Permanent-magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet and synchronous motor technology, applied to synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, magnetic circuit, etc., can solve problems such as torque ripple and induced voltage distortion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
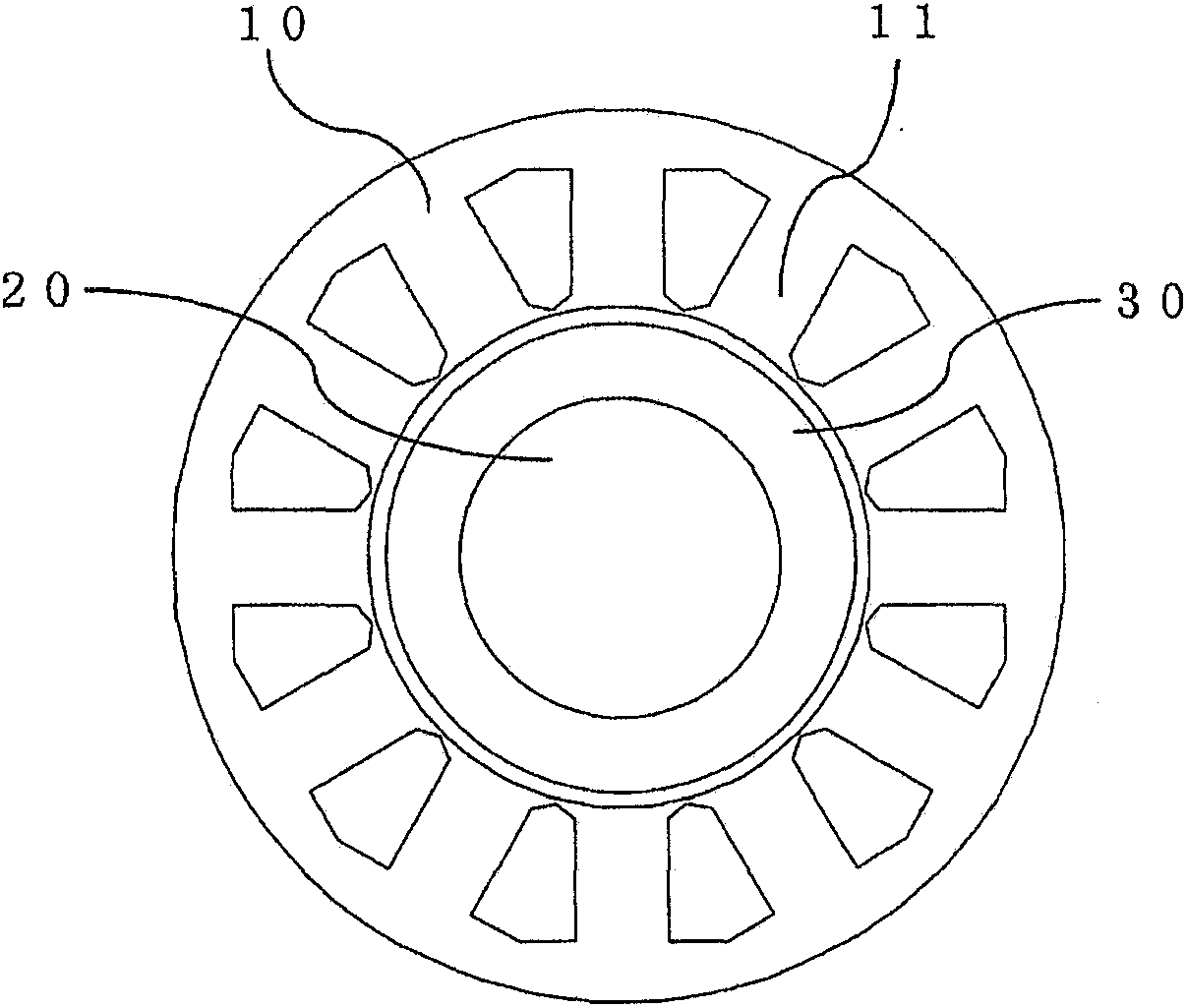
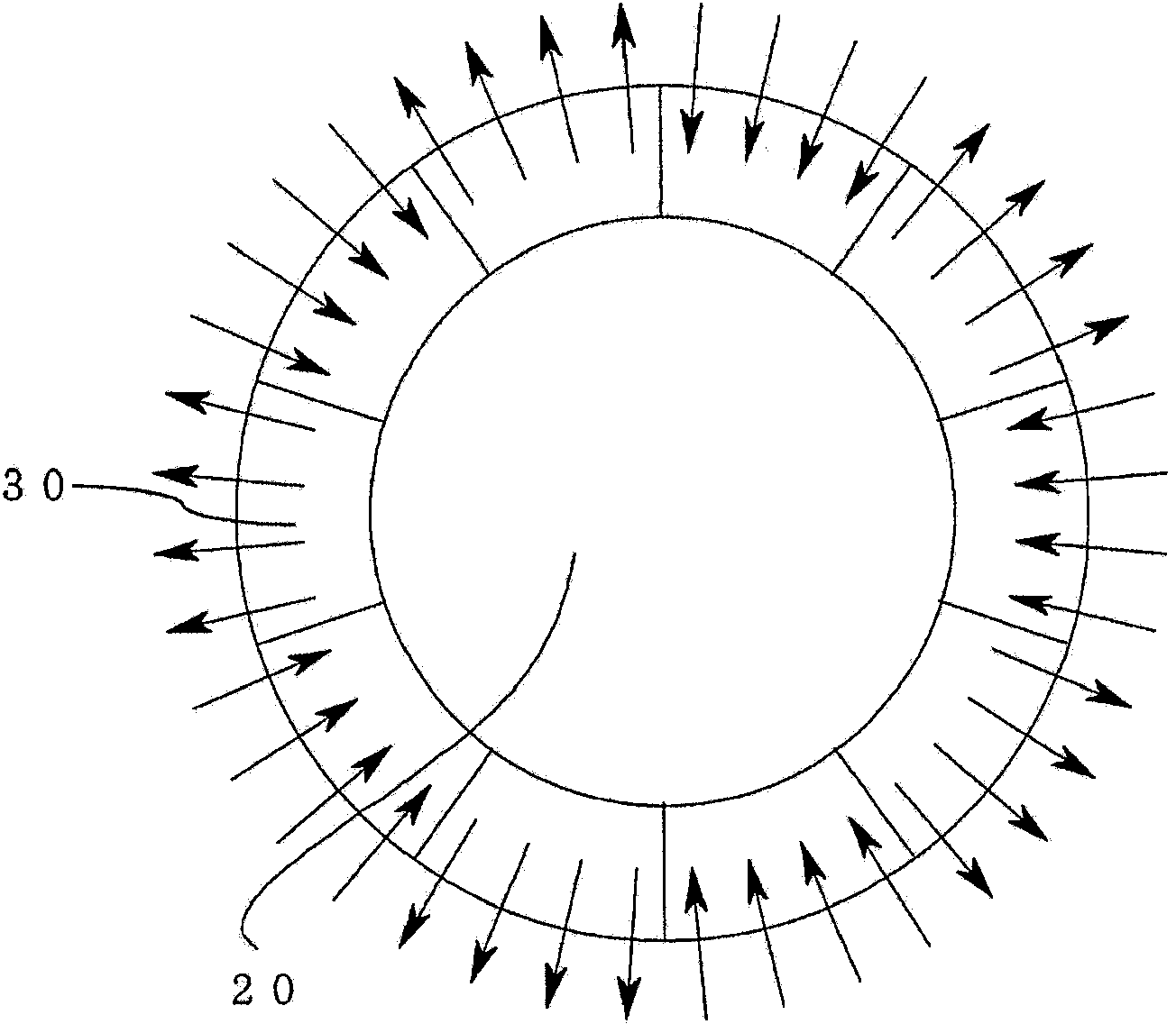
[0032] figure 1It is a sectional view showing a section perpendicular to the axial direction of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and illustrates a motor with 10 poles and 12 slots in the case of Z=12 and 2P=10. Therefore, the value of Z / (3(phase)×2P) corresponds to 12 / (3×10)=2 / 5. figure 1 The permanent magnet synchronous motor of the present invention includes a stator core 10 , a rotor core 20 , and a radially anisotropic ring magnet 30 , and the stator core 10 has a plurality of tooth portions 11 .
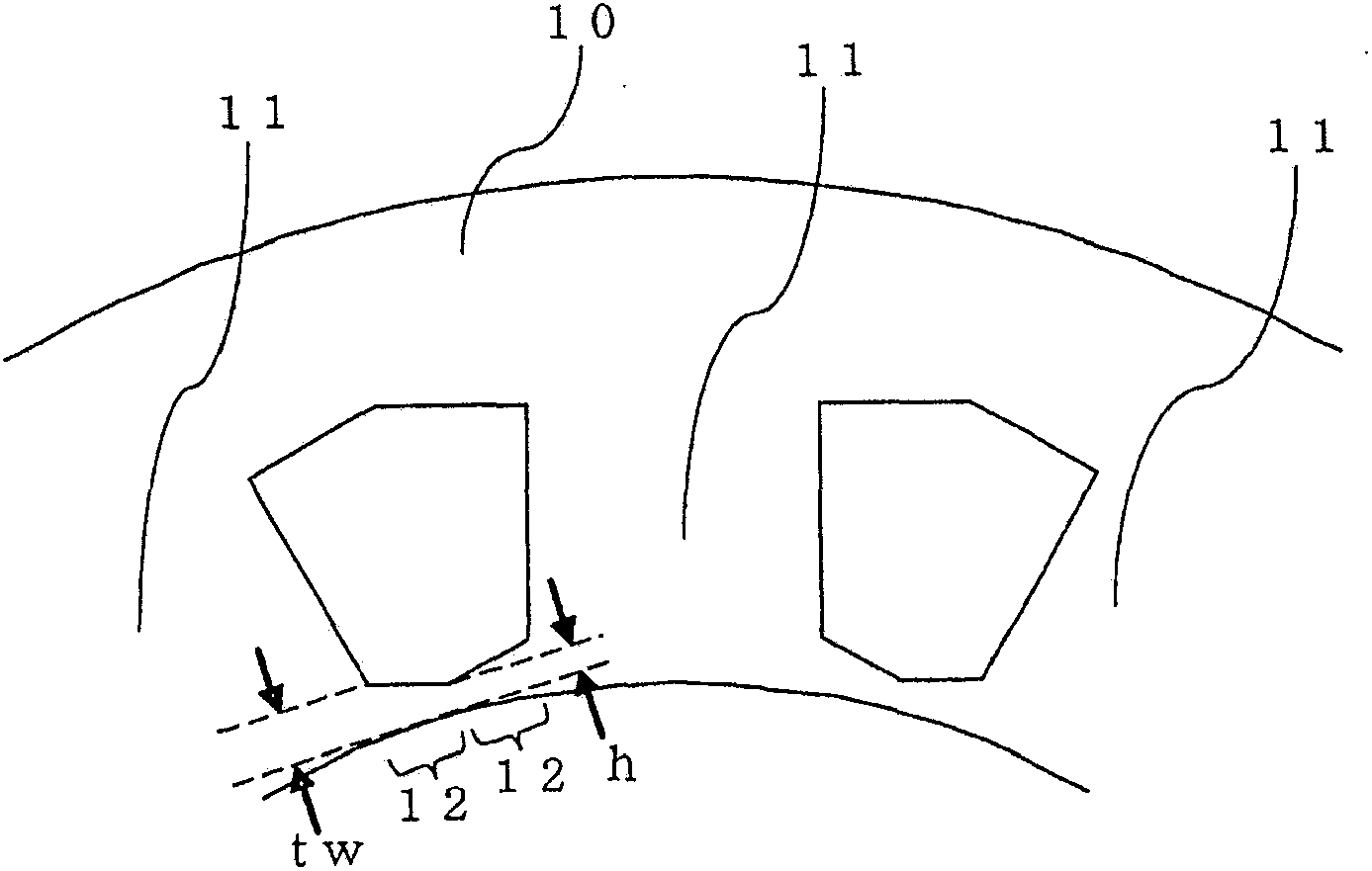
[0033] figure 2 is an enlarged view of the stator core 10 of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and figure 1 The enlarged view of the tooth portion 11 is equivalent. exist figure 1 In the shown 10-pole 12-slot motor, such as figure 2 As shown, there is no gap (so-called slot opening) between adjacent tooth portions 11 . In addition, each tooth portion 11 has a flange portion 12 ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0055] In Embodiment 1 above, a case was described in which a radially anisotropic ring magnet is used in a motor having a small diameter without a gap portion (so-called slot opening) between adjacent tooth portions 11 . On the other hand, in the second embodiment, a case in which a radially anisotropic ring magnet is used in a small-diameter motor having a gap portion (so-called slot opening portion 13 ) between adjacent tooth portions 11 will be described. Condition.
[0056] Figure 7 It is a sectional view showing a section perpendicular to the axial direction of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and illustrates a motor with 10 poles and 12 slots when Z=12 and 2P=10. Therefore, the value of Z / (3(phase)×2P) corresponds to 12 / (3×10)=2 / 5. Figure 7 The permanent magnet synchronous motor of the present invention includes a stator core 10 , a rotor core 20 , and a radially anisotropic ring magnet 30 , and the stator core 10 has ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com