Automatic focusing unit and method
An automatic focusing and defocusing technology, applied in installation, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of large error of automatic focusing accuracy, and achieve the effect of improving the accuracy of automatic focusing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
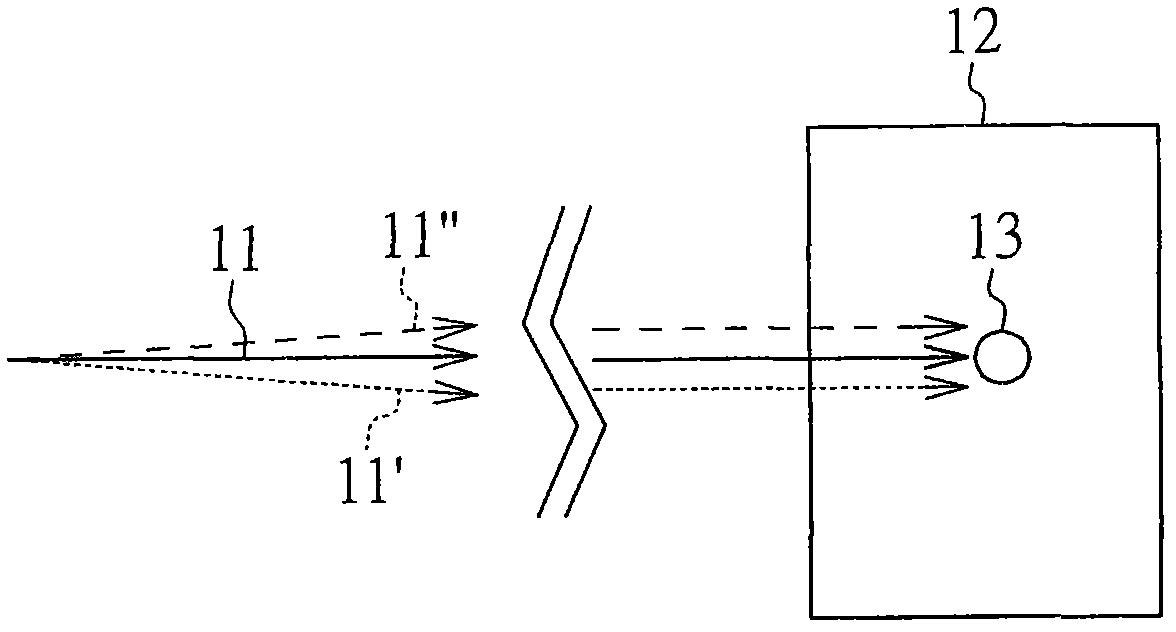
[0051] figure 2 A schematic diagram showing an autofocus device 50 for reducing the influence of light source disturbance on autofocus accuracy according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The autofocus device 50 includes: a light source irradiation unit 100 , an imaging optical path unit 200 and an observation unit 300 . Detectors are represented by reference symbol S. The autofocus device 50 may further include: a signal processing unit 400 and a driving unit 500 .
[0052]The light source irradiation unit 100 includes: a light emitting element 110 , a light path adjuster 101 , light shaping mirrors 102 and 103 , a light interrupter 104 , beam splitters (BS, beam splitter) 105 and 106 , and an objective lens 107 . The light emitting element 110 is, for example but not limited to, a laser diode (LD).
[0053] The imaging optical path unit 200 includes: an objective lens 107 , beam splitters 105 and 106 , a focusing lens 201 and an optical sensor 202 . In t...
no. 2 example
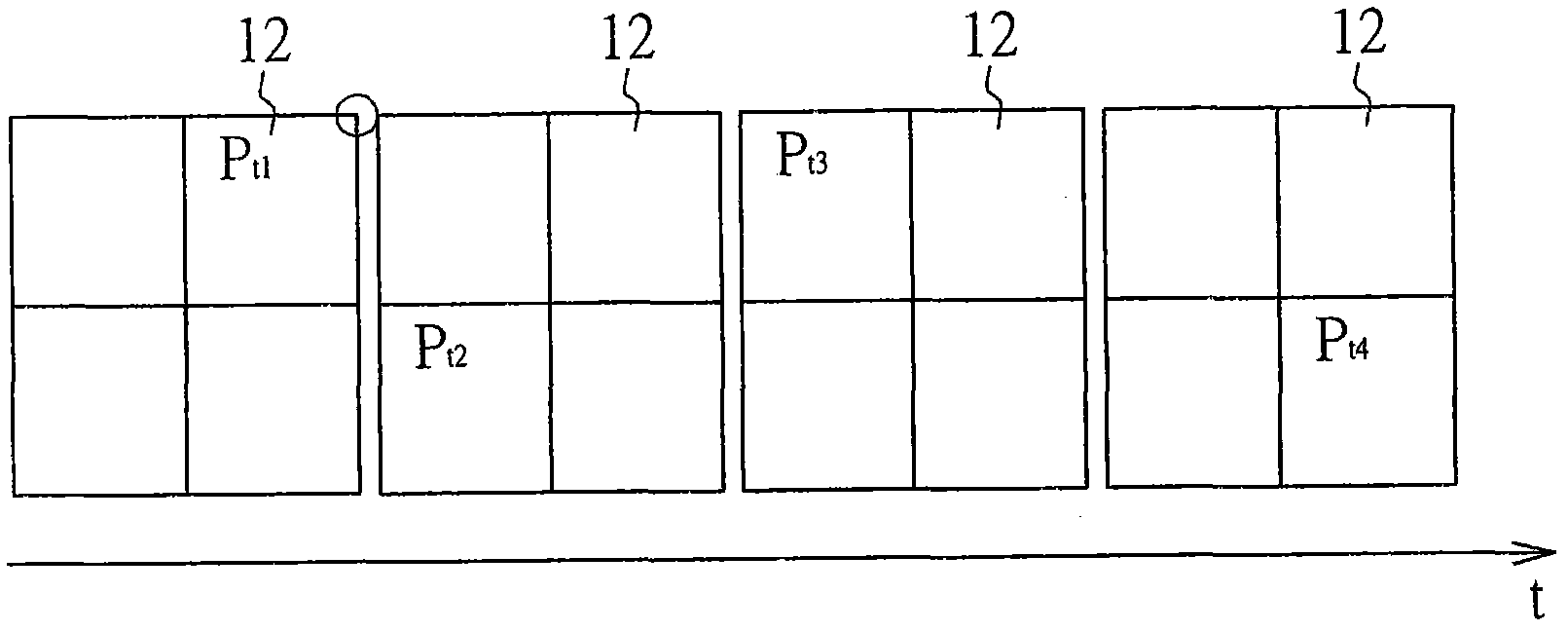
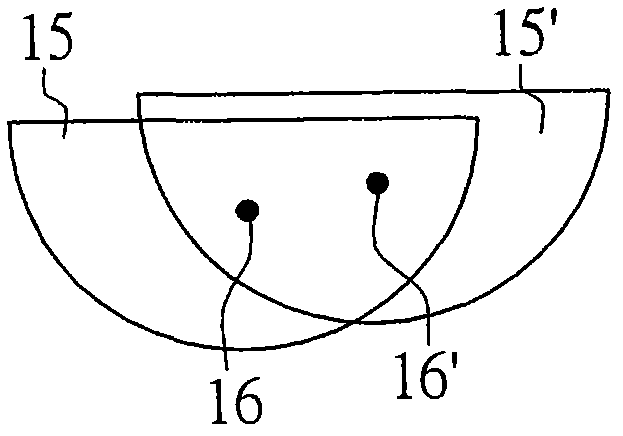
[0063] In the second embodiment of the present invention, a signal algorithm is used to further improve the precision of autofocus. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the center of gravity positions 222 and 232 of the images 221 and 231 imaged on the light sensor 202 at different time points will be different due to different time points. But for images 221 and 231, the relative position δ between their geometric center points 223 and 233 and their center of gravity positions 222 and 232, in principle, even if the optical axis changes, the relative position δ will not change accordingly. change. Therefore, in the second embodiment of the present invention, the relative position δ (the relative position between the geometric center point of the image and its center of gravity) of the image imaged on the optical sensor can be used as the basis for judging the defocus distance and defocus direction, In order to further improve the accuracy of autofocus. In particular, in the second e...
no. 3 example
[0065] In the third embodiment of the present invention, a signal algorithm is used to further improve the precision of autofocus. Such as Image 6 As shown, the geometric areas A of the images 221 and 231 imaged on the optical sensor 202 at different time points will not be different in principle due to different time points. Even, in principle, even if the optical axis changes, the theoretical geometric area of the image A will not change accordingly. Therefore, in the third embodiment of the present invention, the geometric area A of the image imaged on the optical sensor can be used as the basis for judging the defocus distance and defocus direction, so as to further improve the accuracy of autofocus. In particular, in the third embodiment, the optical path adjuster 101 can even be omitted if further cost saving is desired.
[0066] In summary, it can be seen that in several embodiments of the present invention, the defocus position of the detection object S can be obt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com