Method for implementing multi-stable state of compliant Sarrus mechanism
An implementation method, multi-stable technology, applied in mechanical equipment, belts/chains/gears, transmissions, etc., can solve the problems of Sarrus mechanism service life and motion accuracy reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
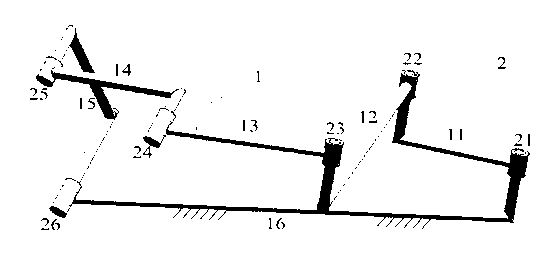
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the rigid Sarrus mechanism is a space six-rod single-degree-of-freedom mechanism formed by rigidly hinged six rigid rods 1 through hinges 2. The six rigid rods are respectively the first rod 11, the second rod 12, the third rod 13, The fourth rod 14, the fifth rod 15 and the sixth rod 16, there are six hinges 2 in total, namely the first hinge 21, the second hinge 22, the third hinge 23, the fourth hinge 24, and the fifth hinge 25 and the sixth hinge 26 .
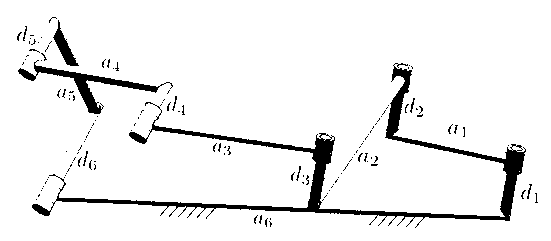
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, the sixth rod 16 is fixed, and the first rod 11 can rotate around the first hinge 21, which satisfies the rod length condition: a 1 -a 2 ≥d 4 +d 5 +d 6 ; The third rod 13 can translate along a straight line, that is, satisfy the rod length condition: a 4 +a 5 > d 1 +d 2 +d 3 .
[0029] When the hinge 2 is partially or completely replaced by a rigid hinge with a compliant hinge, the partially compliant or fully compliant Sarrus mechanism formed ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that the fifth hinge 25 is replaced by a rigid hinge with a partially compliant Sarrus mechanism of a compliant hinge, and the sixth rod 16 is fixed. If the fifth hinge 25 is formed without deformation (the fourth When the angle between the rod 14 and the fifth rod 15 is constant), when the first rod 11 can stay stably in two different positions, the mechanism is a bistable compliant Sarrus mechanism, and the two stable The position corresponds to the two rotational steady-state positions of the first rod 11 and the two linear steady-state positions of the third rod 13; if the fifth hinge 25 is not deformed (the fourth rod 14 and the fifth rod 15), when the first rod 11 can stay stably at three different positions, then the first rod 11 of the compliant Sarrus mechanism has three rotation-type steady-state positions, and the third rod The member 13 has two linear steady-state positions, and the mechanism posi...
Embodiment 3
[0043] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 2, and the difference is that the selected size is: a 1 =0.14m,a 2 =0.3m,a 3 =0.1m,a 4 =0.15m,a 5 =0.1m,a 6 =0.4m,d 1 =0.05m, d 2 =0.05m,d 3 =0.06m,d 4 =0.04m,d 5 =0,d 6 =0.04m.
[0044] When the fifth hinge 25 is not deformed (the included angle between the fourth rod 14 and the fifth rod 15 remains unchanged), when the first rod 11 can stay stably at four different positions, the compliant Sarrus mechanism The first rod 11 has four rotational steady-state positions, the third rod 13 has two linear steady-state positions, and the mechanism positions of the two steady-state positions of the first rod 11 correspond to the third The mechanism position of one linear steady-state position of the rod 13, the mechanism position of the other two steady-state positions of the first rod 11 correspond to the other linear steady-state position of the third rod 13 location of the institution.
[0045] Such as Figure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com