Free-draining finned surface architecture for a heat exchanger
A technology of heat exchangers and fins, applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, heat exchanger types, heat exchange equipment safety devices, etc., can solve problems such as exposure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
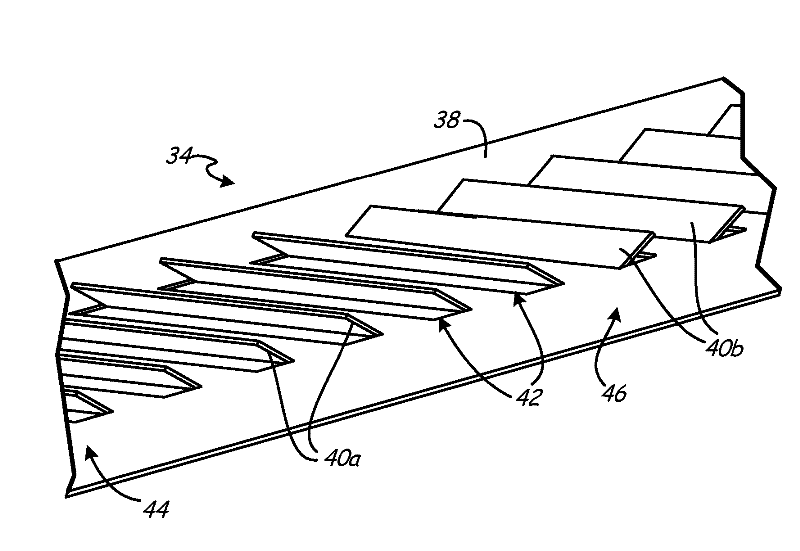
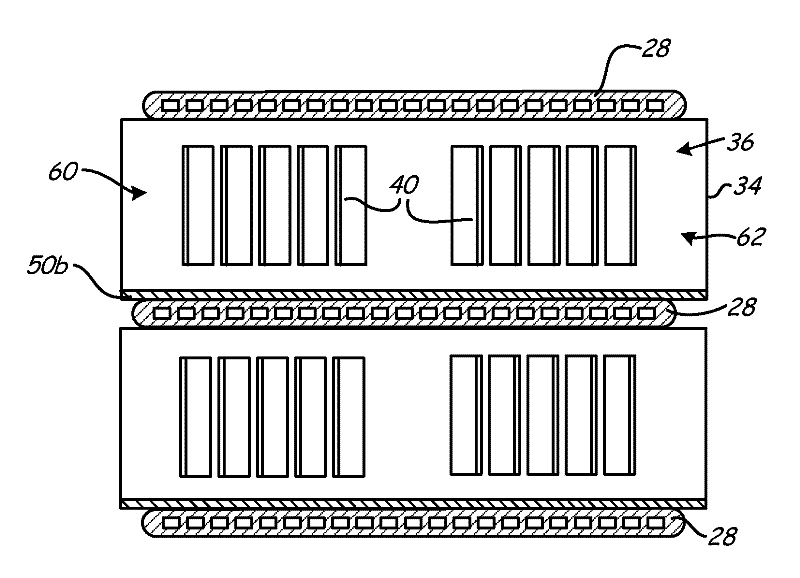
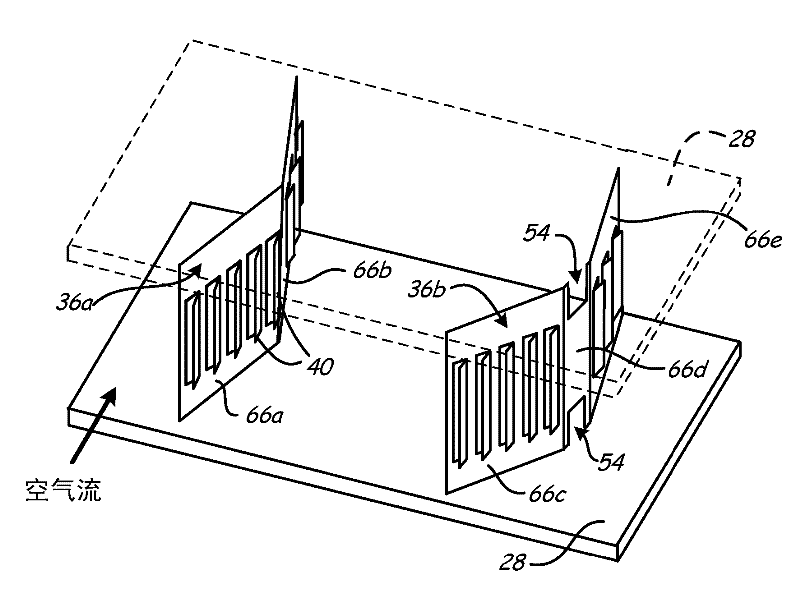
[0018] The present invention describes a fin structure with grids and drainage enhancing features that provide improved liquid drainage within the heat exchanger. The fin structure allows water to drain more easily and improves water removal from the outer surface of the heat exchanger. This fin structure works for any type of tube-fin heat exchanger and is particularly useful for aluminum microchannel heat exchangers, especially aluminum microchannel condensers. Although specific embodiments are described with reference to aluminum microchannel heat exchangers, the invention may provide benefits to other tube-fin heat exchangers as well. Aluminum microchannel heat exchangers generally have a more compact structure than other heat exchangers. Typical fin pitches vary between about 5.5 fins per centimeter (14 fins per inch) and about 9.1 fins per centimeter (23 fins per inch), while typical heat exchange tube pitches are around 0.5 cm (0.19 in) ) and approximately 1.0 cm (0.3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com