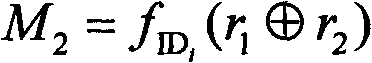RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Device) mutual authentication method based on Hash
A technology of two-way authentication and reader, applied in the field of RFID two-way authentication, can solve the problem of low efficiency in retrieving target tags, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of calculation and improving efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
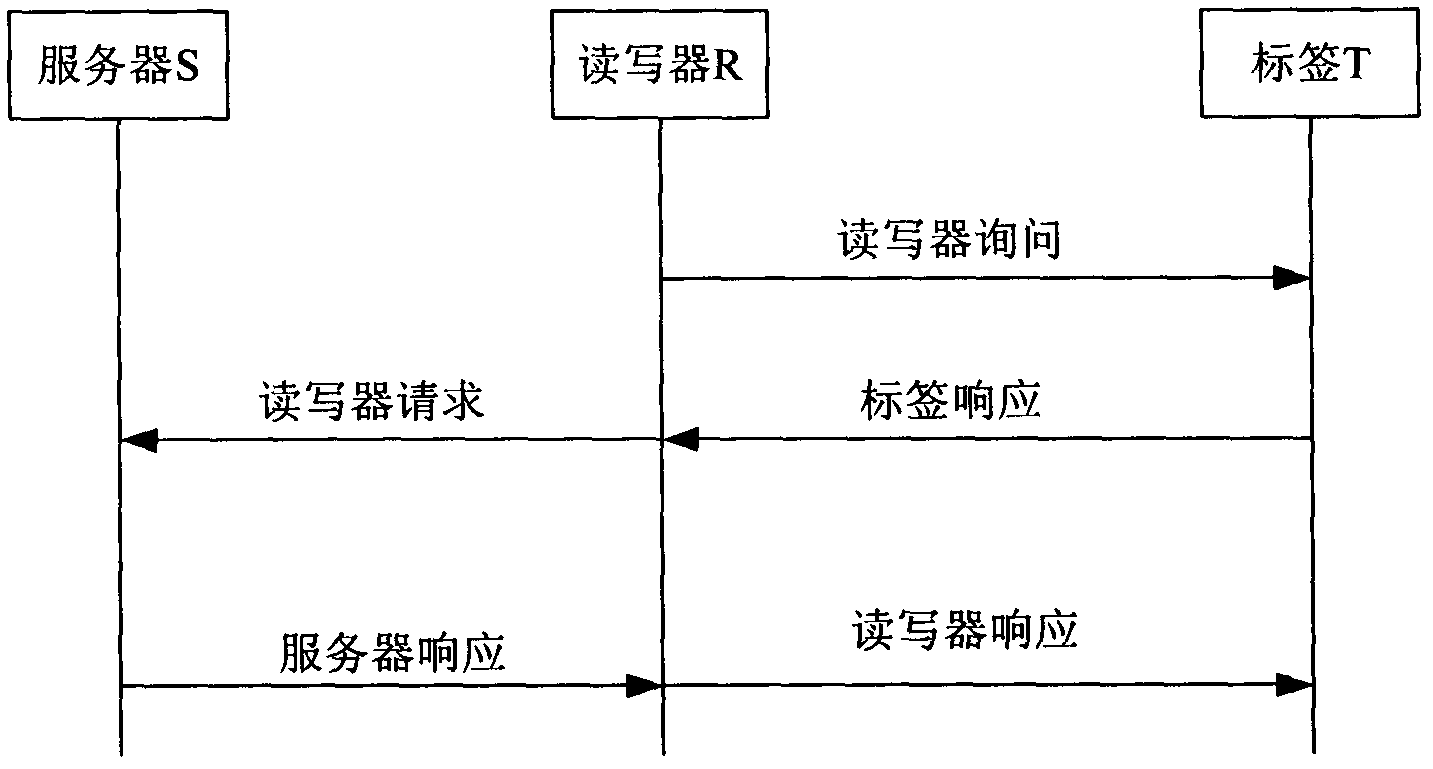
[0027] Glossary:
[0028] N: the maximum number of tags in the RFID system;
[0029] i: positive integer (1≤i≤N);
[0030] new : The subscript new indicates the current value;
[0031] old : The subscript old indicates the previous value;
[0032] ID i : the tag identifier stored in the tag;
[0033] l: data length, usually set to the length of the tag identifier;
[0034] h(x): Hash function, h: {0, 1}l→{0, 1}l, x is an independent variable;
[0035] f k (x): Hash function f with key k : {0, 1} l × {0, 1} l → {0, 1} l , where k is the encryption key and x is the argument;
[0036] ID inew : the current tag identifier stored in the database;
[0037] ID iold : the previous tag identifier stored in the database;
[0038] h inew : the hash value of the current tag identifier stored in the database;
[0039] h iold : the hash value of the previous tag identifier stored in the database;
[0040] D. i : Details of tags stored in the database;
[0041] r 1 : ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com