Application of carbon monoxide molecules in inhibition on acute rejection after skin grafting
A technique for skin grafting, acute rejection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
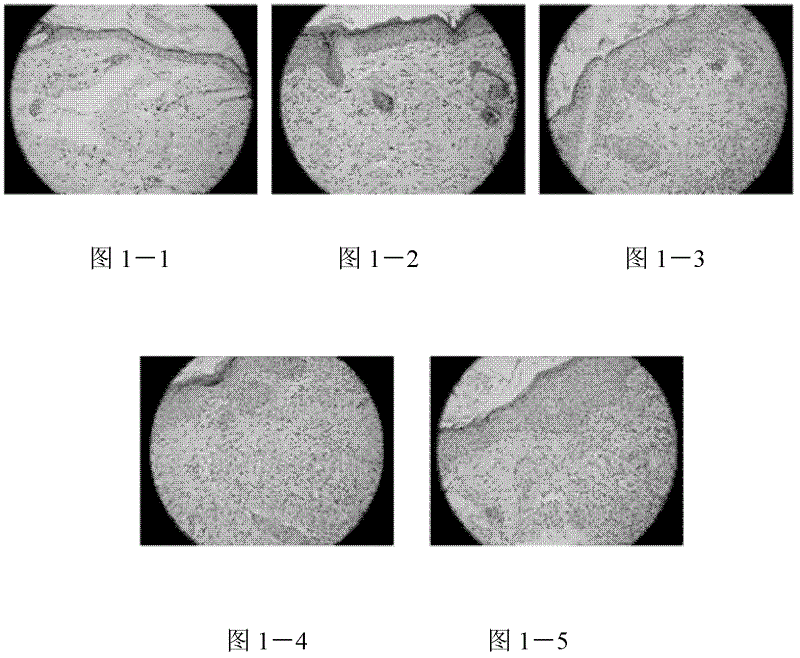
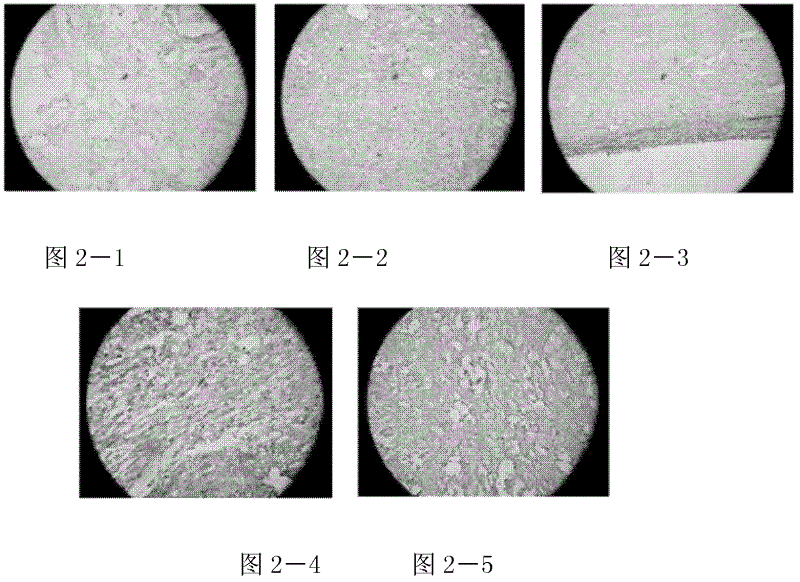
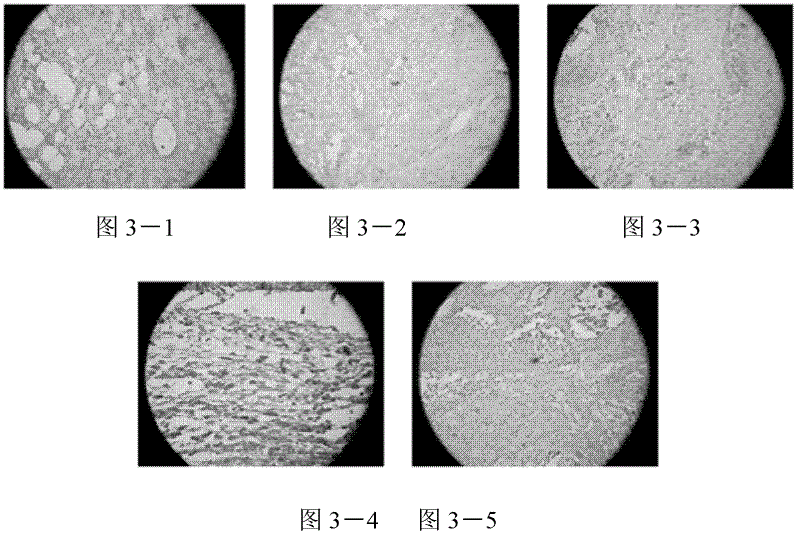
[0022] Experimental observation of exogenous carbon monoxide releasing molecule CORM-2 on grafts after skin transplantation in allogeneic mice Test method:
[0023] (1) Animal and allogeneic mouse skin graft models
[0024] Clean-grade ICR mice and BALB / C mice were used as donors and recipients to establish allogeneic skin transplantation models, which were divided into 5 groups: 1 group of sham operation group, 2 groups of allogeneic skin transplantation group, and 3 groups of allogeneic skin transplantation Allogeneic skin transplantation + CORM-2 group, 4 allogeneic skin transplantation + iCORM-2 groups, 5 allogeneic skin transplantation + CsA groups; postoperative administration was given according to the requirements of each group, and the degree of rejection of the grafted skin was observed. The observation period was 7 days. At the end of the observation period, the grafted skin pieces were removed and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, sectioned, ro...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Effects of exogenous carbon monoxide releasing molecule (CORM) 2 on spleen lymphocyte function after skin transplantation in allogeneic mice
[0059] Acute rejection after allogeneic skin transplantation in mice is mainly characterized by monocyte-mediated cellular immunity dominated by T lymphocytes. Among them, the ratio of the two subsets of T lymphocytes (CD4 + / CD8 + ) has been recognized to a certain extent in reflecting the degree of immune rejection of transplantation. CD4 + T cells are helper T lymphocytes, which are the main cells in the process of immune response to transplantation, and CD8 + T is cytotoxic T lymphocytes, which are effector cells in the process of transplantation immune response and play a certain role in regulating immune cells. CD4 + / CD8 + The increase of the ratio is closely related to the degree of acute rejection, so it can be used as an important index to measure the degree of rejection.
[0060] In addition, after transplantati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com