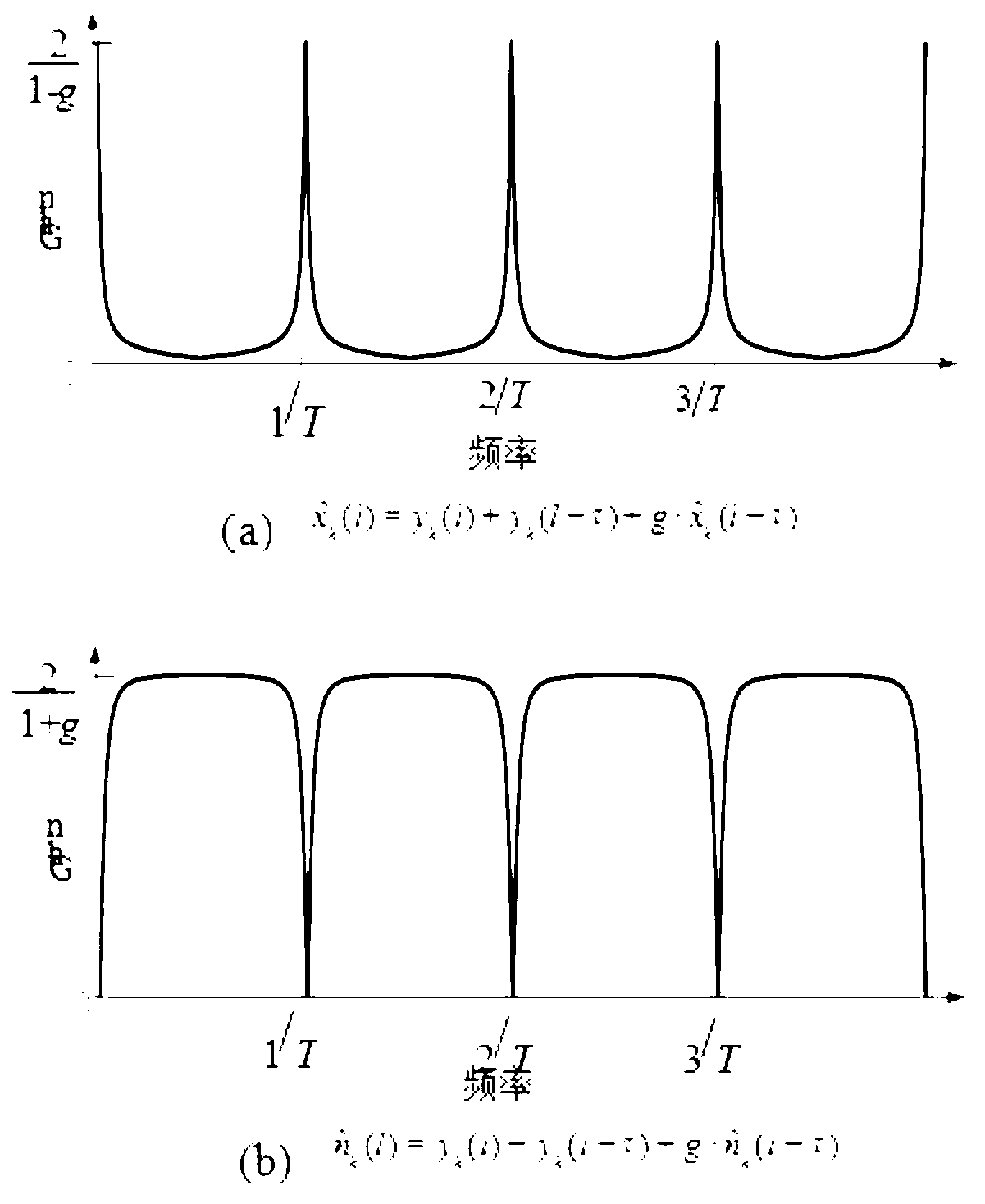
ActiveCN103263260AReduce vibration effectsAvoid vibrationRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsMeasurement precisionSleep Stages
The invention discloses a physiological parameter monitoring system with a comb filter and a monitoring system for the depth of sleep. External interference signals which are transmitted onto a bed from a floor are eliminated by a unique technology so as to improve the measurement precision of the detecting system. A sensor acquires physiological signals of a human body, and data are processed by the comb filter, so that signal waveforms of heart rate numbers, breathing numbers and the turnover frequency of the human body can be acquired, the data of sleep stages are continuously extracted, and a sleep status is presumed according to high-precision pulse and body movement data. In addition, a sleep stage classification technology and a unique sleep presumption technology are adopted for a sleep stage algorithm for speculating the depth of the sleep, so that the sleep stage presumption accuracy is improved, and the measuring system can precisely detect sleep indexes.
Owner:BEIJING BOSHI LINKAGE TECH
System and method for determining the position of defects on objects, coordinate measuring unit and computer program for coordinate measuring unit
InactiveUS20150226539A1Improve accuracyReduce impactOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansLight beamDetector array
A system, a method and a coordinate measuring machine is disclosed for determining the position of defects on objects. An interface is provided so that alignment and coordinate information from the inspection device can be sent to the coordinate measuring machine. A special illumination and detection arrangement is used with a plurality of optical elements in order to obtain a signal from defects on the unpatterned object. The light source of the illumination and detection arrangement is a laser light source for providing a partially coherent light beam. A computer calculates from the data provides by the detector array and the alignment and coordinate information of the object from the inspection device a position of the defect on the object.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
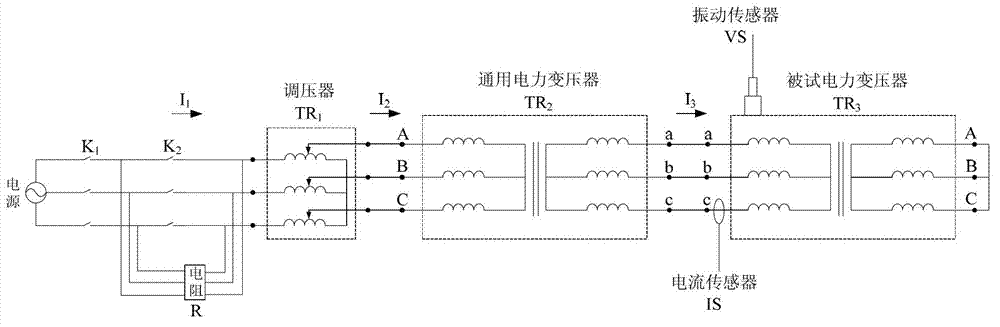
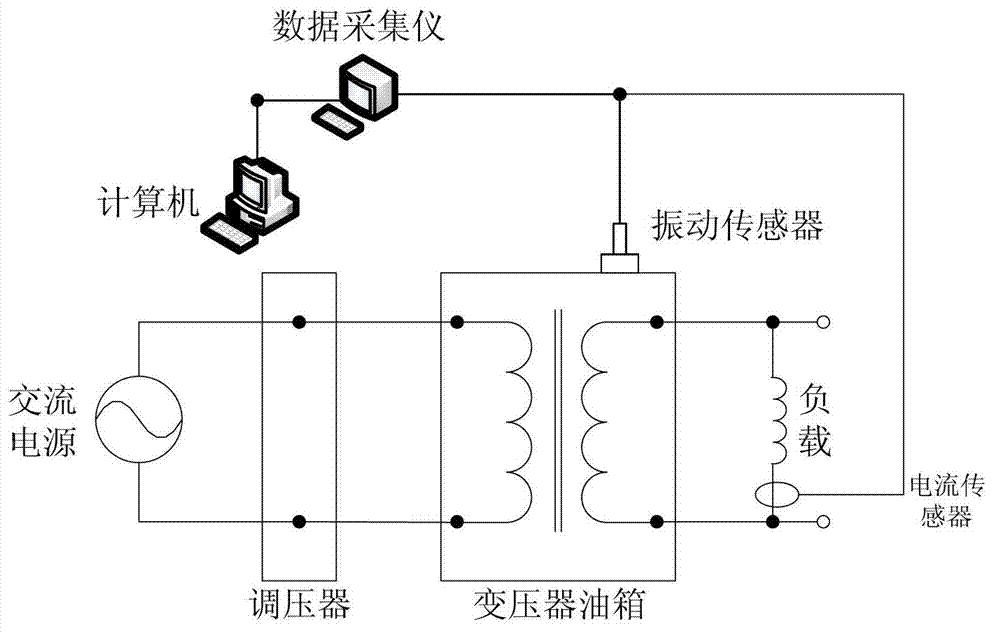
Power transformer winding fault simulation test method
ActiveCN102735969AEasy to measureUniversalVibration measurement in solidsCurrent/voltage measurementTest powerLow voltage
The invention discloses a power transformer winding fault simulation test method and belongs to the field of power transformer winding fault simulation test. The method comprises the following steps that: the high-voltage side of a universal power transformer is connected with an alternating current power supply through a voltage regulator, a resistor for limiting magnetizing rush current is connected in series between the voltage regulator and an electric switch; a bypass switch is connected in parallel at two ends of the resistor; the low-voltage side of the universal power transformer is connected with the low-voltage side of a tested power transformer provided with a winding fault; the high-voltage side of the tested power transformer is in short circuit; the voltage regulator is regulated, so that the tested power transformer acquires different required testing current; and a vibration signal on the surface of an oil tank of the tested transformer is acquired through a vibration sensor, and a current signal which reflects load of the tested transformer is measured through a current sensor so as to be processed and analyzed by a computer. The requirement of the power transformer winding fault simulation test on the power capacity is reduced, the method is easy in operation and readily available in parameters and has universality on similar transformers.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
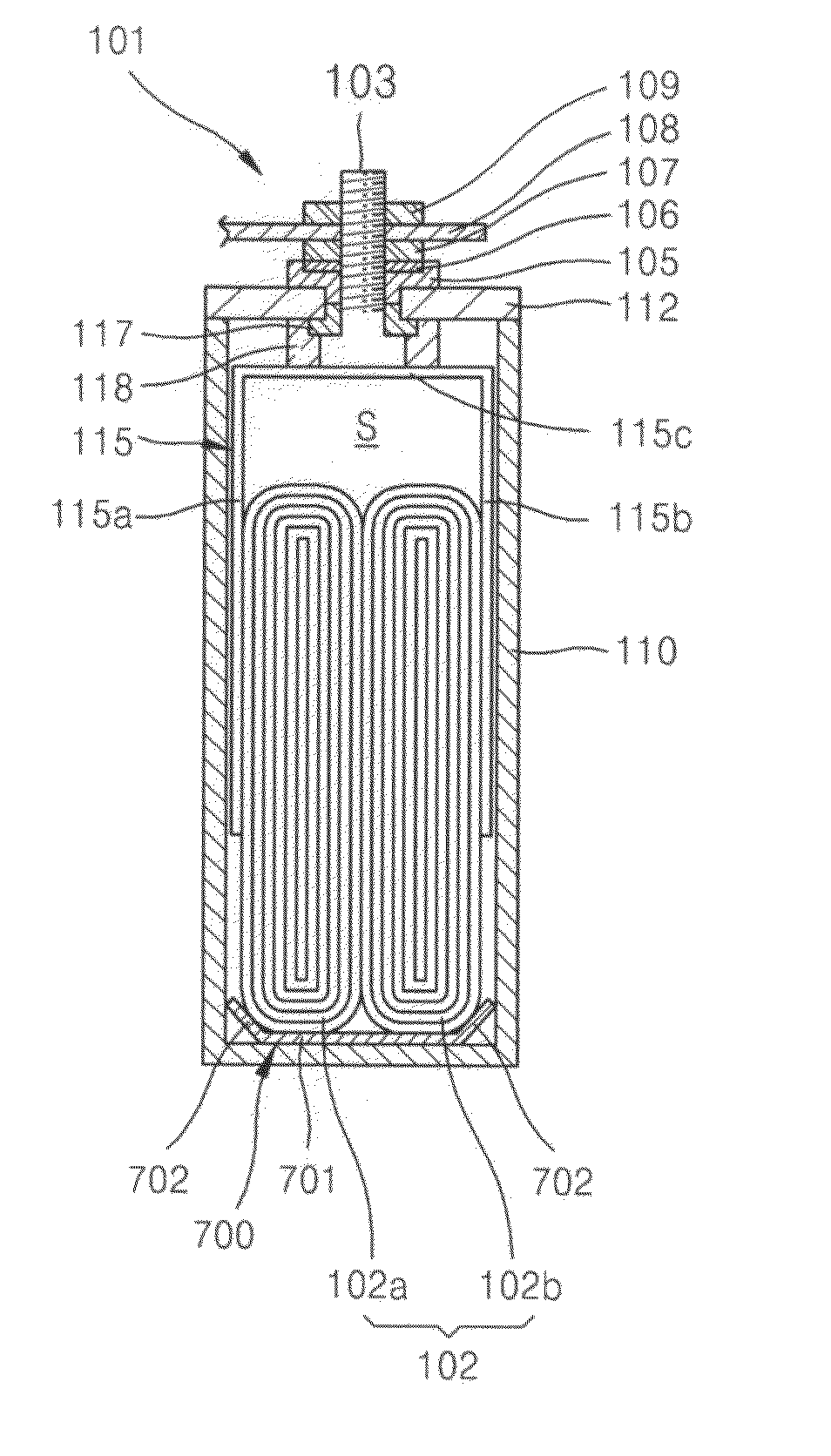
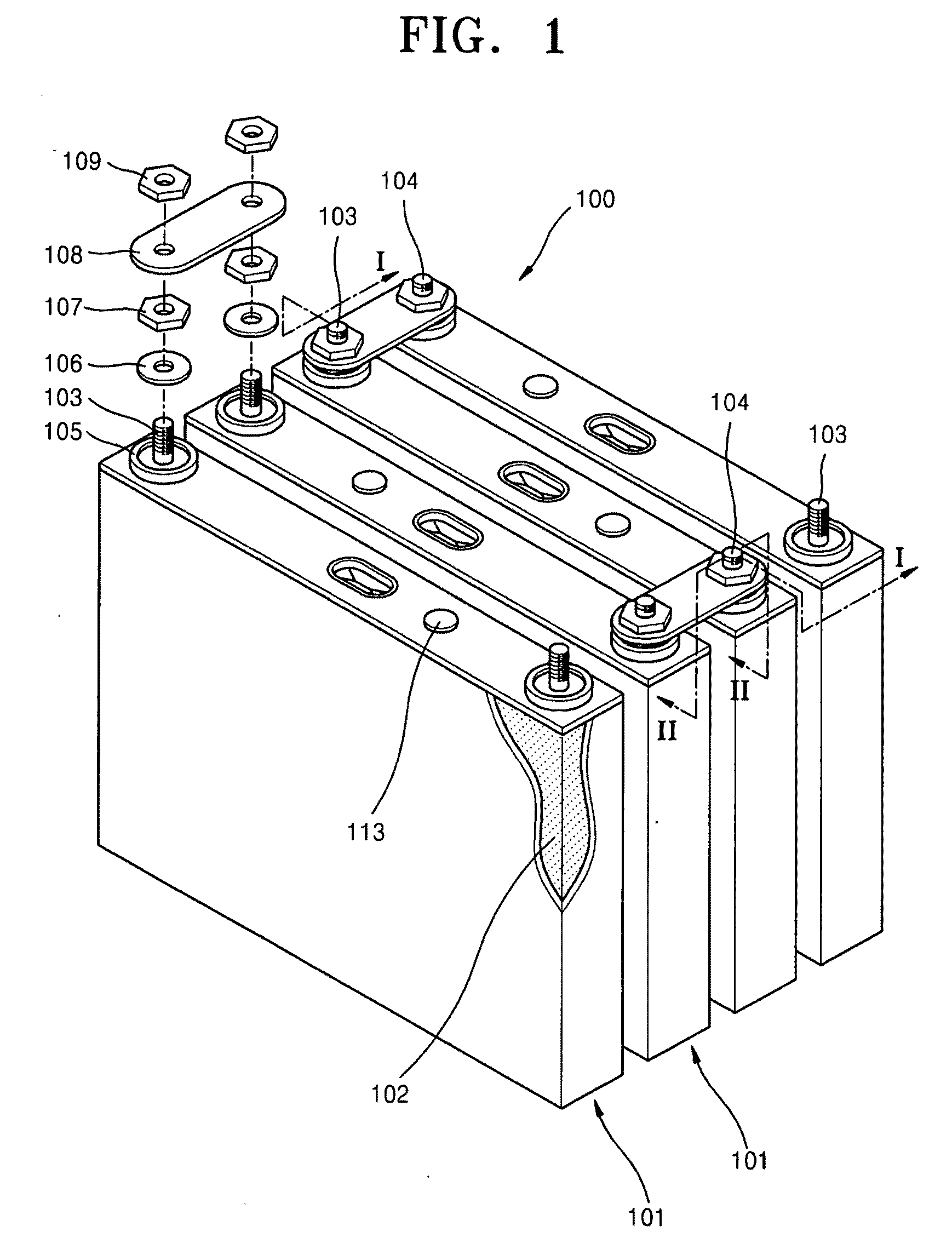
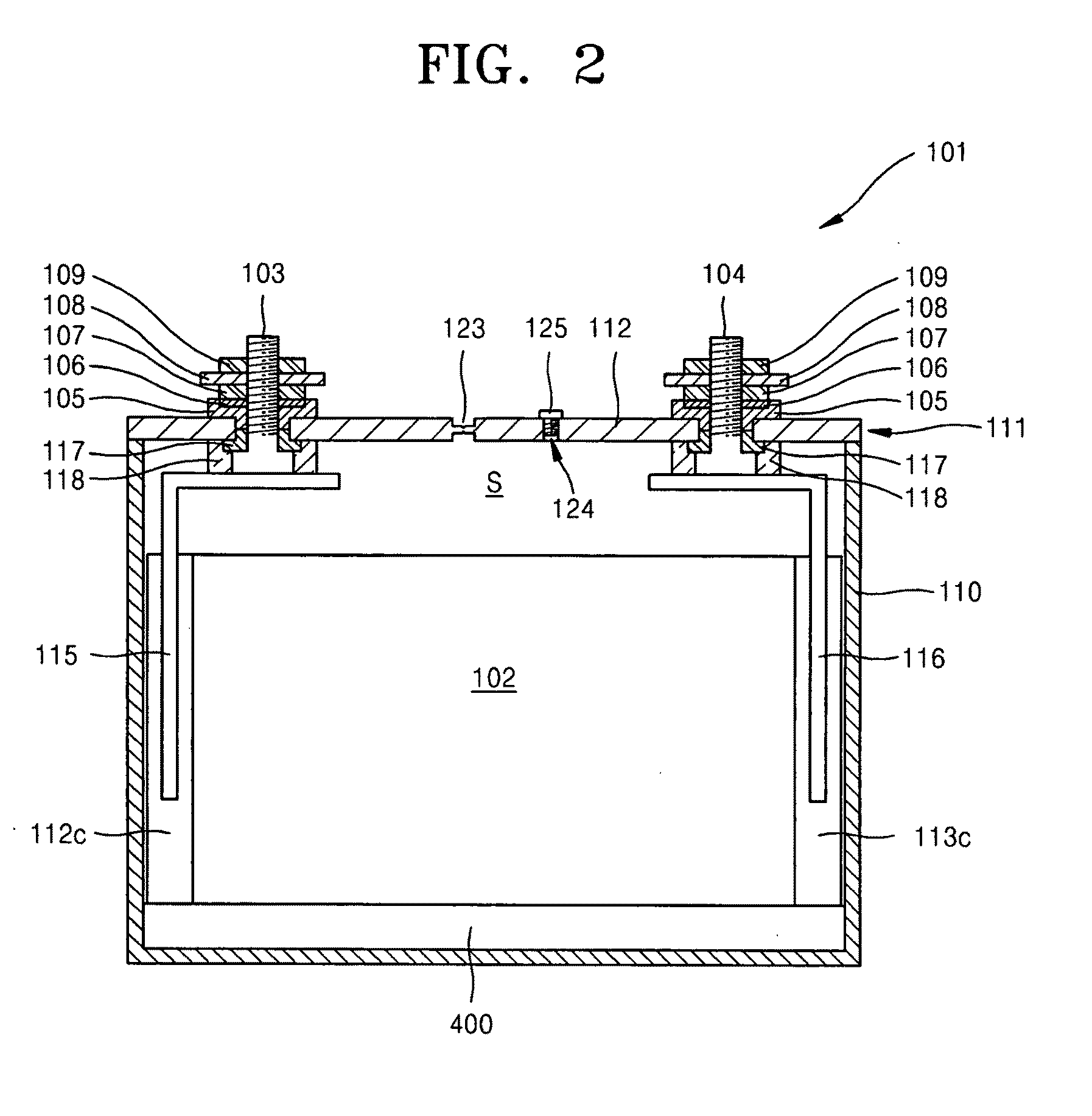
Battery module
ActiveUS20110117402A1Reduce vibration effectsPrevent movementCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufactureEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A battery including a battery case, an electrode assembly in the battery case, the electrode assembly including a plurality of windings that are wound about a winding axis, the winding axis being oriented parallel to a bottom surface of the battery case, and a deformable member between the electrode assembly and the bottom surface of the battery case, the deformable member being pressed between the electrode assembly and the bottom surface of the battery case.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
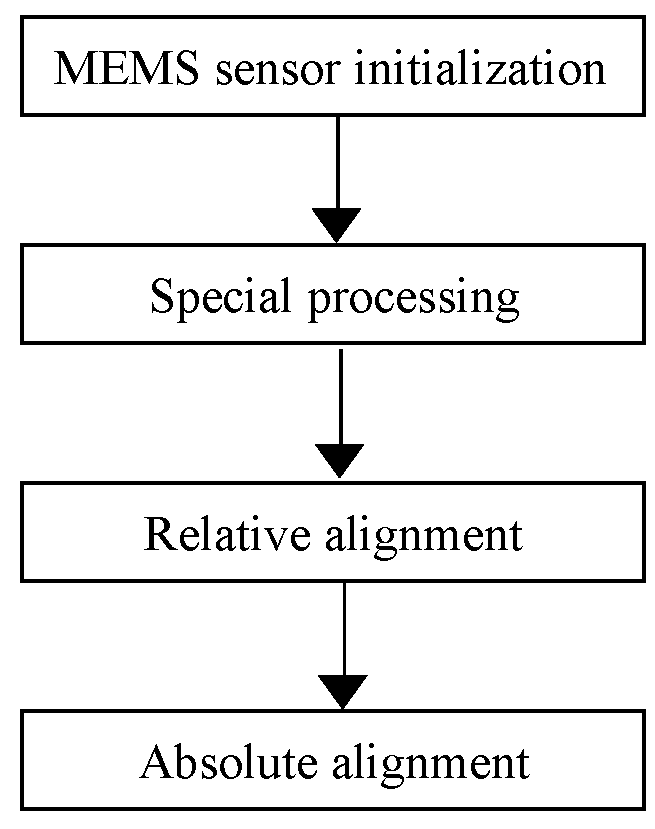
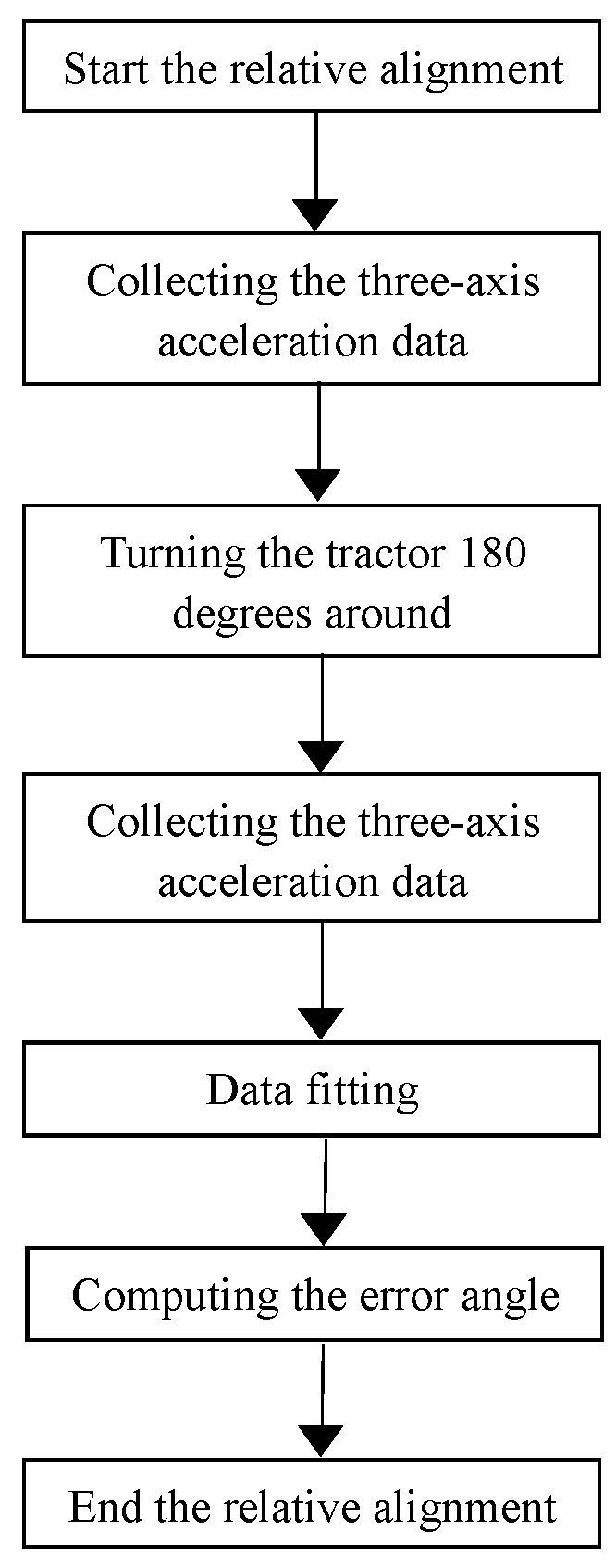
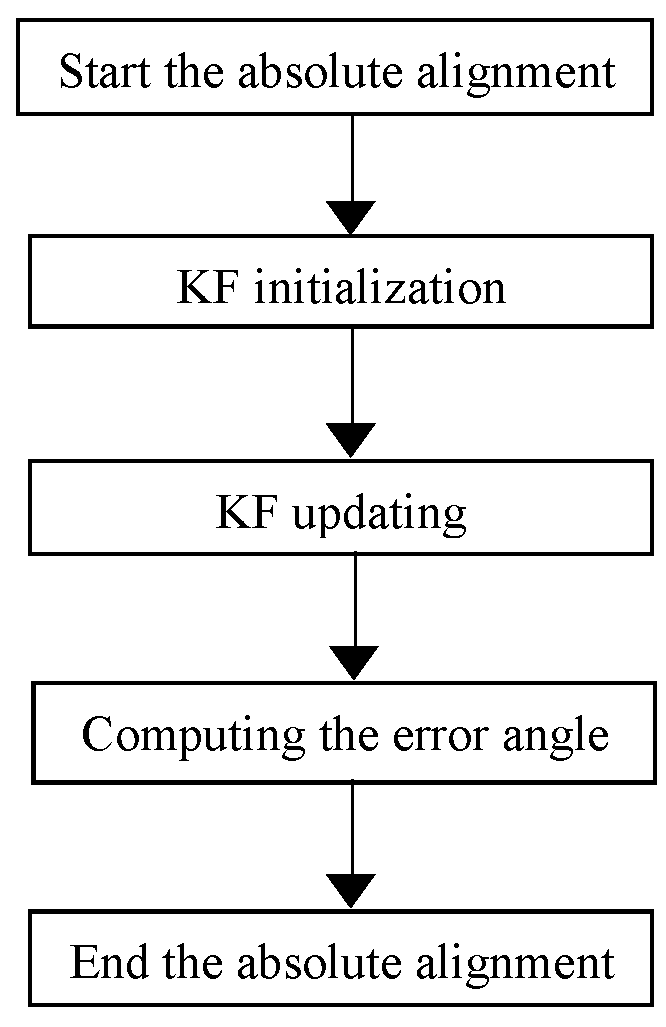
A method for initial alignment of an inertial navigation apparatus
ActiveUS20180274940A1Convergence can be speededImprove accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterComputer vision
A method for initial alignment of an inertial navigation apparatus, comprising the following steps: providing an apparatus loaded with a sensor, and preprocessing the sensor; carrying out relative alignment to calculate an installation error angle of the sensor; carrying out absolute alignment to calculate an installation attitude angle error of the sensor to increase an accuracy of an error attitude angle calculated during the relative alignment. The relative alignment process calculates a relative error attitude angle, the relative error attitude angle being used as the initial value for attitude error in a stat vector in the absolute alignment process, thereby accelerating convergence of the Kalman filter. Alignment precision is further enhanced by the absolute alignment process.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUACE NAVIGATION TECH
Hand-held power tool
ActiveUS20100149790A1Better securingProtection outputLighting support devicesLighting elementsHand heldEngineering
A hand-held power tool comprising an output shaft rotatable around a tool axis of rotation, a tool housing portion radially disposed relative to the output shaft, an illuminating element for illuminating a work area of the tool, a lens positioned adjacent the illuminating element, and a cover that secures the lens and the illuminating element to the tool housing portion. At least a portion of the cover is closer to the axis of rotation than the lens is to the axis of rotation.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Underground station constructed by prefabricated parts and construction method thereof
ActiveCN105089669ARealize industrializationEasy to industrializeArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresEnvironment effectSpatial structure
The invention discloses an underground station constructed by prefabricated parts and a construction method thereof. The underground station comprises an upper station layer and a lower station layer; the upper station layer and the lower station layer are both formed by assembling a plurality of prefabricated parts, the lower station layer is communicated with the upper station layer, upper and lower station layer stairways are arranged at the communicating position, and the lower station layer is provided with a platform; the upper station layer is communicated with the ground, and a plurality of ground stairways communicated with the ground are arranged in the upper station layer. The lower station layer and the upper station layer are constructed in sequence, stiffening rib steel structures are dismantled after assembly of the prefabricated parts is completed, and an underground station space structure is formed; a top plate of the lower station layer and a bottom plate of the upper station layer are connected through bolts, pouring and leveling treatment is performed on bottom plates of the two layers, combined structure columns in the station are bound, and concrete is poured for reinforcement; then the station is decorated to complete station construction. The method has the advantages that construction is flexible and rapid, small-buried depth construction can be performed, influences on traffic and environment are small, and industrial production can be achieved.
Owner:山东轨道交通勘察设计院有限公司 +1
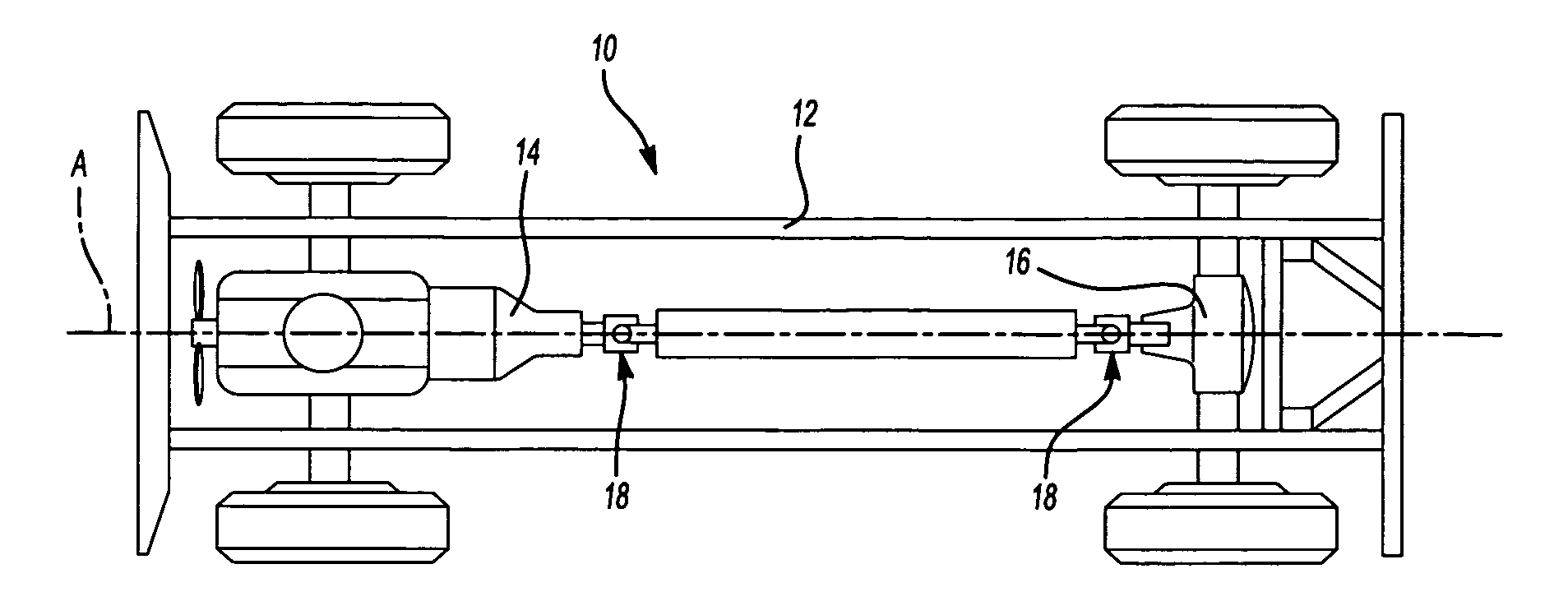
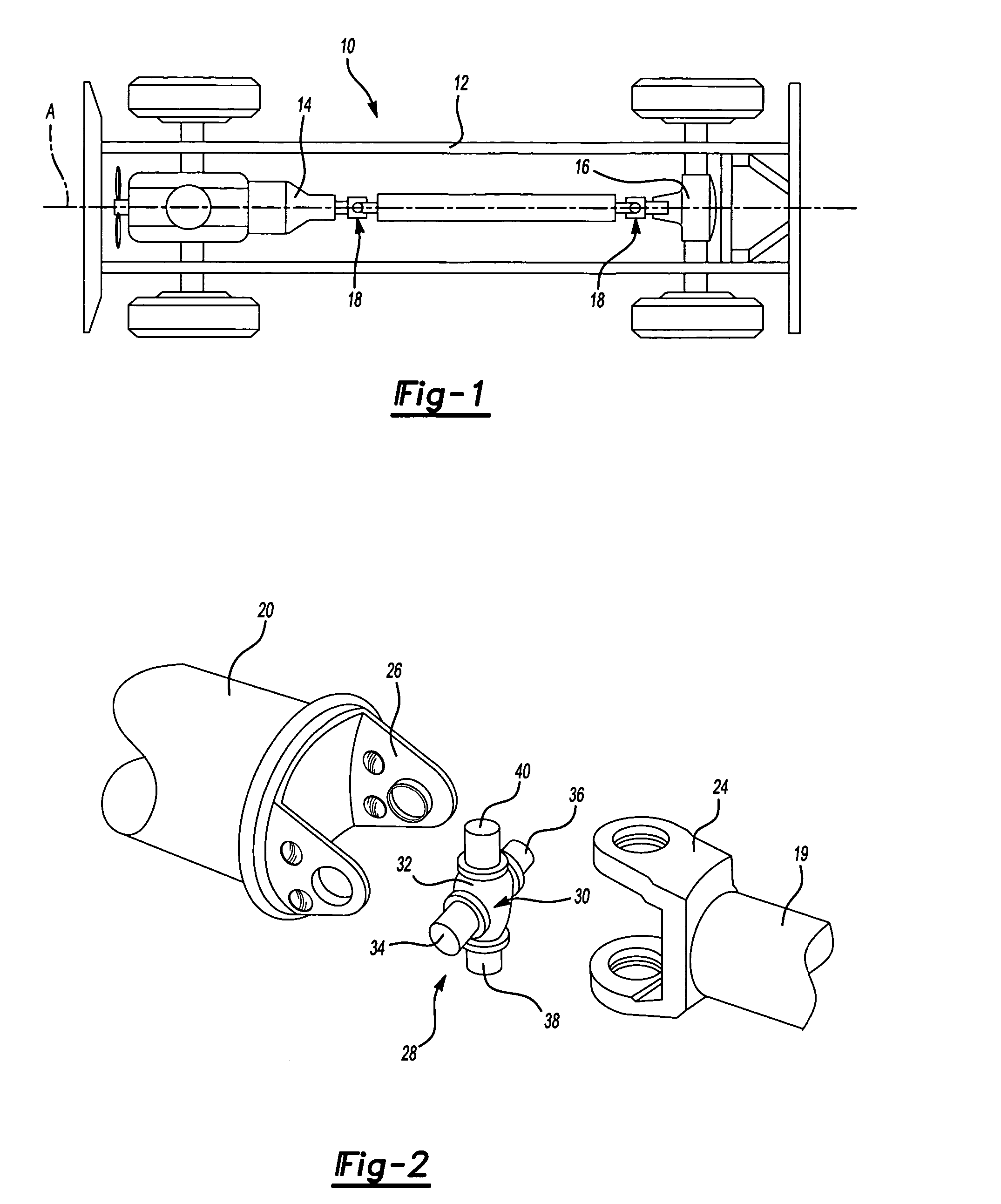
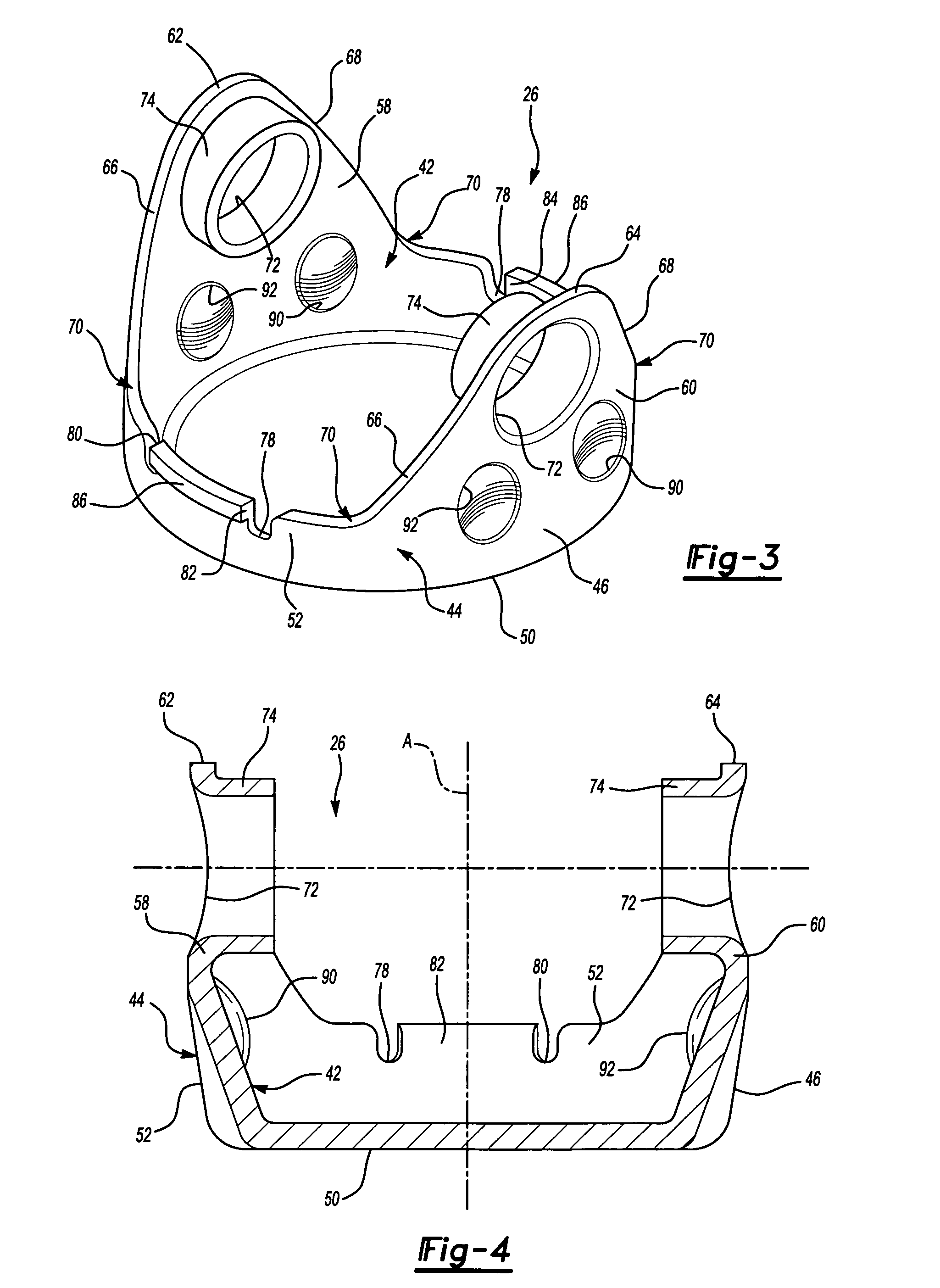
Universal joint assembly for an automotive driveline system
A driveline system for an automotive driveline system includes a transmission device, a differential device, and a universal joint having a drive shaft presenting terminal ends and interconnecting the transmission and differential devices. A yoke is connected to each of the terminal ends of the drive shaft and presents an internal surface and an external surface having generally equal thickness defined therebetween to form a dish of the yoke having a tubular monolithic structure. The yoke portion includes a bottom and a pair of spaced lugs each presenting sloping side walls for reinforcing the lugs as said yoke is rotated around a longitudinal axis.
Owner:RONJO
Test device and test method for fatigue life of bearing with ultra-low temperature and high DN value
PendingCN109975022AImprove cooling effectReduce vibrationMachine bearings testingRubber CupEngineering
The invention discloses a test device and a test method for fatigue life of a bearing with ultra-low temperature and a high DN value. The test device comprises a device housing, wherein the device housing is connected with an axial flexible loading device and a radial flexible loading device; the axial flexible loading device and the radial flexible loading device are connected with a test rotor respectively; the test rotor comprises a main shaft; a tested bearing, a supporting process bearing, two loading process bearings and a shaft sleeve are installed on the main shaft; the main shaft andend covers are sealed by means of rubber cup sealing pieces; a force transmission sleeve having a through hole is installed between the axial flexible loading device and the radial flexible loading device; and a tested bearing outer sleeve and a front pressing cover fix a tested bearing outer ring through threaded connection, the tested bearing outer sleeve is connected with a front intermediate sleeve, and the front intermediate sleeve is connected with a front positioning cover. The test device and the test method realize the simulation of actual operating conditions of a low-temperature bearing in a turbopump of a low-temperature liquid rocket engine, including the ambient temperature, load, rotational speed and cooling flow rate being consistent or approximated to the actual operatingconditions.
Owner:北京宇航推进科技有限公司
Linear guide rail precision automatic measuring device and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN103438839AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilityUsing fluid meansElectrical and Electronics engineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SU CHUNGUANG
Collision-prevention electronic device control box
InactiveCN107493666ANot easy to damageAvoid damageNon-rotating vibration suppressionCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsEngineeringElectron
The invention provides an anti-collision electronic device control box, which relates to the field of electronic devices. The anti-collision electronic device control box includes a fixing plate, four corners of the bottom of the fixing plate are fixedly installed with connecting blocks, and the bottom of the connecting blocks is fixedly connected with the top of the first pressure rod. The bottom end penetrates the first shock absorber and extends to the inside of the first shock absorber and is fixedly connected with the top of the first pressing block. The anti-collision electronic device control box drives the second splint to clamp and fix the front and back of the box through the second shock absorber, and drives the first splint to clamp and fix the left and right sides of the box through the screw, so that the box is clamped and fixed. Reliably fixed, through the first shock absorber and the buffer shock absorption, the fixed plate drives the box body to move along the surface of the guide rod, so as to effectively buffer the box body and make it difficult for the box body to separate from the base. The electronic devices inside the protection box are not easily damaged, and the use cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:石国华
Impact tool
ActiveUS20090236110A1Avoid interferenceImprove the ease of assemblySleeve/socket jointsTurning machine accessoriesEngineeringLubricant
It is an object of the invention to provide a technique which is effective in improving the durability of an angular positioning device of a tool bit and in reducing weight of a tool body in an impact tool. A representative impact tool includes a tool body, a lubricant sealed in the housing space, a driving mechanism, a tool holder, an angular positioning device disposed on a tip end side of the tool body and serves to fix a position of the tool bit around the axis with respect to the tool body. The angular positioning device includes first and second locking members. The first locking member is disposed between the tool body and the tool holder. The second locking member is disposed opposite to the first locking member. One end of the first locking member in the axial direction of the tool bit extends into the housing space of the tool body and is connected to the tool body within the housing space.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
Container having liquid detecting function
InactiveUS20060152539A1Improve accuracyHigh detection sensitivityOther printing apparatusLevel indicators by physical variable measurementEngineering
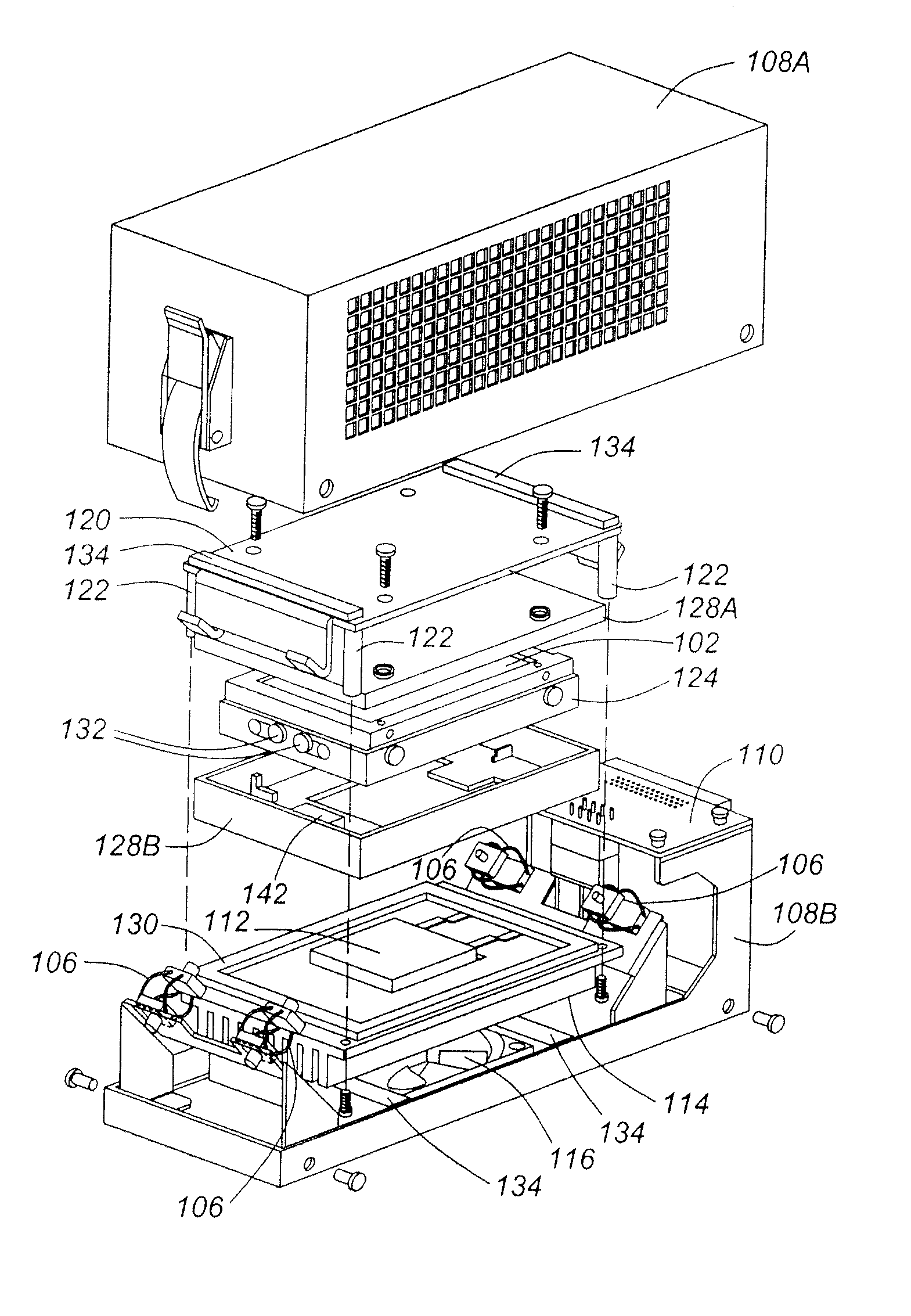
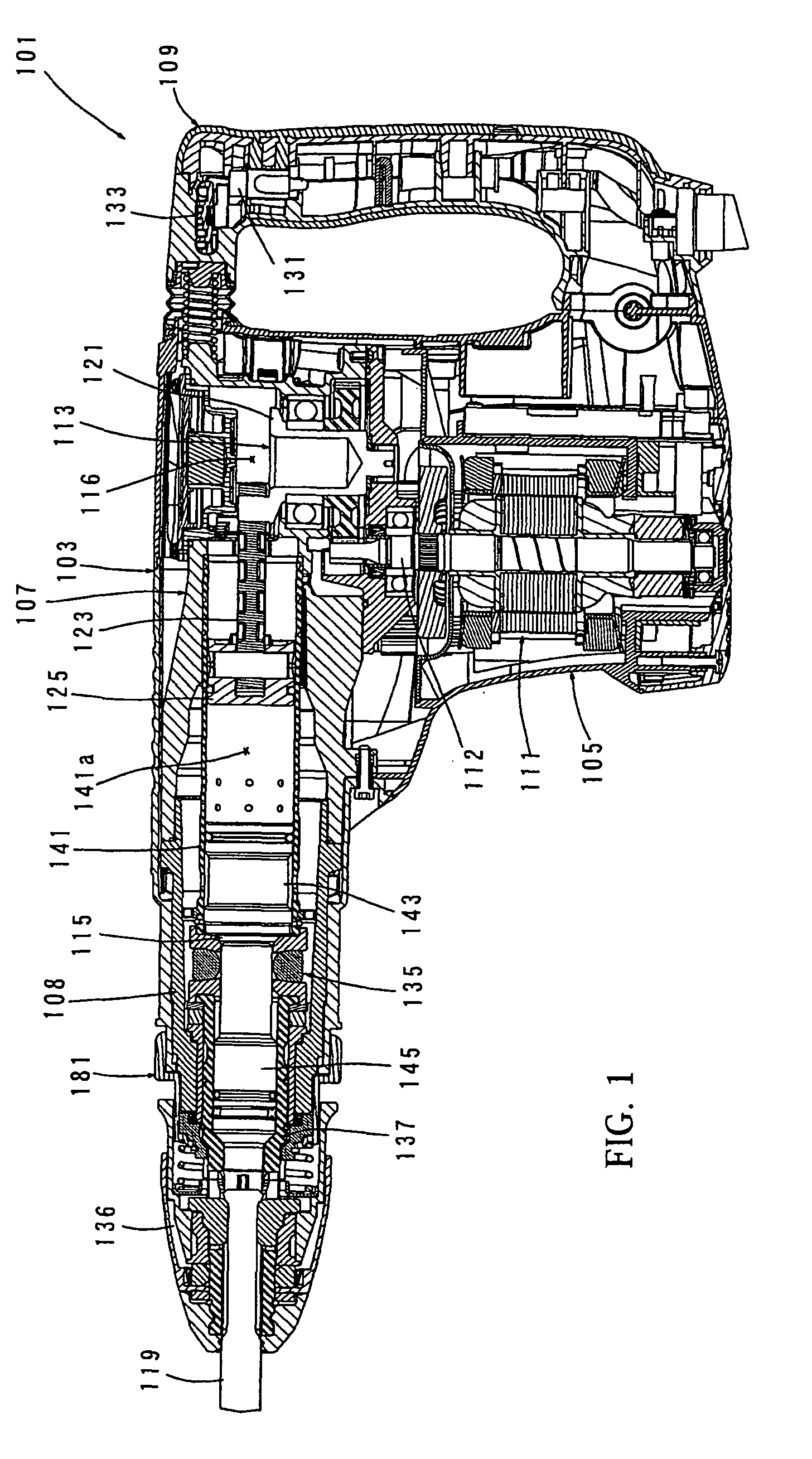
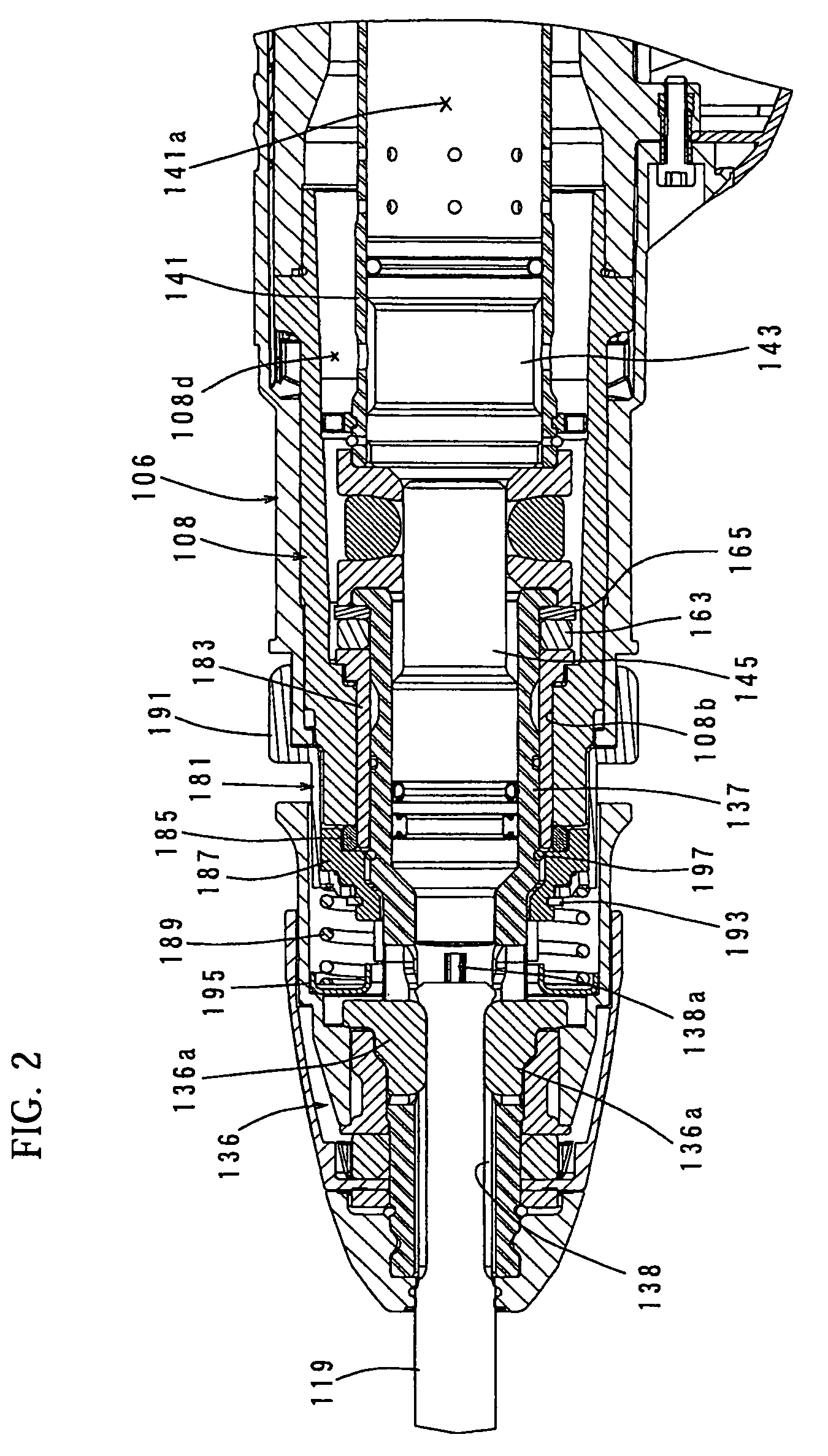
A container having a liquid detecting function includes a cartridge case 101 having a sending passage for sending out a liquid stored therein, buffer chambers 122 and 123 disposed in the vicinity of the end of the sending passage, and a sensor unit 200 disposed to face on the buffer chambers. A sensor chip 230 provided in the sensor unit includes a sensor cavity 233 communicating with the buffer chambers, a vibration plate 233 closing an opening side of the sensor cavity opposite to the side communicating with the buffer chambers, and a piezoelectric element 234 which is disposed on the surface of the vibration plate opposite to the surface facing the sensor cavity, emits a vibration wave to the sensor cavity and the buffer chambers through the vibration plate, receives a reflected wave returning from the buffer chambers through the vibration plate, and then converts the reflected wave into an electrical signal. The compliance values of the buffer chambers 122 and 123 are set to be ten times greater than the compliance value of the sensor cavity.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Hydraulic pressure suspension polishing method and device thereof
ActiveCN105538046AImprove stabilityReduce vibration effectsGrinding drivesGrinding feed controlEngineeringForce sensor
The invention discloses a hydraulic pressure suspension polishing method and a device thereof. A servo motor and a synchronous pulley drive a shaft sleeve and a ball spline shaft so as to directly drive a polishing disk to rotate at high speed, and the processing efficiency is improved. A wedge groove is formed in the polishing disk pasted with a workpiece, and a wedging effect is formed at high speed and in small gap, so that the polishing disk drives the ball spline shaft to float upwards along the shaft sleeve, and uniform non-contact polishing is realized. A bottom container is lifted through an electric lifting platform to realize initial positioning. A force measuring sensor is mounted at the top and is used for positioning a cutter between the polishing disk and the container to ensure the reliability of positioning. The spline shaft is connected with a balance plate together through a supporting seat, and four groups of springs are arranged between the balance plate and a bottom plate and are used for overcoming the gravity of a polishing component. A laser displacement sensor mounted on the bottom plate is used for measuring the distance of floating up or down of the balance plate in the polishing process. An electrical vortex sensor and a pressure sensor are mounted at bottom container and are used for detecting the size of a polishing gap and hydraulic pressure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Article surface morphology detection method and device
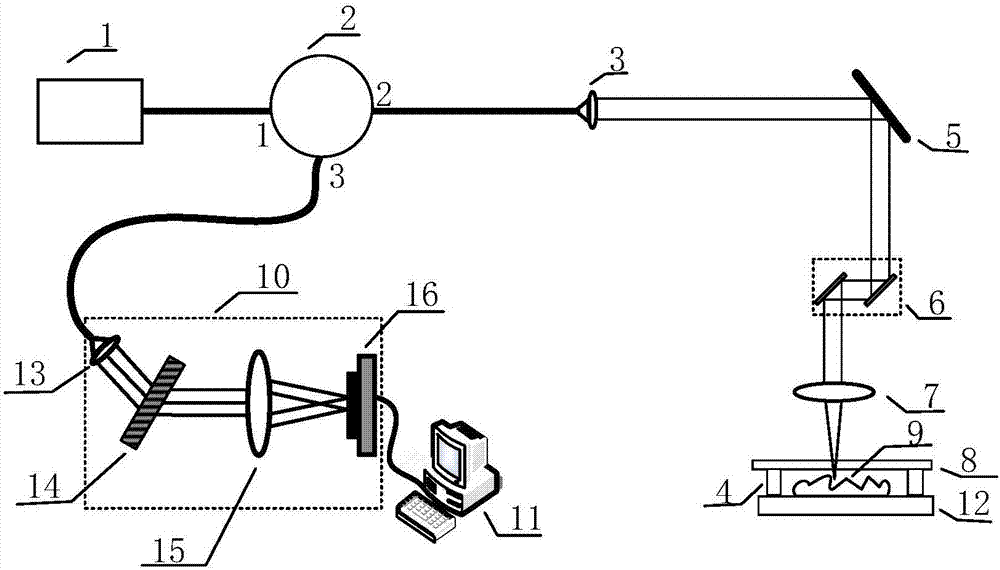
An article surface morphology detection method disclosed by the present invention comprises the following steps that (1) the low-coherence light rays irradiate in from a port 1 of a three-end circulator, irradiate out from a port 2, irradiate in from an x galvanometer in an x-y scanning galvanometer after being collimated by a first lens, and irradiate out from a y galvanometer;(3) the irradiated out light rays are focused by a second lens and then are divided into two parts of light rays by a light splitter, one part of the light rays are reflected from the undersurface of a glass as the reference light, and the other part of light rays penetrate the glass and then irradiate to the surface of a sample to be reflected as the sample light; (4) the two parts of light rays are returned in a common light path, are gathered to the y galvanometer of the scanning galvanometer via the second lens, irradiate in the x galvanometer via the y galvanometer, and then are irradiate out; (5) the light rays are gathered by the first lens to enter the port 2 of the three-end circulator, and then irradiate out from a port 3; (6) the light rays irradiated out from the port 3 enter a spectrograph, and the spectrograph transmits the data to a computer; (7) the scanning galvanometer scans the sample point by point; (8) the computer calculate the phase difference of the adjacent positions and the depth difference delta Z, thereby obtaining the final quantitative distribution situation of the surface morphology of the sample.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Elevator rope sway mitigation
A method of operating an elevator system includes detecting a building sway which causes sway of elevator suspension or compensation members. An elevator control system is switched into a building sway mode, and operation of one or more elevator cars of the elevator system is changed via the building sway mode to mitigate vibratory effects of the building sway on the one or more elevator cars.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com