Solar energy base plate for improving fracture strength
A solar substrate and rupture strength technology, applied in the field of solar substrates, can solve problems such as wafer rupture and vulnerability to external force impacts, and achieve the effects of reducing the possibility of rupture, increasing stress intensity, and increasing rupture strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
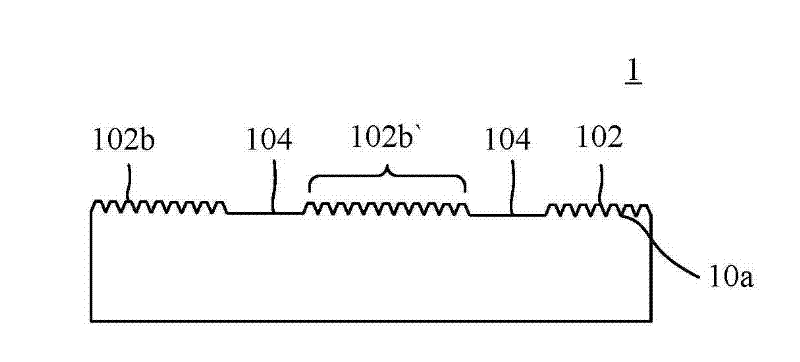
[0027] See Figure 2A , Figure 2A A cross-sectional view of a solar substrate according to a specific embodiment of the present invention is shown. As shown in the figure, the solar substrate 1 of the present invention includes an upper surface 10a, a plurality of first protruding structures 102 and a plurality of first recessed regions 104 . Each first protruding structure 102 is formed on the upper surface 10a. Each first recessed area 104 is formed around the first protruding structures 102 . The above-mentioned components will be described in detail below.
[0028] The solar substrate 1 of the present invention is an amorphous substrate, a single crystal substrate or a polycrystalline substrate. In practice, the solar substrate 1 is often based on semiconductor wafers such as silicon, that is, the solar substrate 1 can be an amorphous silicon substrate, a single crystal silicon substrate, or a polycrystalline silicon substrate. Here, the present invention is not limi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com