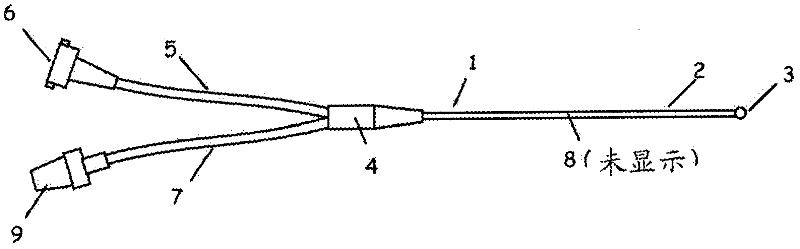
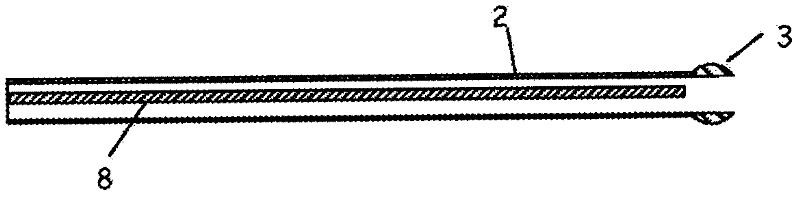
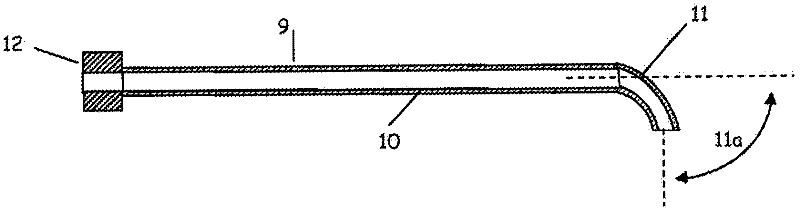
Methods and apparatus for sub-retinal catheterization
A retinal and catheter-based technology, applied in the macular area, can solve the problems of the delicate structure of the retina, the limited availability of interventional procedures, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1 : Two enucleated rabbit eyes and human cadaver eyes were prepared for testing. The ciliary pars plana region of the sclera was dissected with an approximately 4 mm incision to expose the choroid. A series of round steel probes were used to apply pressure to the choroid and retina to determine if a specific size range of the atraumatic catheter tip would help prevent inadvertent penetration into the posterior chamber.
[0052] Round steel probes with tip diameters indicated in Table 1 were tested during dissection of the choroid to the subretinal space. Table 1 also shows the resulting effects observed.
[0053] Table 1. Probe Tip Diameters and Dissection Results
[0054] Probe Tip Diameter
[0055] Results from enucleated rabbit eyes and human cadaver eyes indicated that rounded tips less than 220 microns in diameter easily penetrated into the posterior chamber and provided no protection against penetration through the retina.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: Use of enucleated human cadaver eyes to determine the mechanical properties of stem atraumatic delivery in the subretinal space. Eyes were prepared in an "open sky" approach by dissecting the anterior segment of the globe at the level of the ciliary body and removing the lens. In the living eye, retinal tissue is connected to the RPE by interdigitation of cells and the RPE's fluid pump mechanism. Post-mortem, the retina is no longer strongly connected to the RPE, so a method was used to maintain retinal orientation during the experiment. A heavy fluid with a density of 1.707 Kg / L, perfluoromethylcyclopentane (Flutec PClC, F2 Chemicals LTD), was injected into the vitreous cavity to replace the vitreous humor and hold the retina in place, similar to that seen in retinal detachment repair use heavy fluids. A notch was cut in the eyeball down to the level of the anterior insertion of the retina to gain direct access to the retina via an internal route.
[00...
Embodiment 4
[0071] Example 4 : Internal and external access to the subretinal space was tested in a live animal study using a rabbit model. The study was performed under a protocol approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Rabbits were anesthetized, draped and prepared for ophthalmic surgery per protocol.
[0072] To test the transintrinsic approach in rabbit eyes, two small pars plana incisions were made with an MVR knife for infusion and vitrectomy access, and a 23 gauge sclerostomy opening was placed in the ciliary In the pars plana, for the placement of tubular introducers and catheters. After performing a vitrectomy, a thin-walled introducer with a curved tip is placed through a 23-gauge opening. The introducer was constructed as in Example 2. The introducer is advanced across the eyeball and the distal tip is inserted into the peripheral retina to allow passage of the catheter into the subretinal space. The catheter tip is placed through the introduc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com